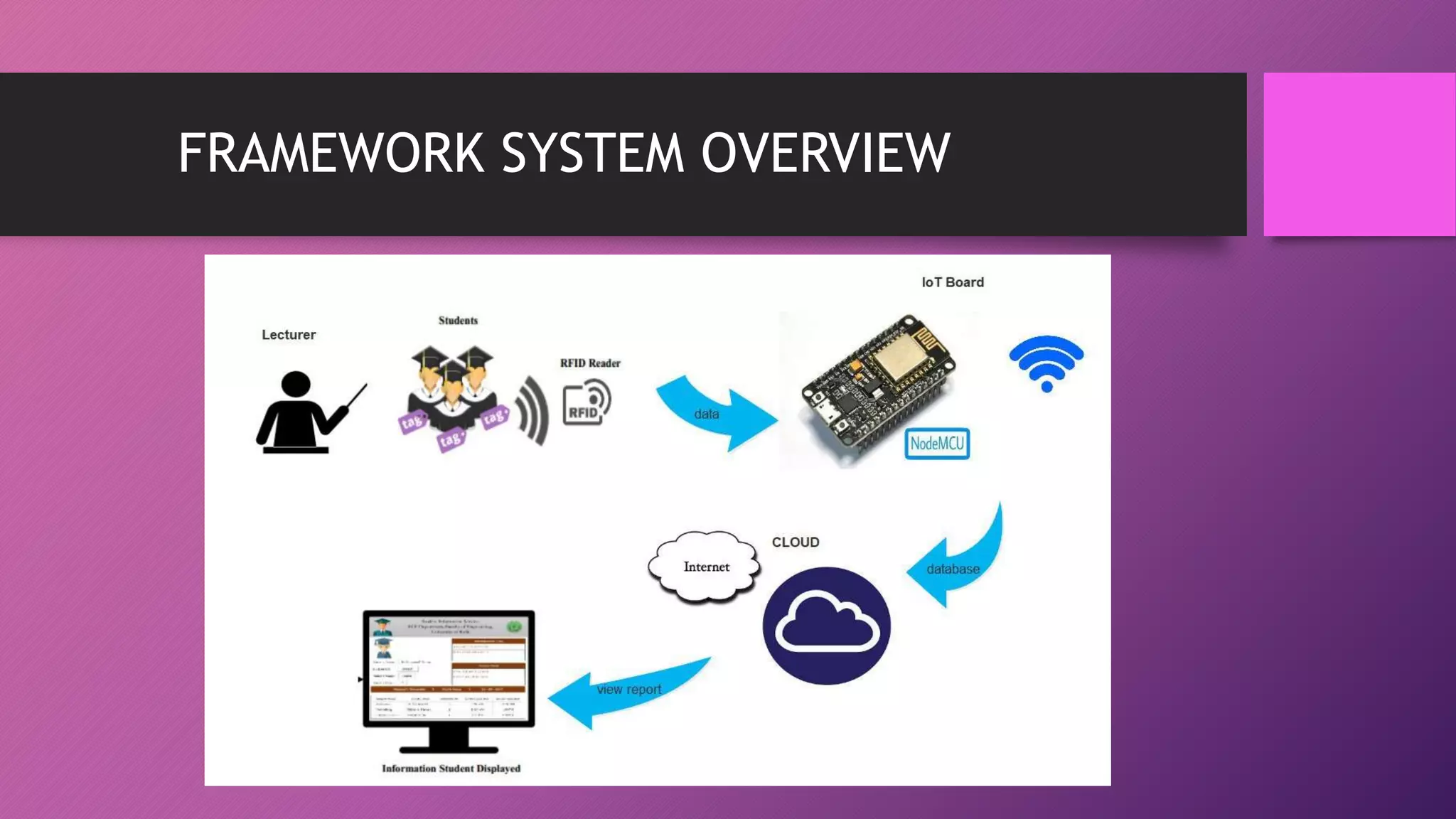
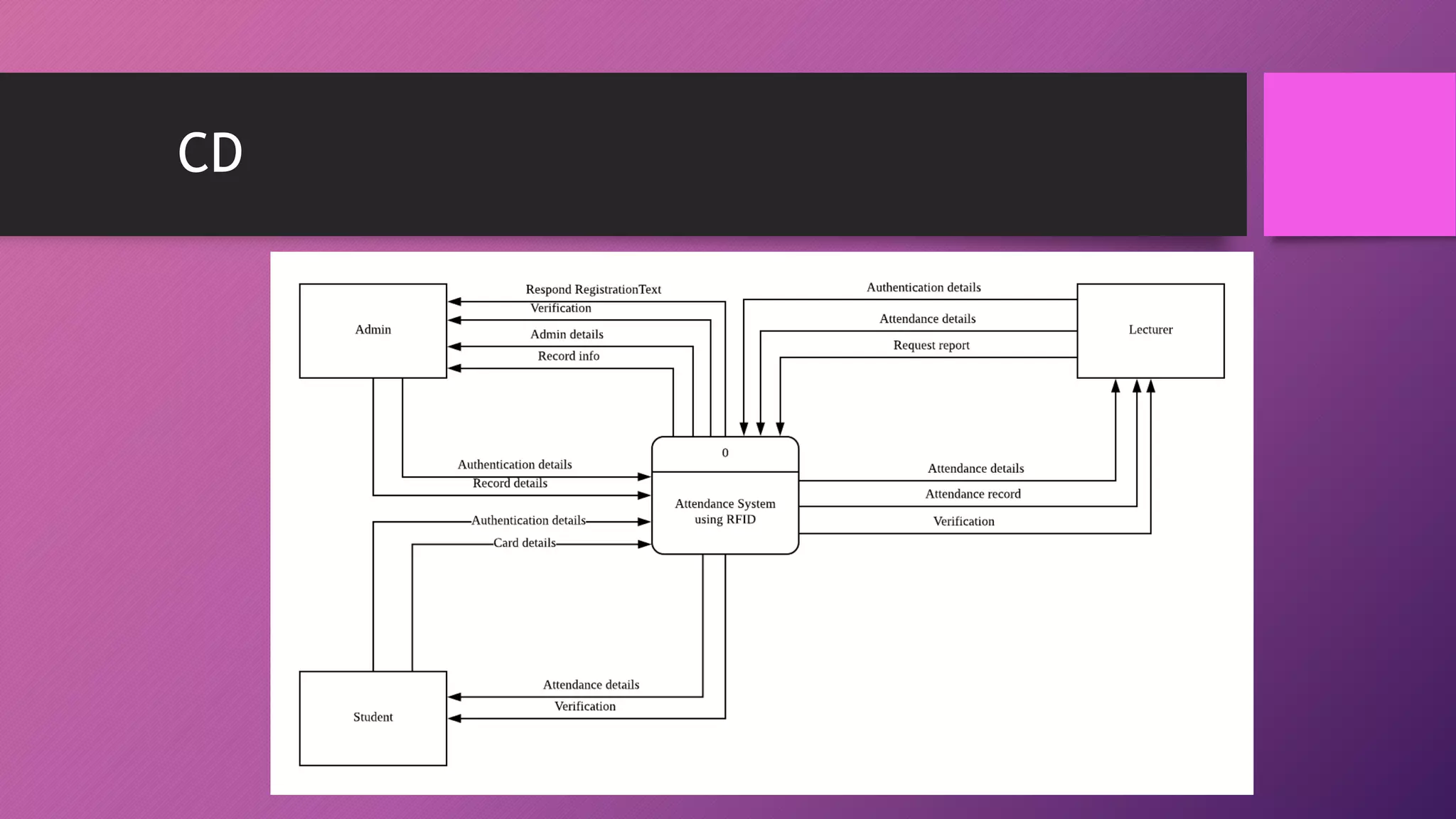
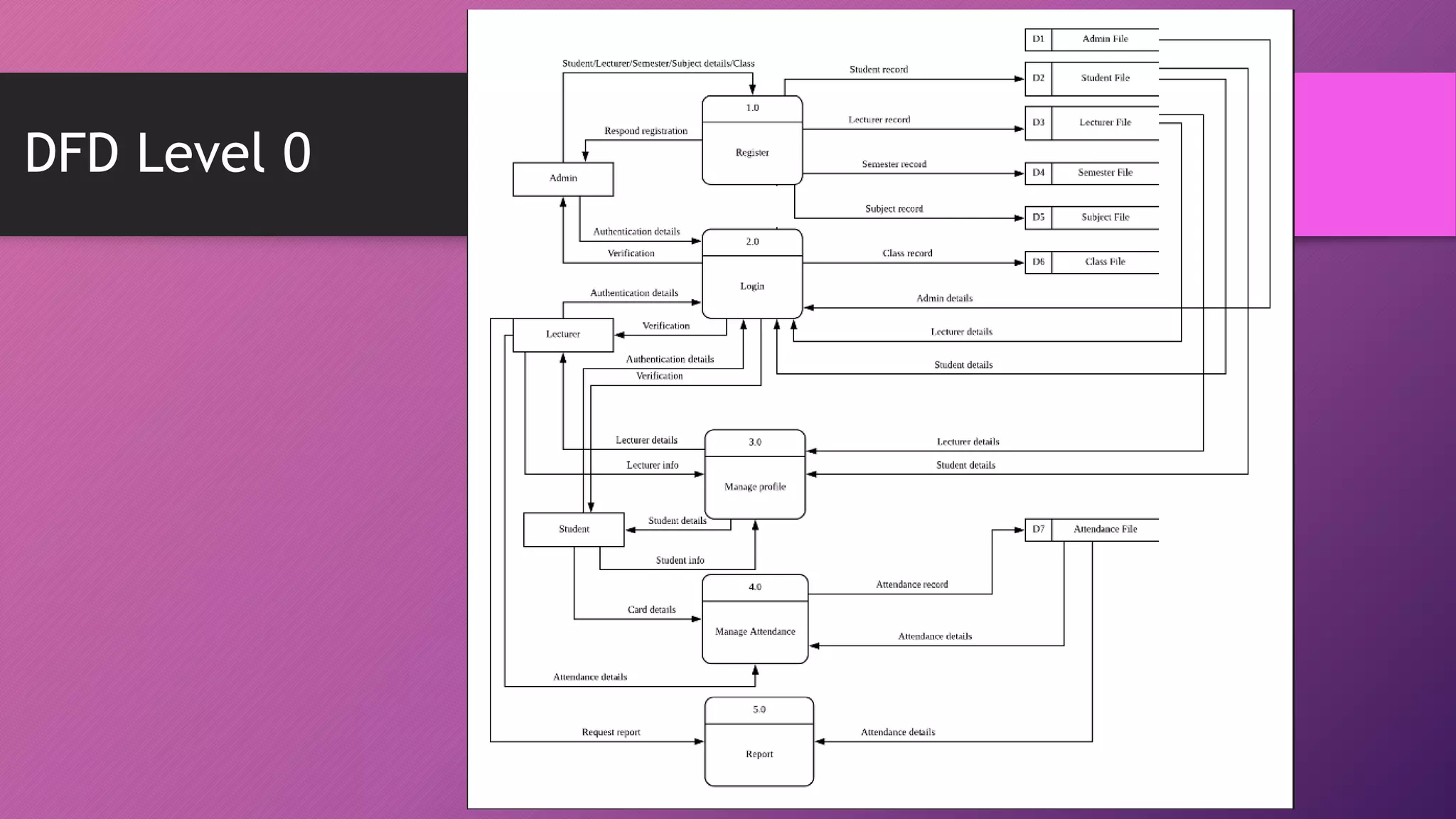
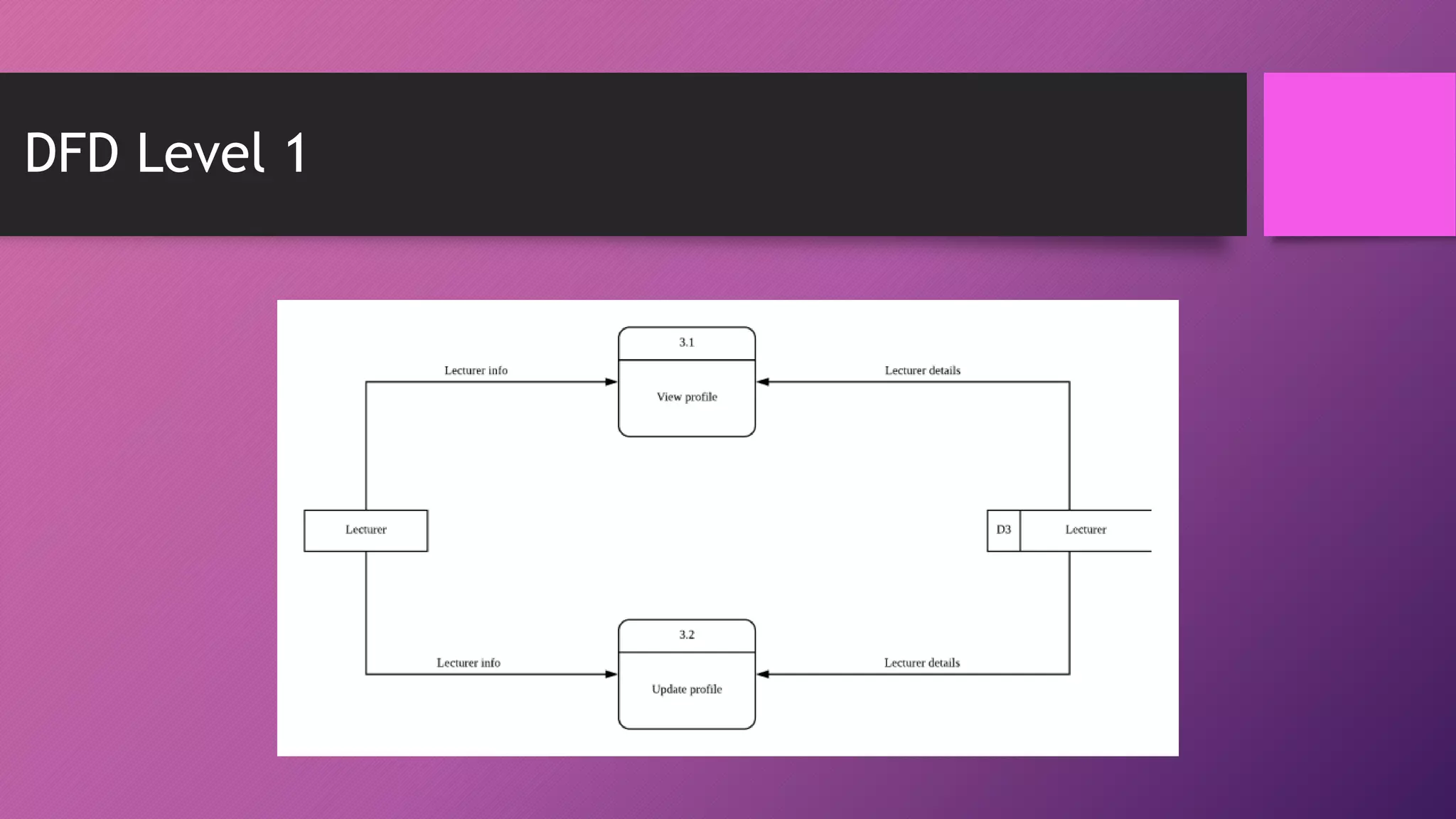
