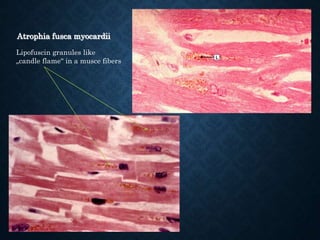
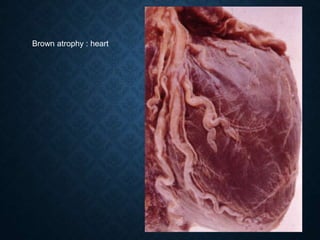
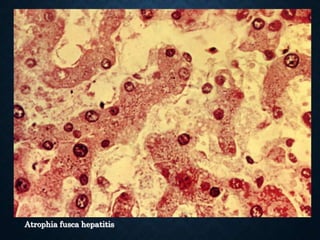
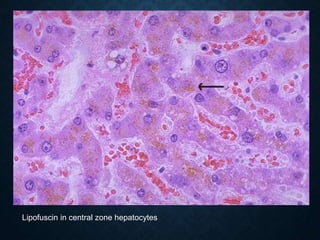
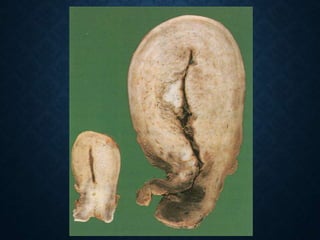
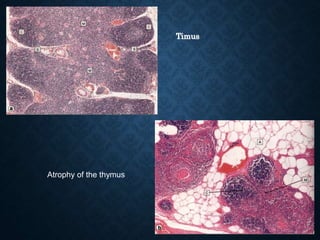
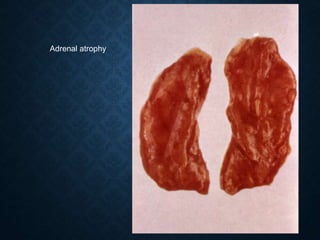
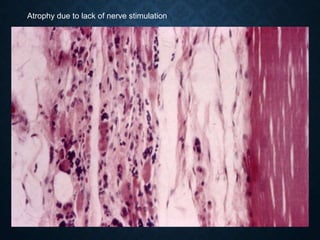
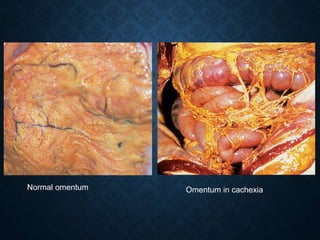
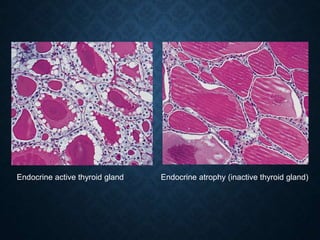
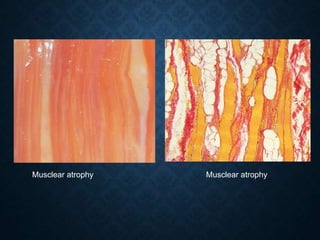
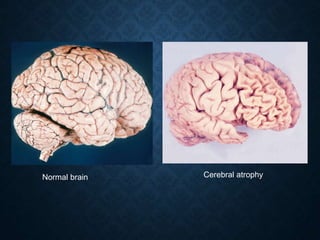
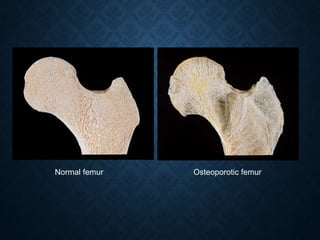
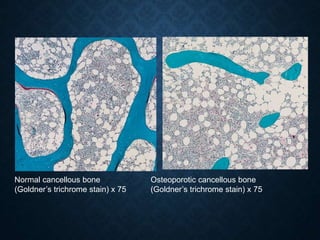
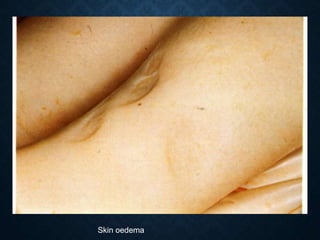
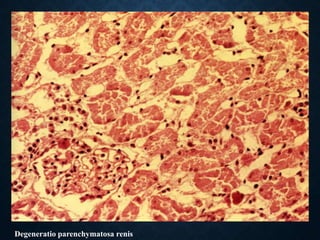
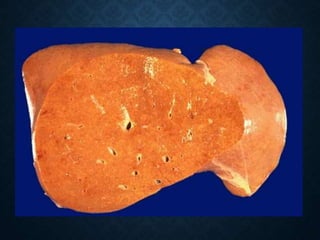
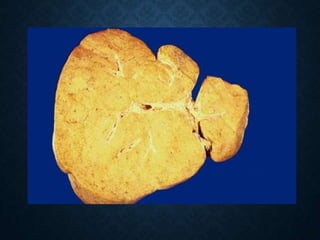
