This document provides an introduction to music fundamentals including:
- Why music is beneficial to the human brain and promotes social bonding, confidence, and stress relief.
- Actively making music through playing an instrument is more enjoyable than passive listening.
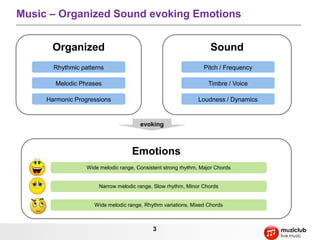
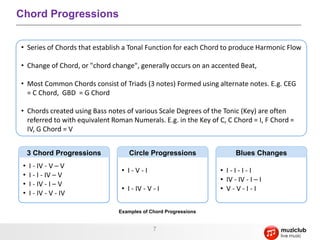
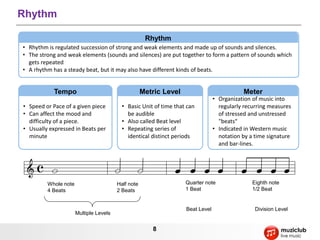
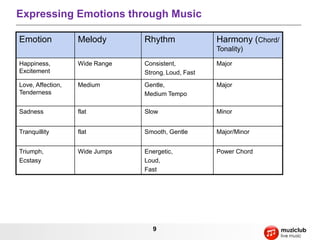
- Music is organized sound that evokes emotions through elements like rhythm, melody, harmony, pitch, and timbre.
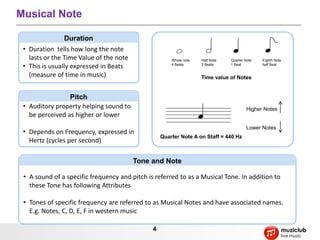
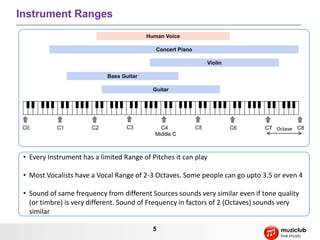
- It describes musical concepts such as notes, scales, chords, harmony, rhythm, tempo, and how these elements can be combined to express different emotions.