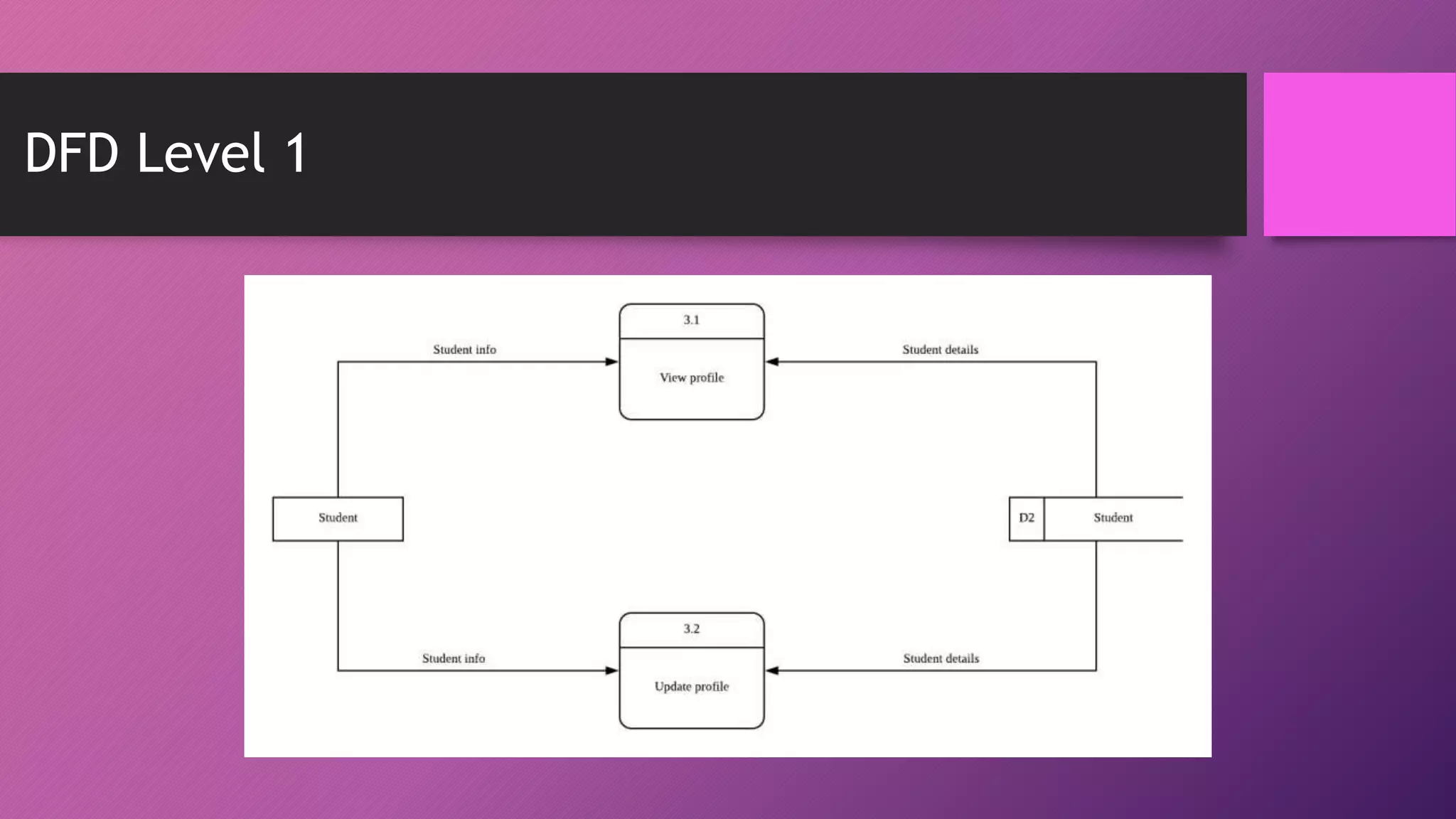
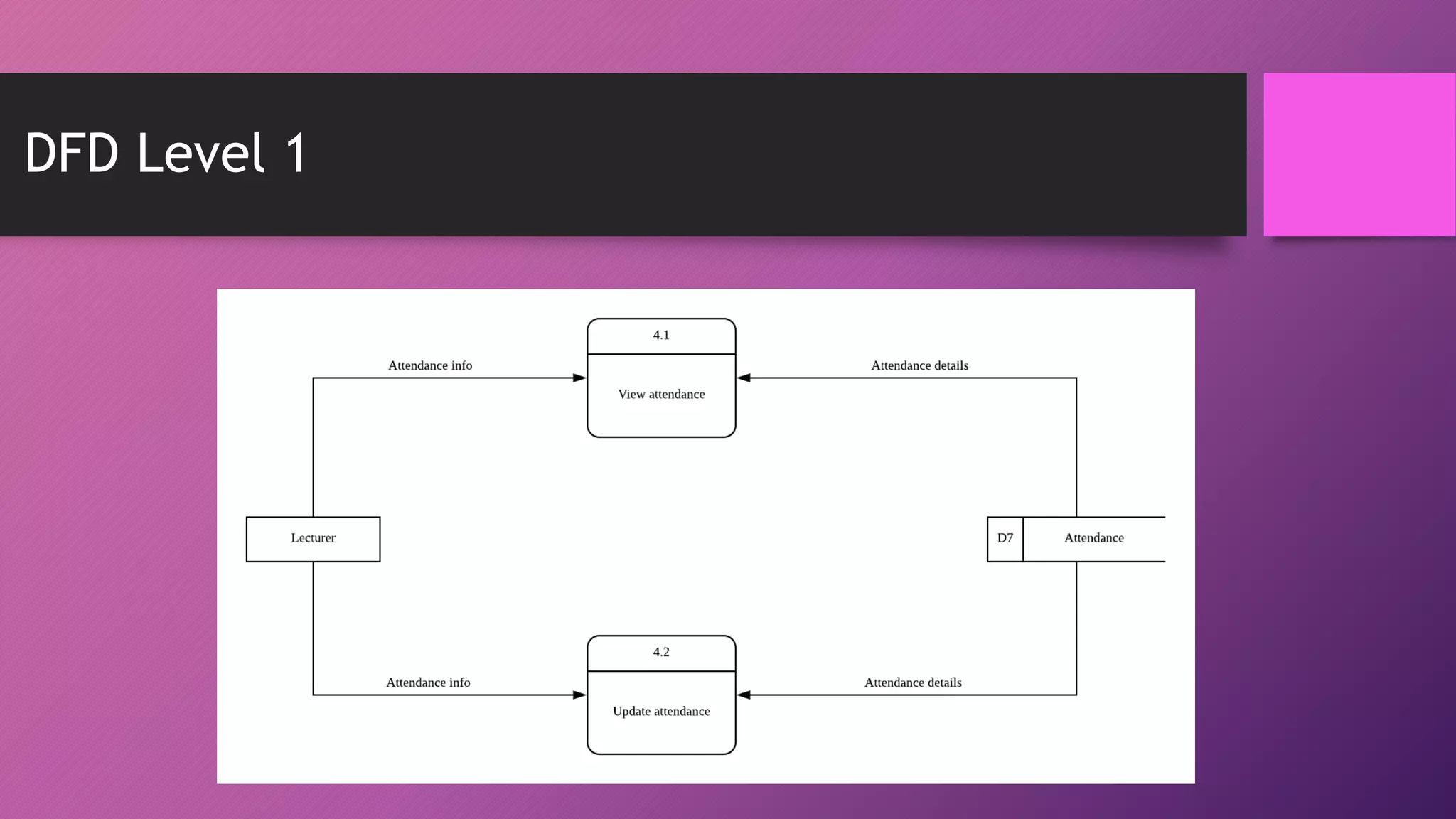
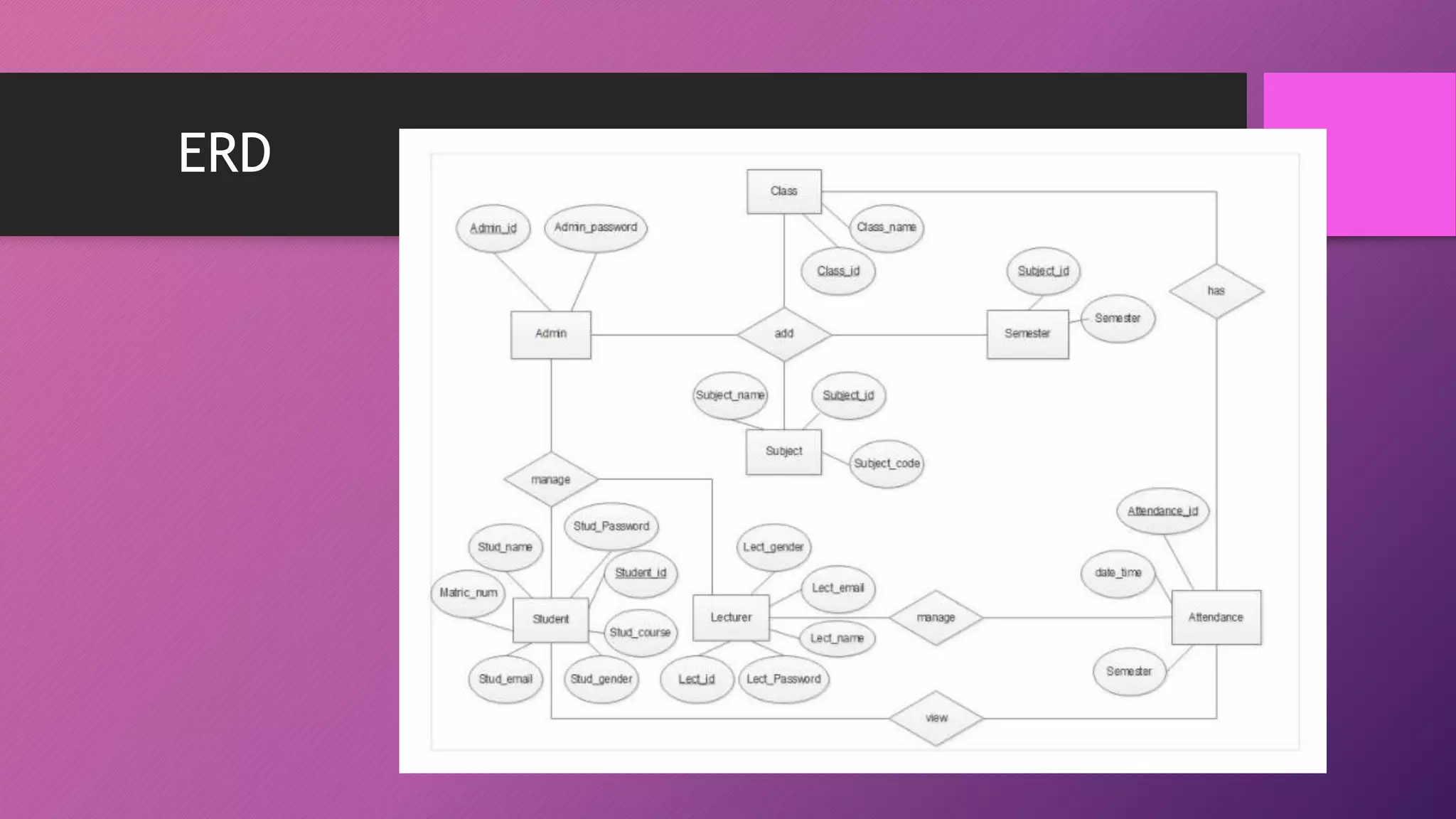
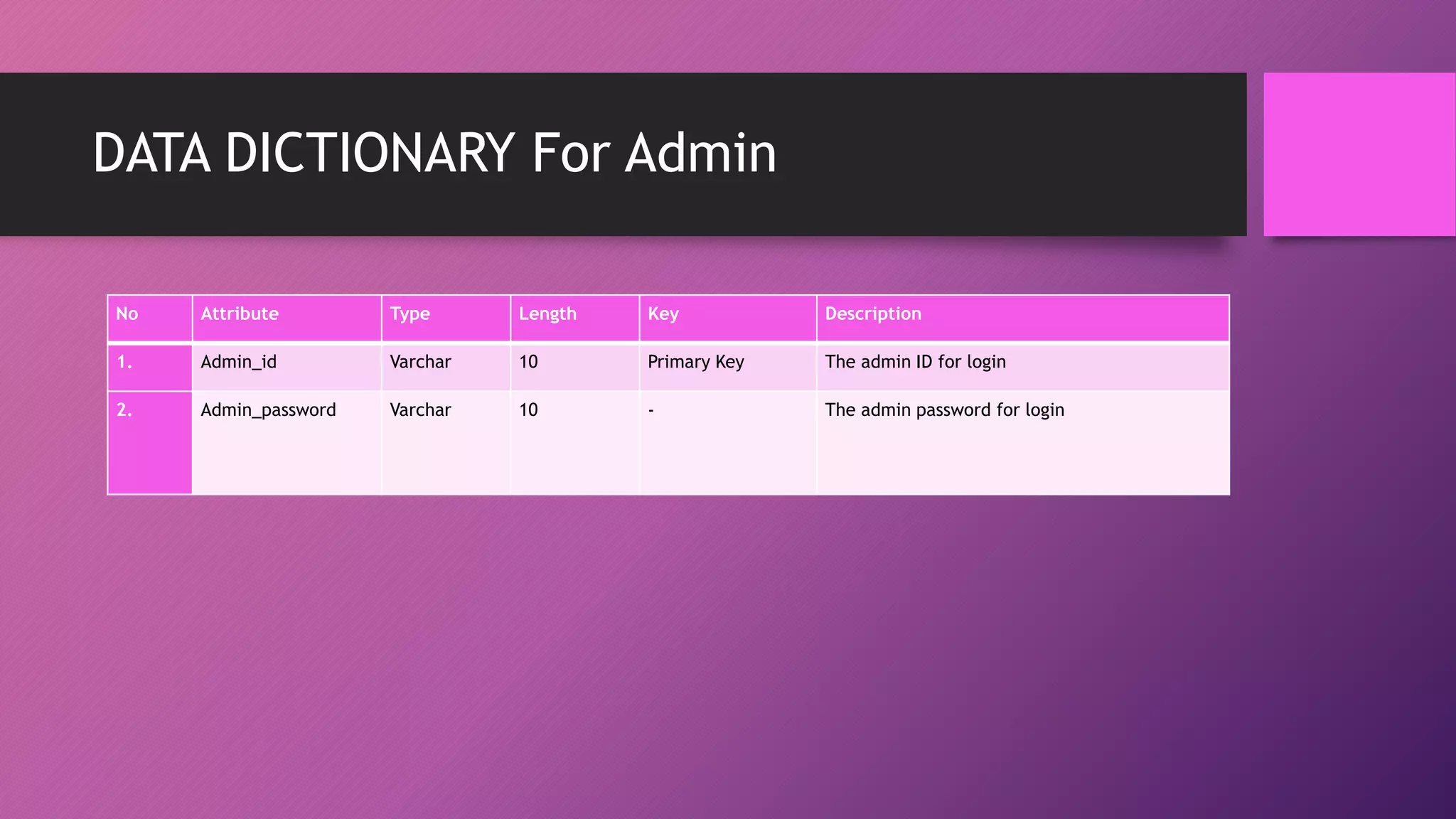