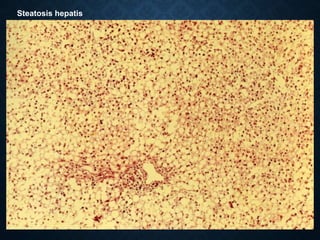
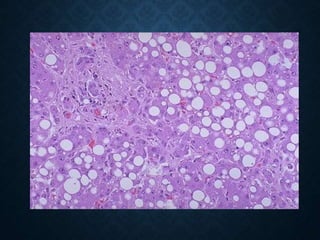
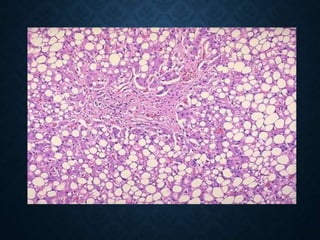
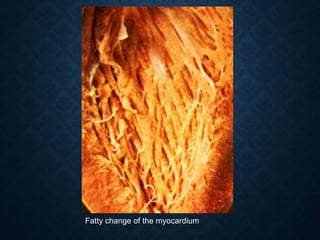
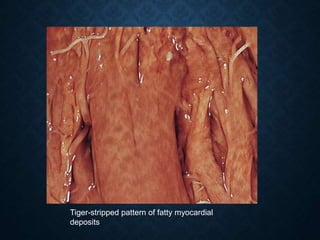
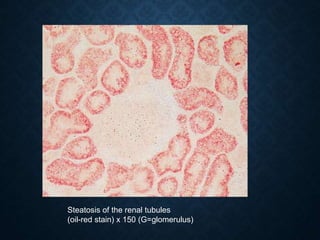
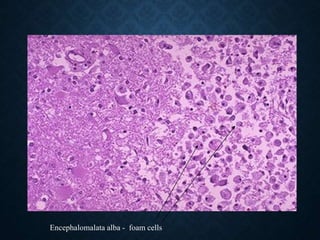
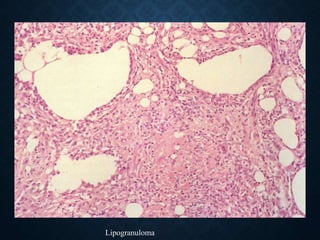
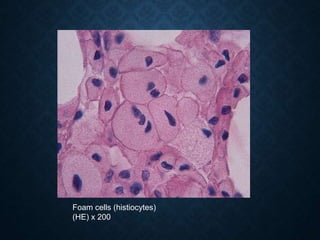
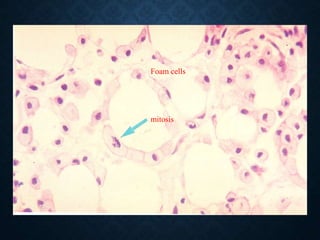
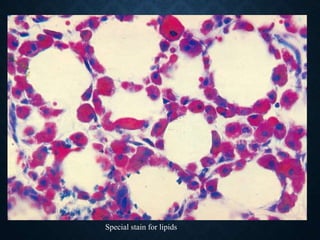
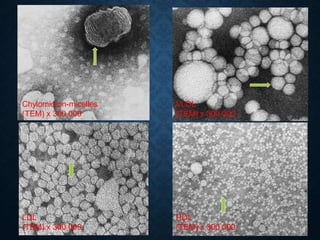
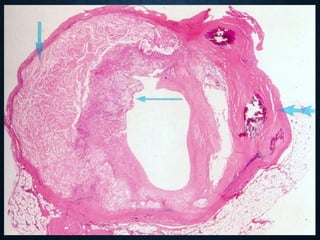
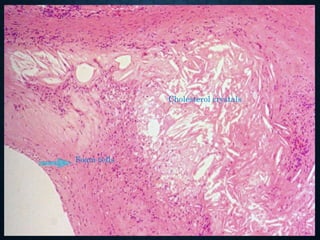
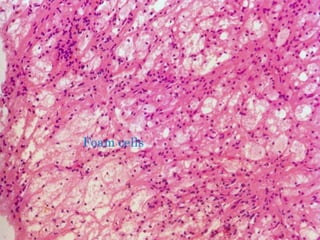
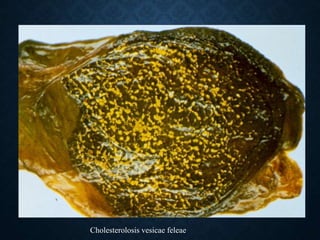
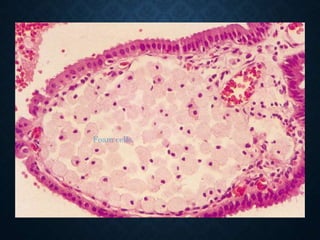
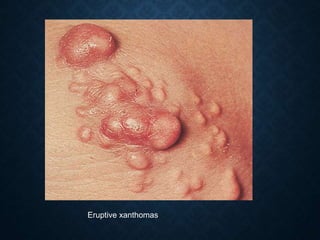
