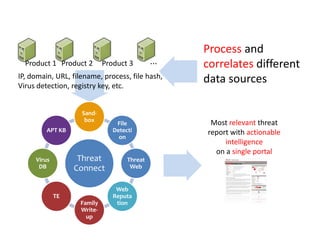
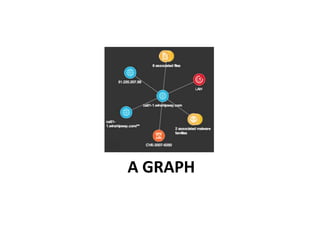
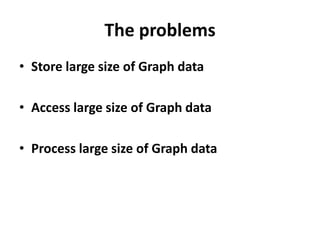
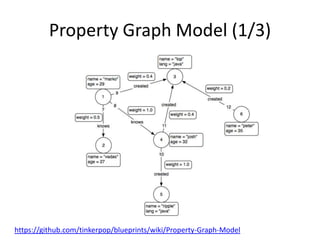
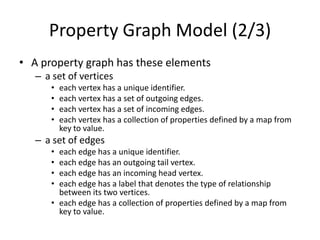
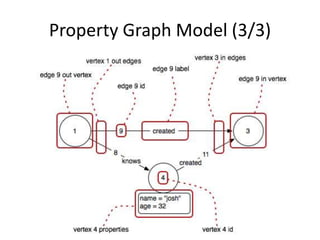
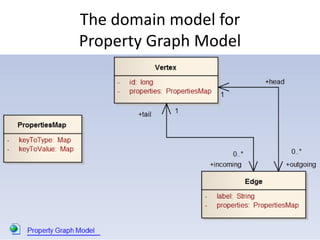
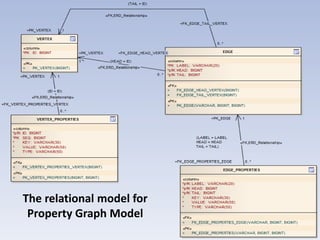
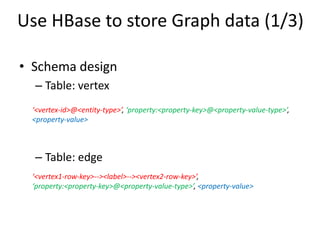
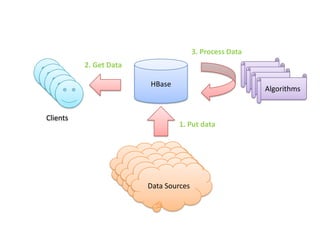
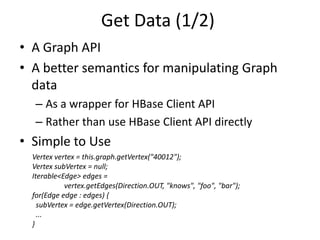
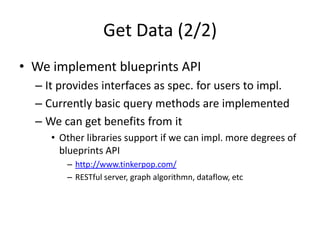
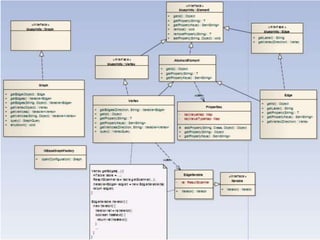
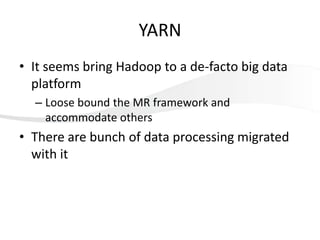
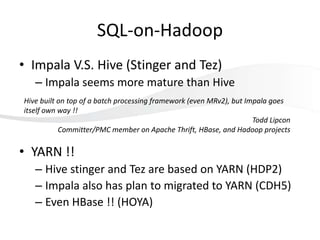
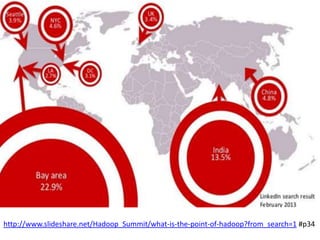
This document discusses using HBase to store graph data. It proposes using HBase's key-value data model to represent graph elements like vertices and edges. Sample schema designs are provided to store vertices in one HBase table and edges in another. The document also discusses building a graph API on top of HBase client APIs to more easily manipulate the graph data and implementing graph algorithms like PageRank using the stored graph data.