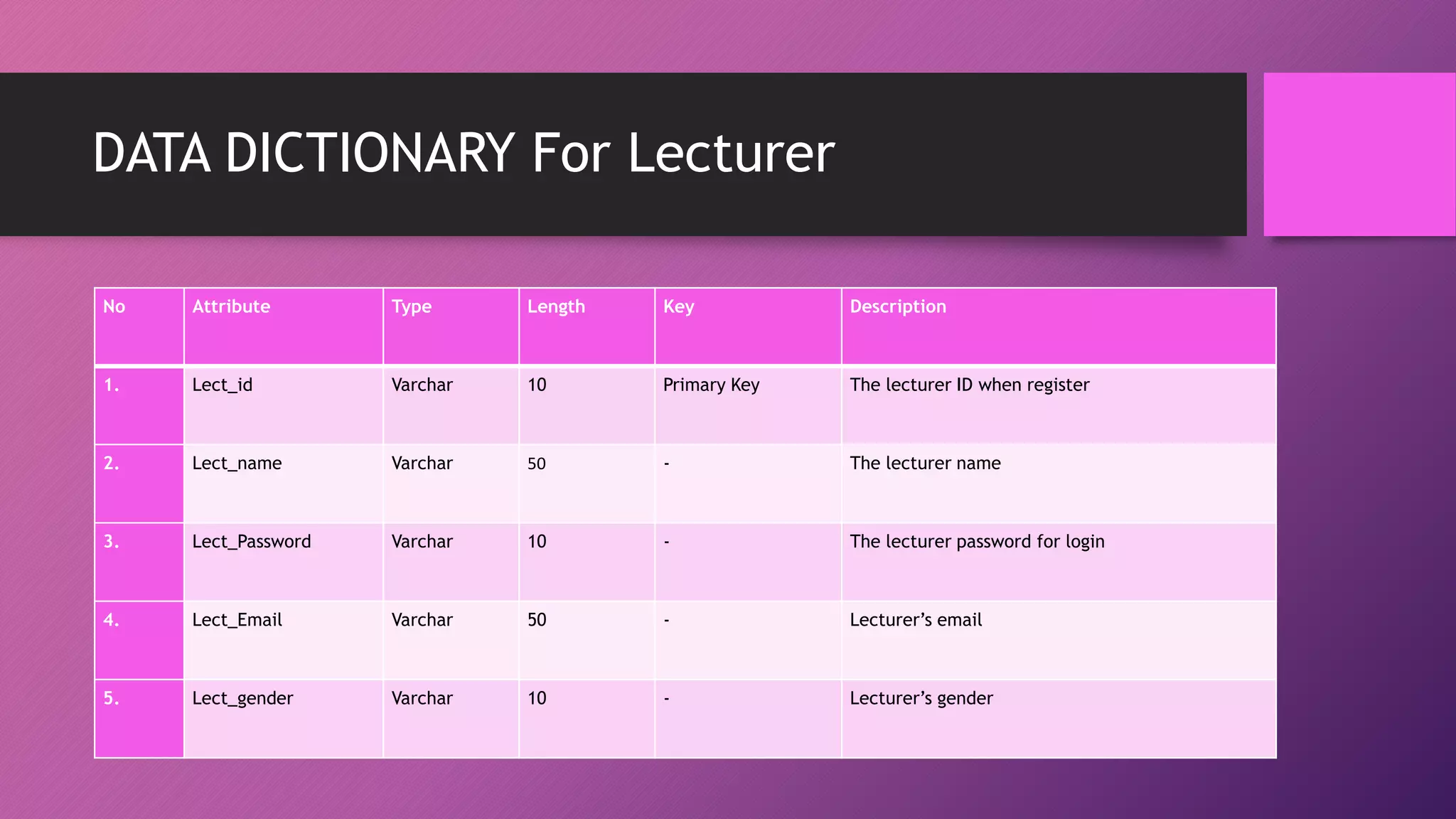
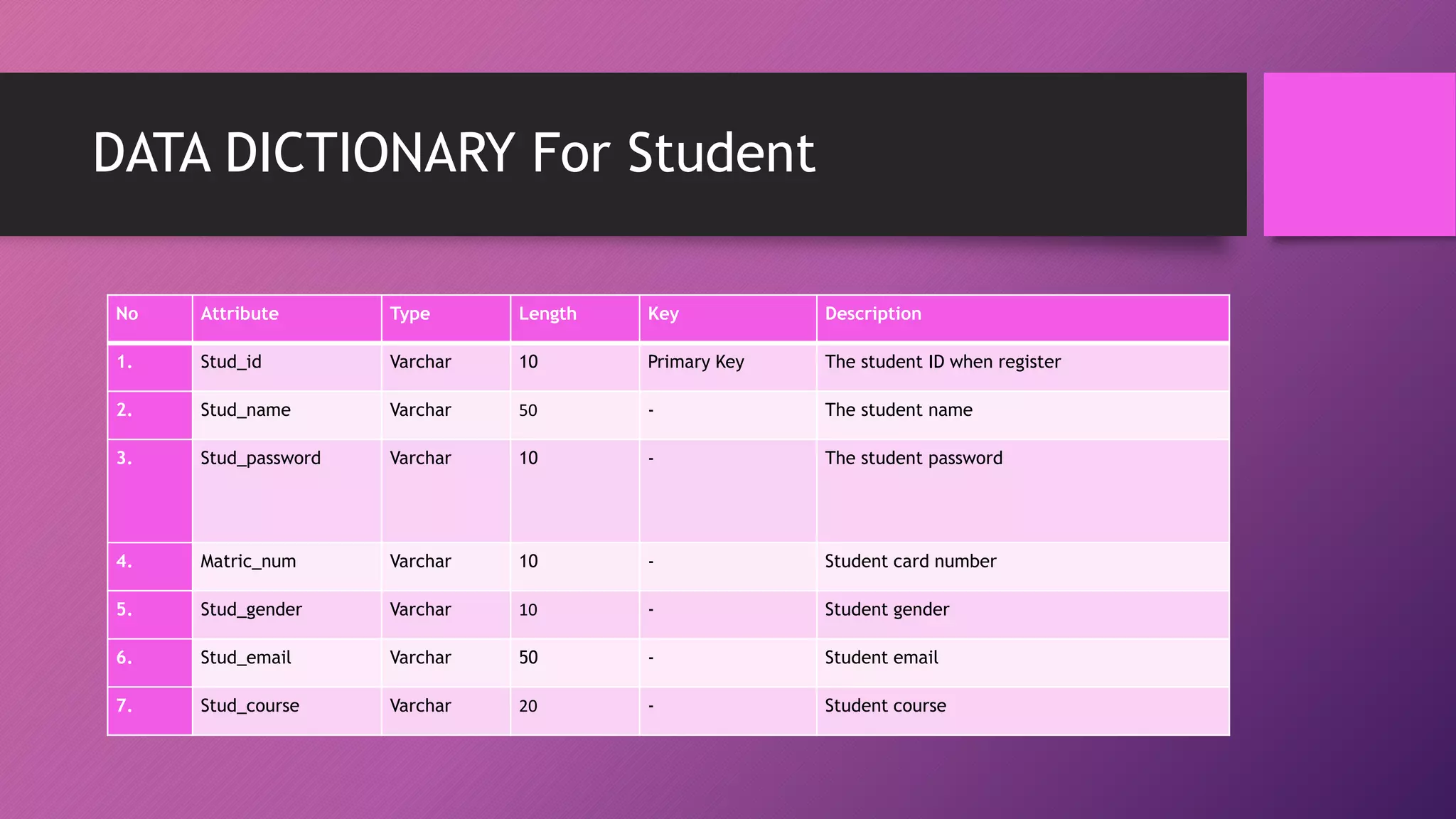
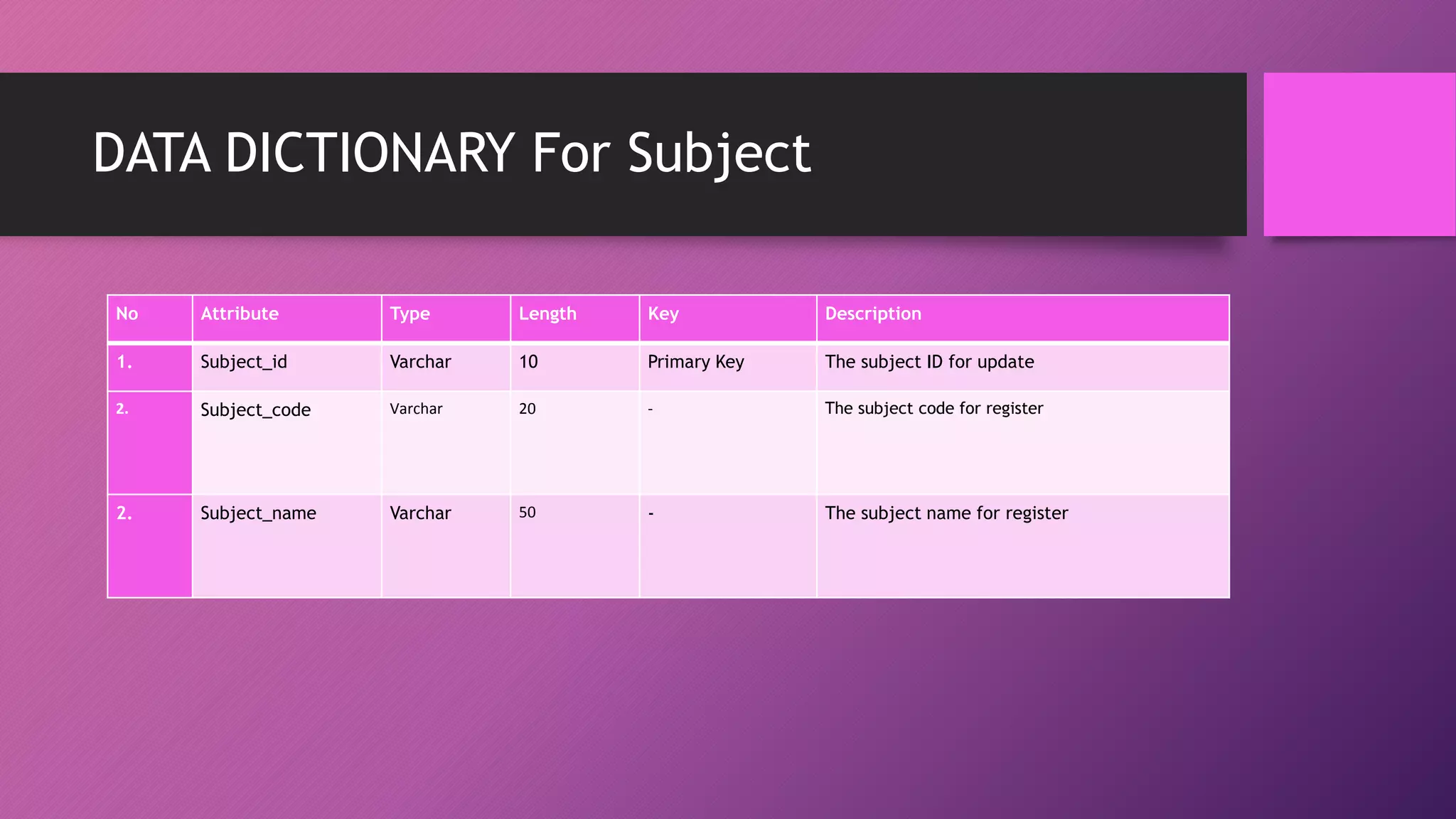
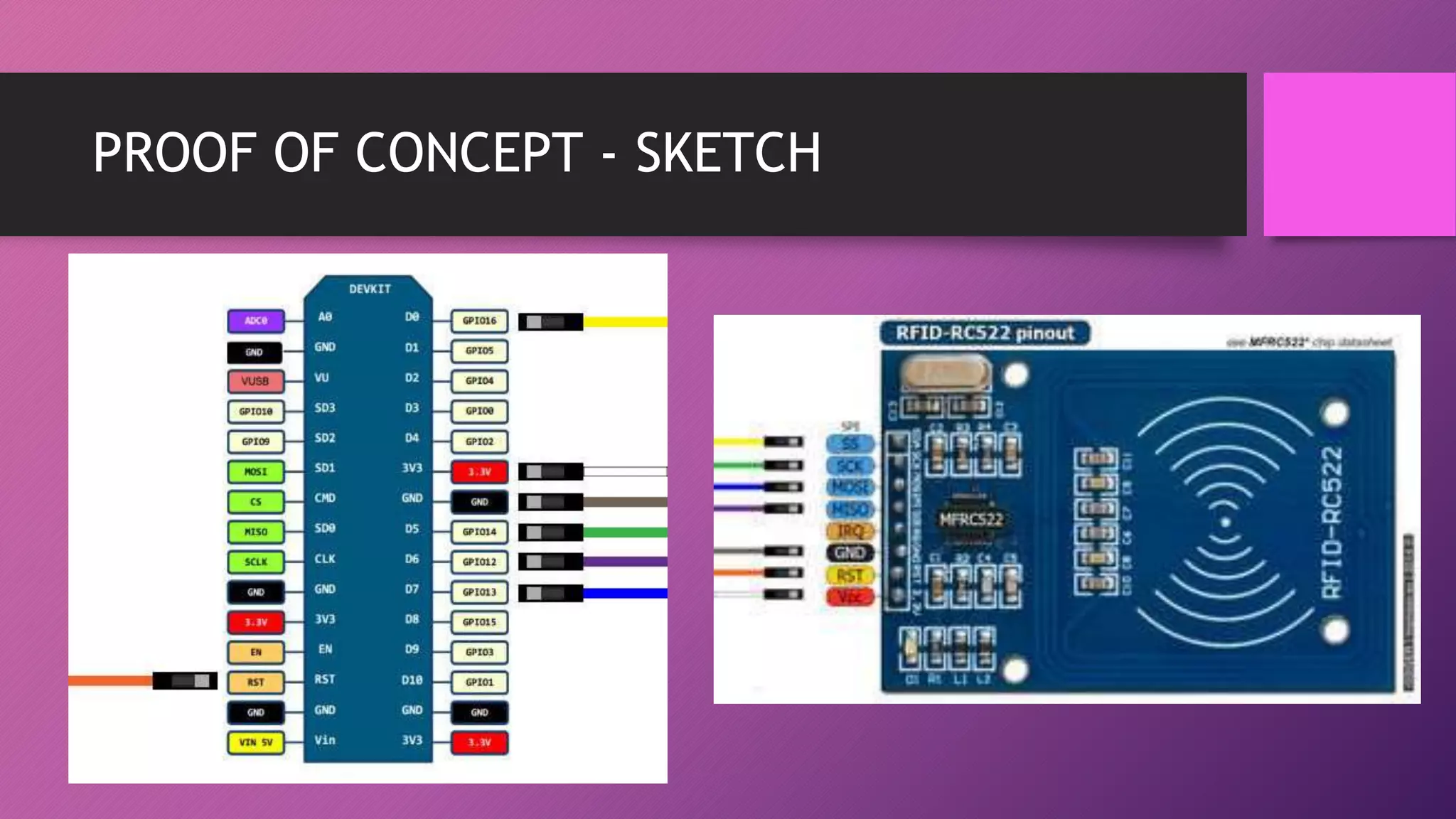