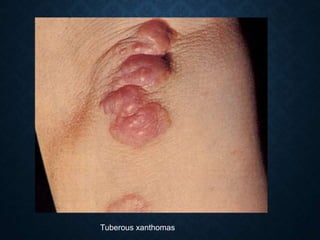
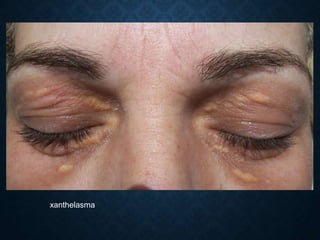
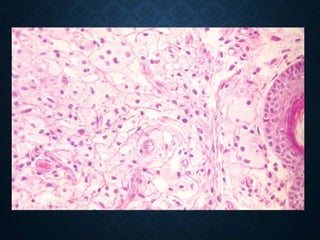
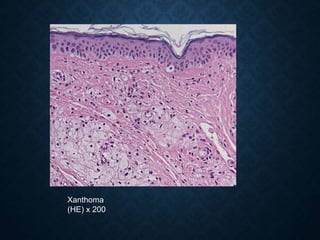
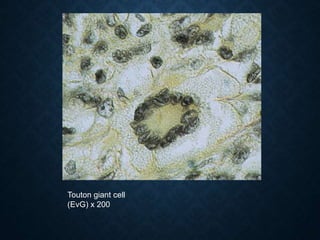
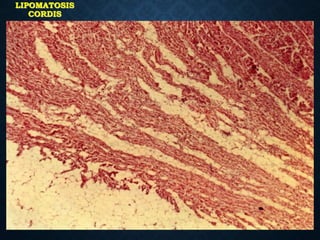
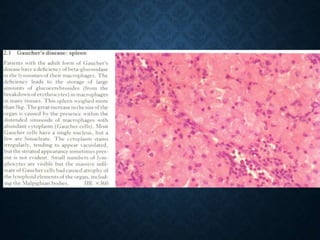
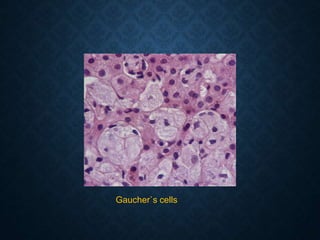
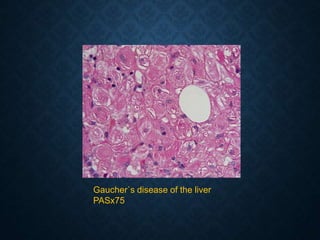
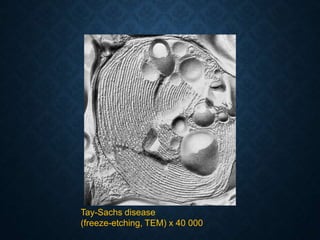
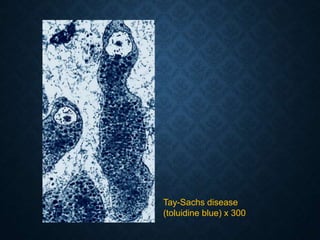
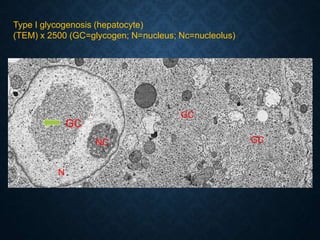
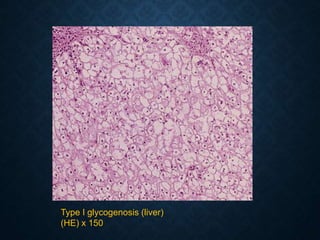
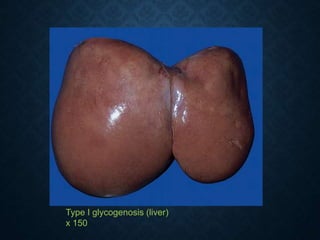
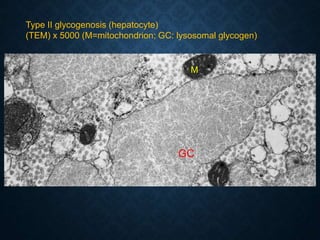
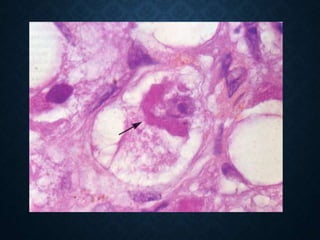
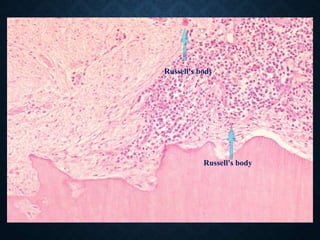
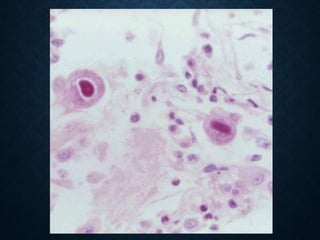
