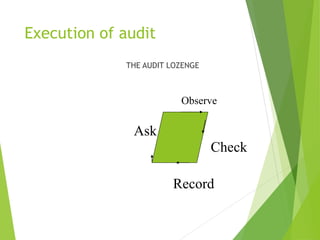
This document provides an overview of quality auditing, including definitions, types of audits, auditor qualifications, and the audit process. It describes what a quality audit is, why organizations conduct audits, and who can be a quality auditor. The audit process involves three main steps - planning and preparation, carrying out the audit, and reporting and follow-up. Detailed information is given about each step, such as establishing the audit scope and team, notifying the auditee, performing the audit using techniques like observation and documentation review, and compiling findings into a report.