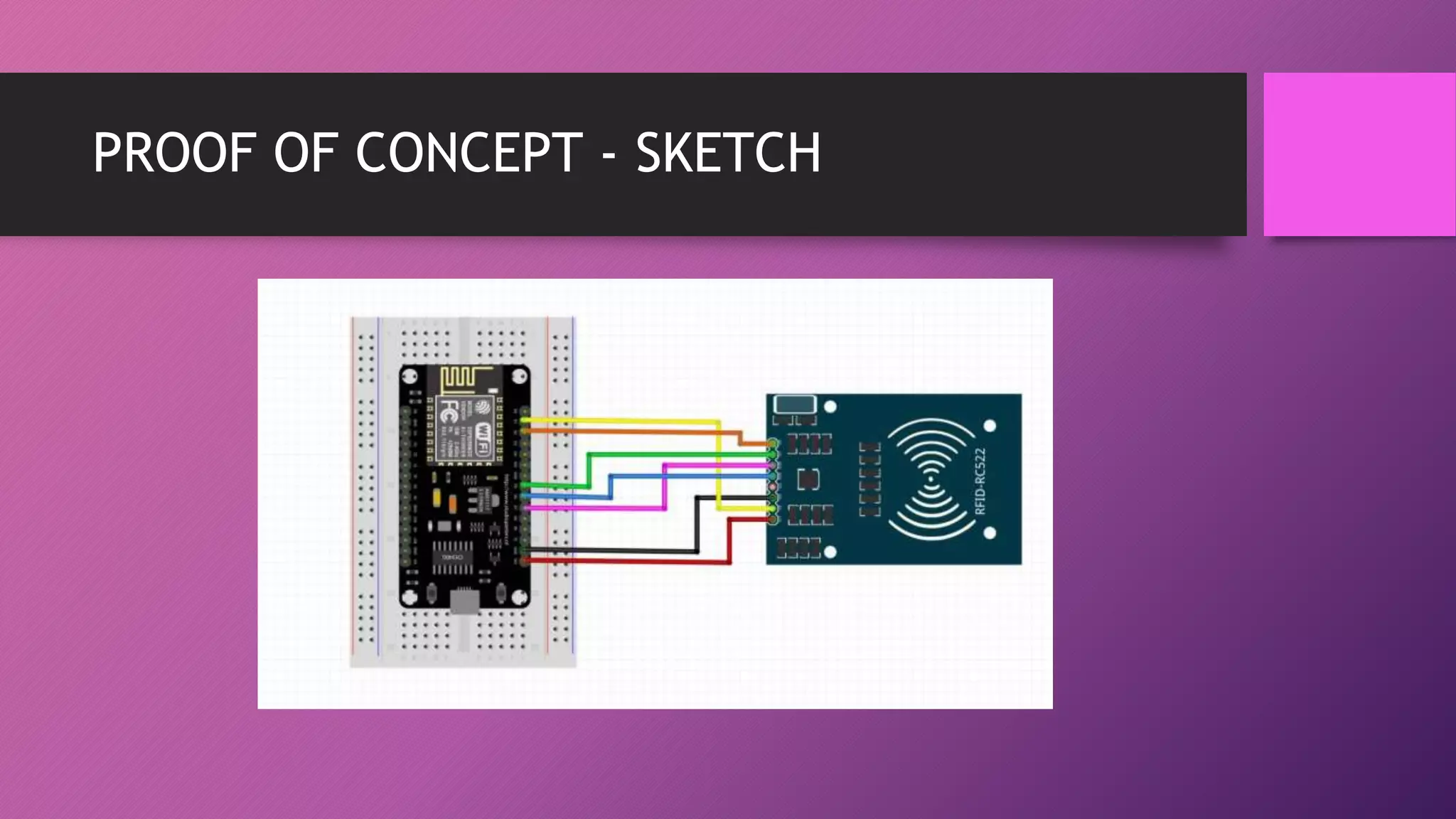
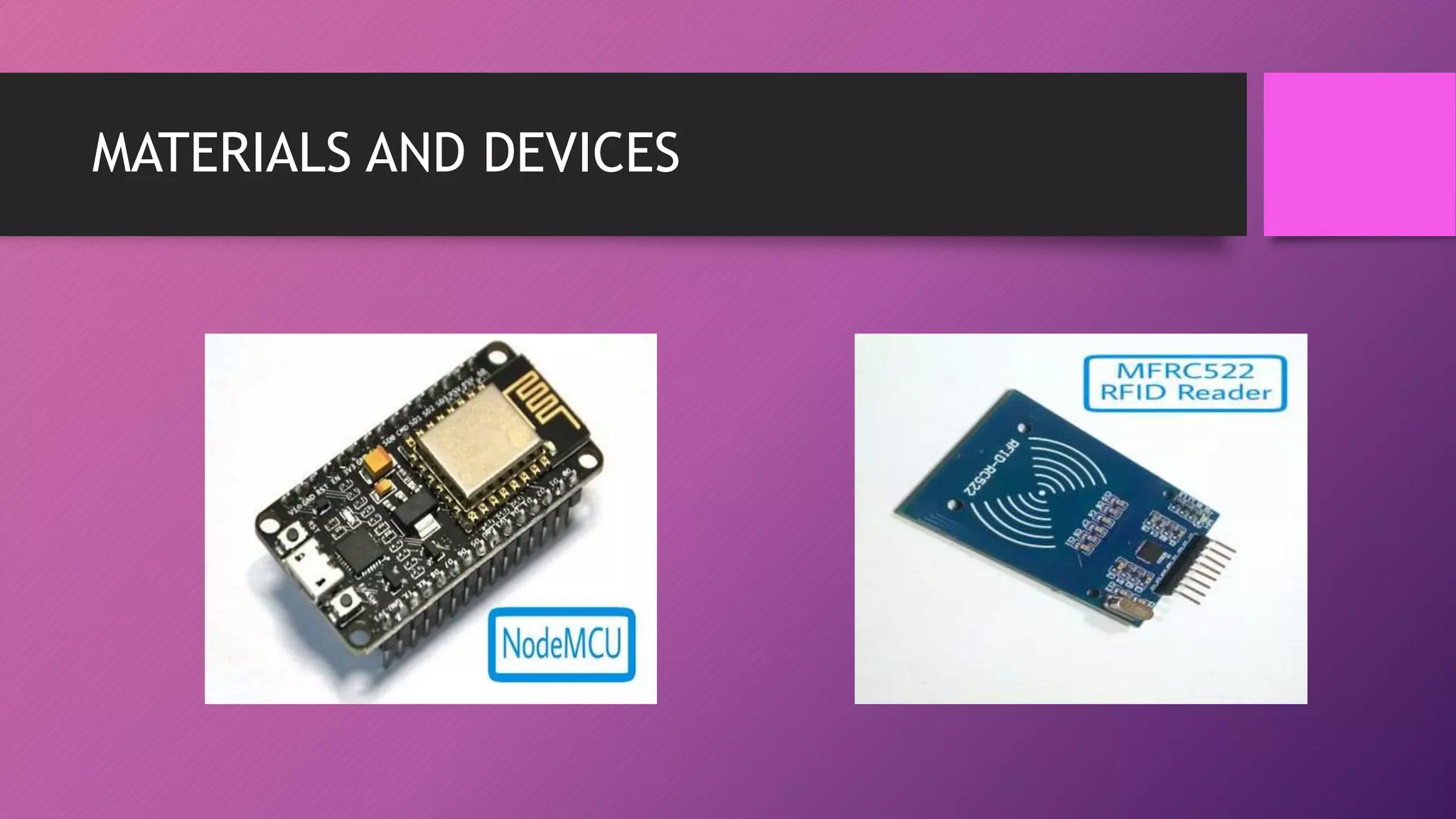
This document presents an automated attendance system using RFID (radio-frequency identification) and IoT (Internet of Things) technologies. The system aims to address issues with the current manual attendance recording process. It will allow students to have their attendance automatically captured when they flash their student ID cards, which are tagged with RFID passive tags, at RFID readers. The attendance data will then be updated and stored in an online database system. The key objectives are to develop a real-time attendance system using RFID and test its functionality. The system will consist of an admin interface to manage users and schedules, and interfaces for lecturers to view and edit attendance reports and for students to update their profiles.