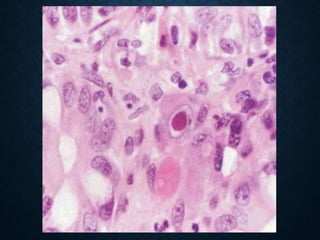
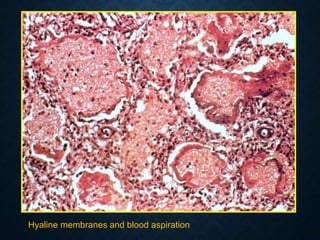
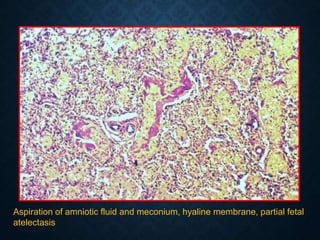
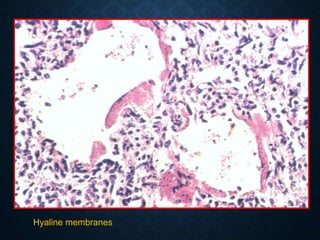
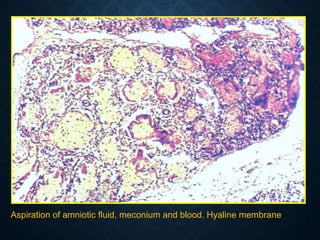
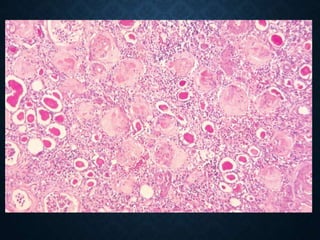
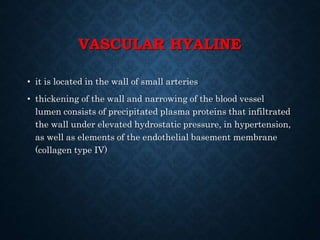
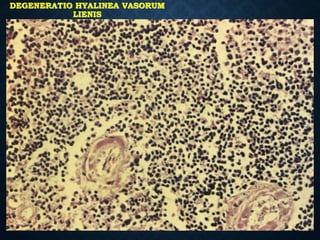
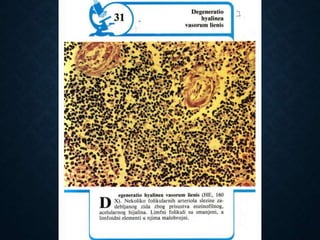
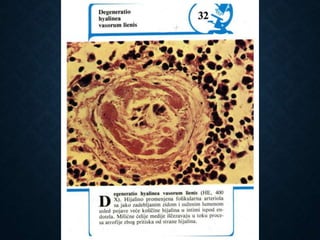
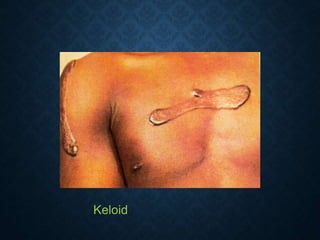
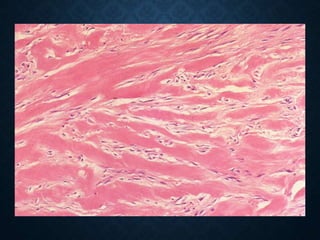
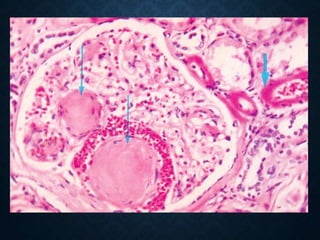
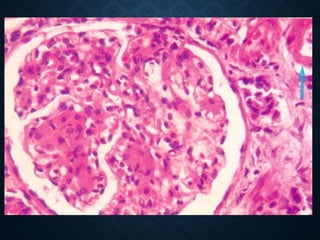
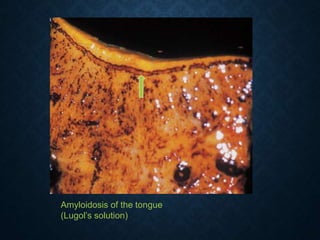
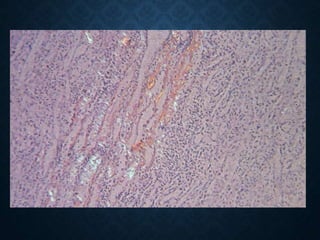
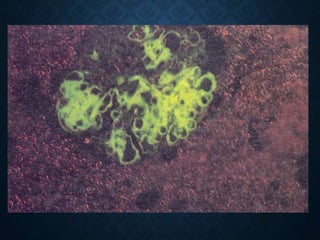
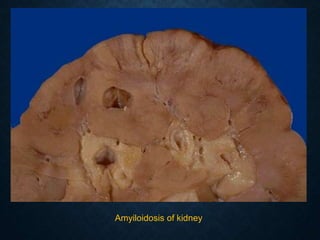
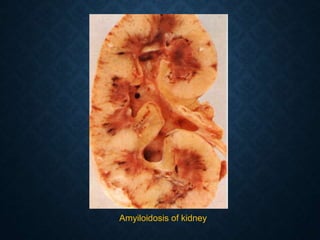
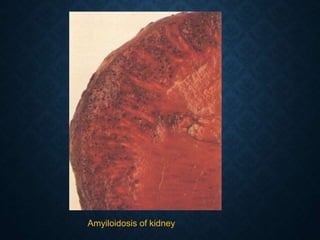
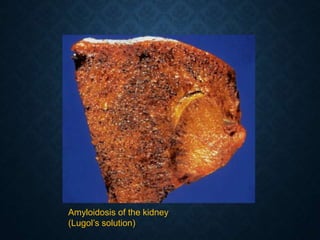
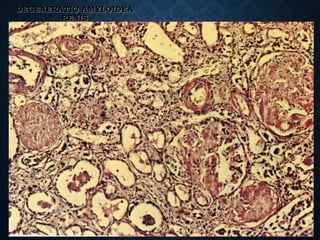
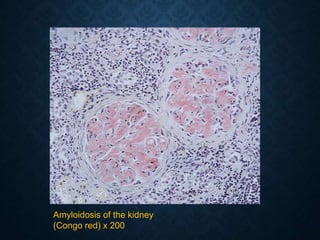
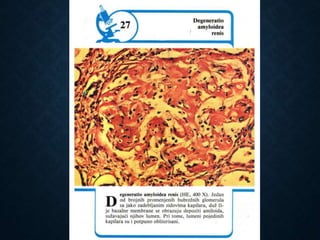
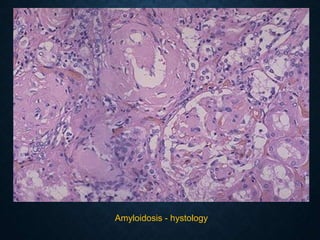
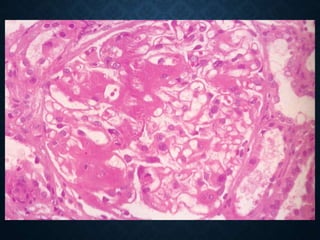
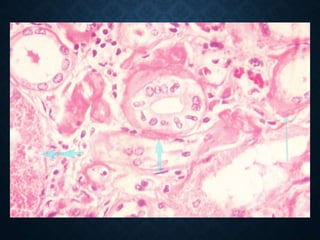
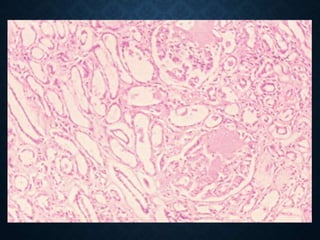
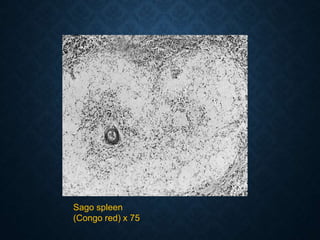
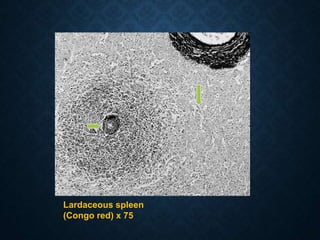
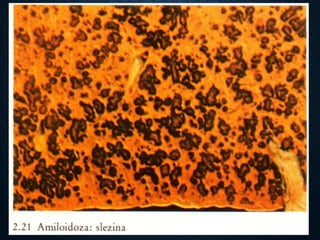
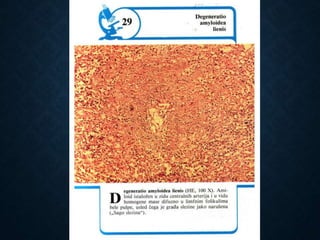
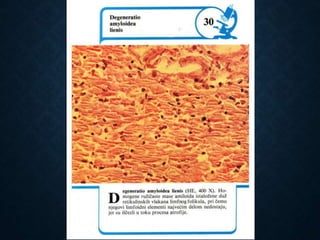
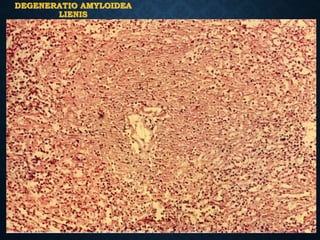
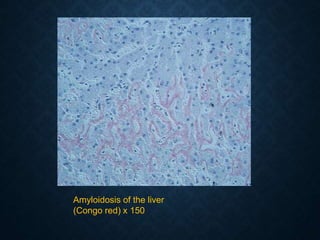
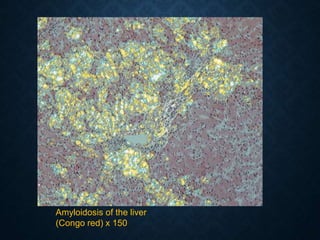
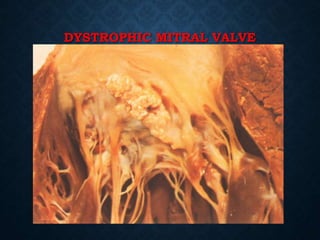
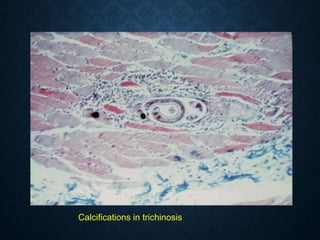
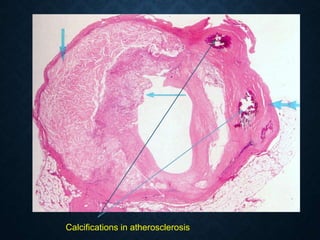
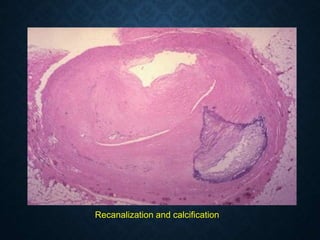
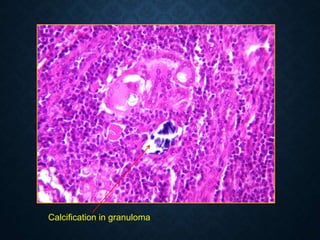
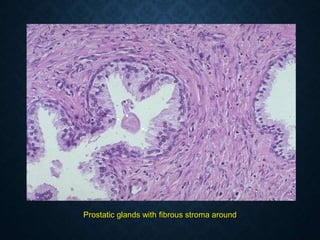
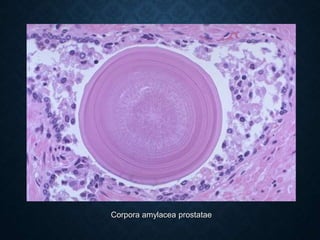
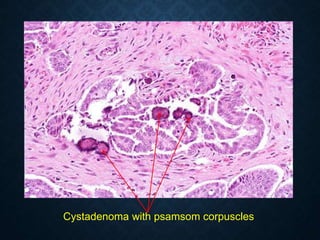
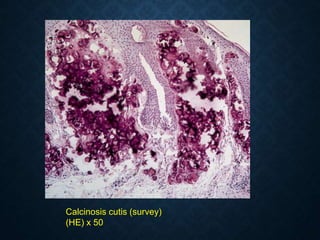
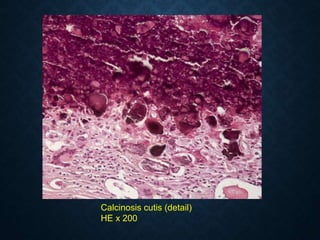
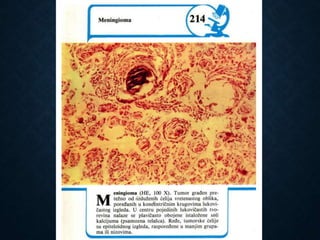
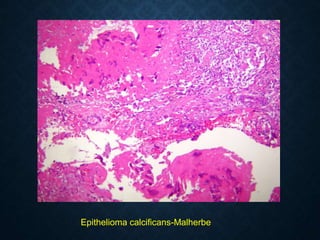
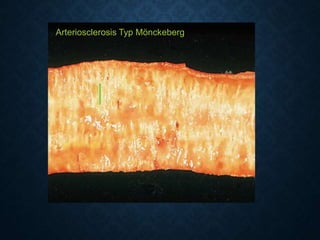
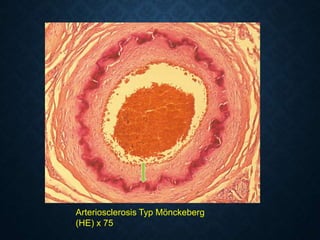
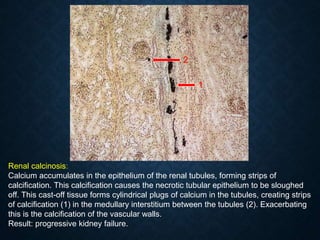
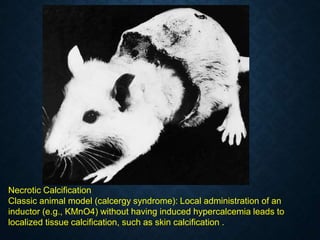
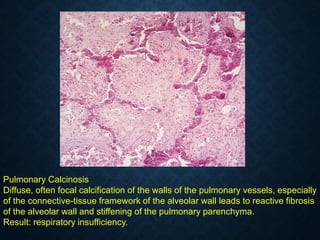
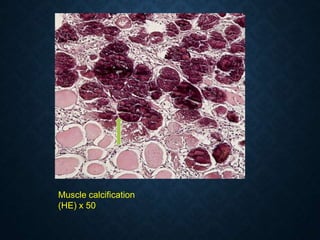
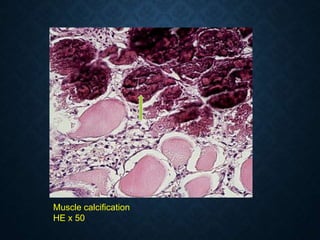
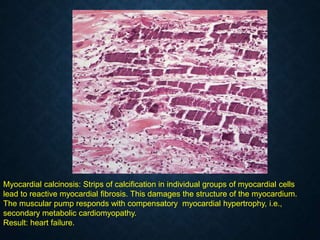
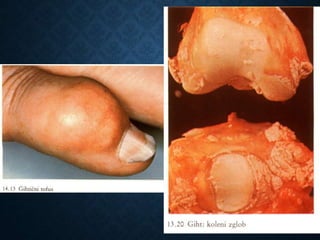
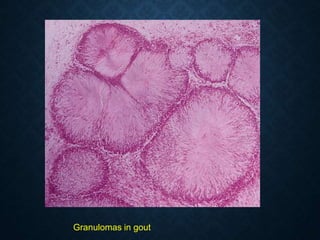
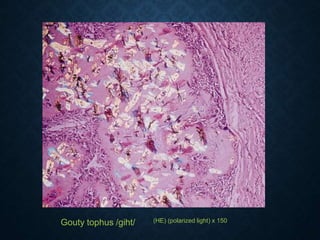
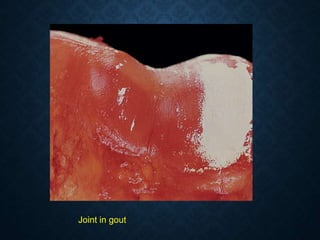
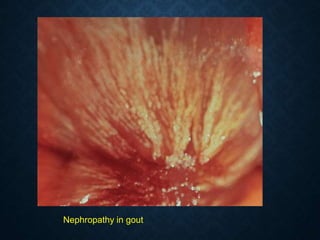
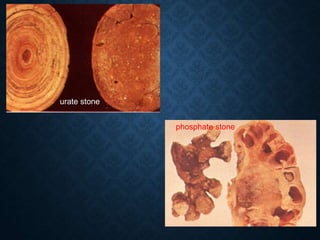
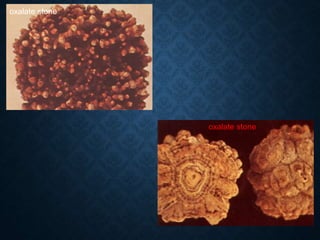
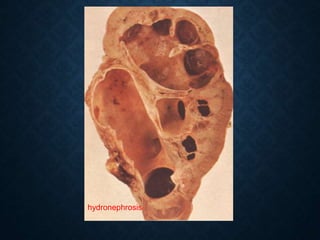
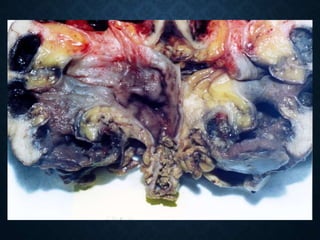
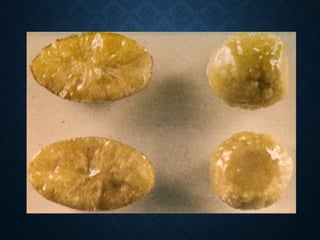
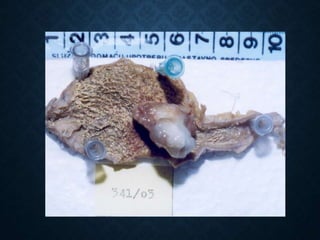
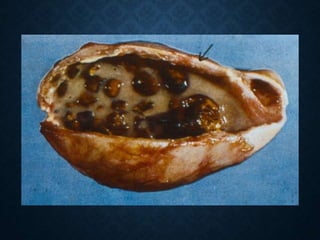
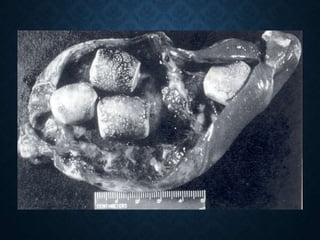
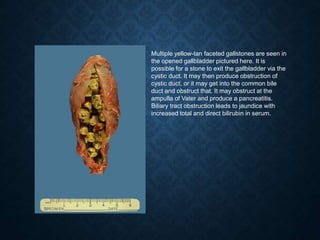
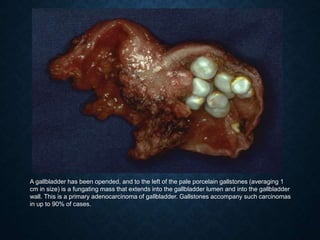
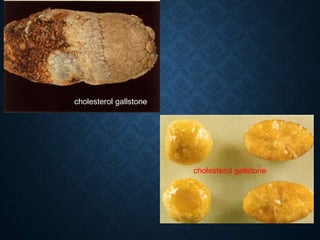
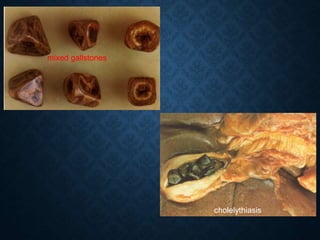
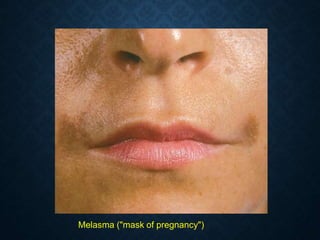
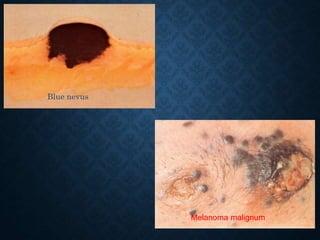
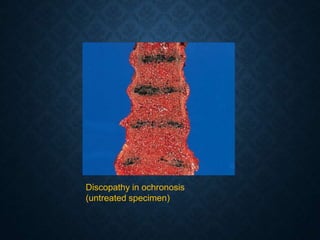
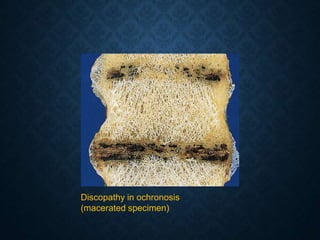
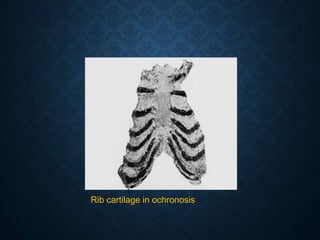
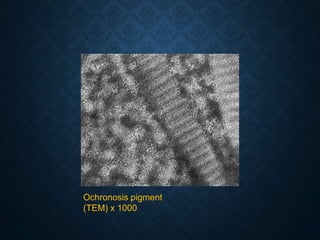
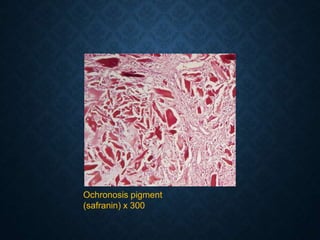
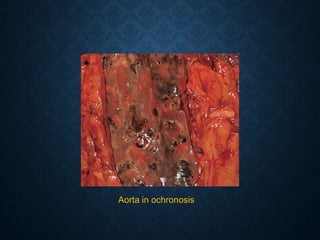
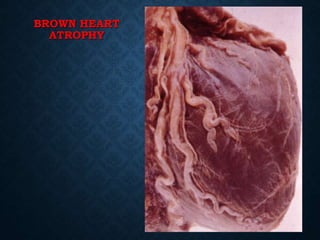
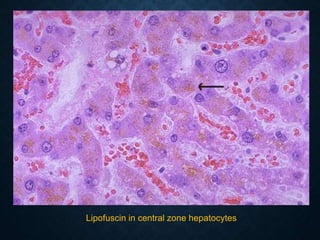
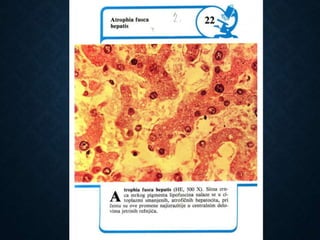
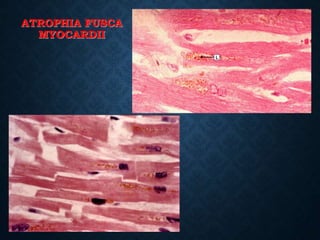
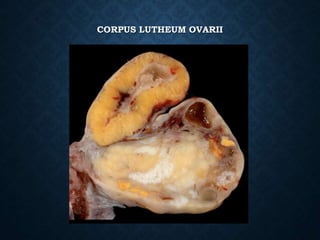
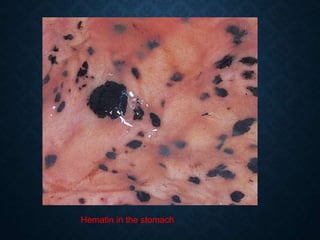
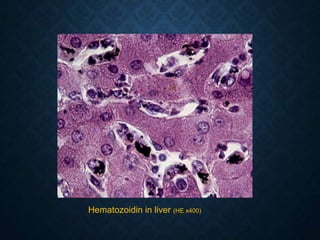
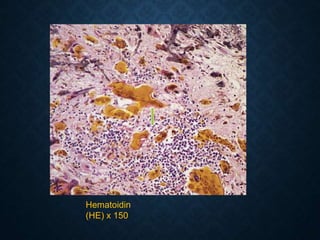
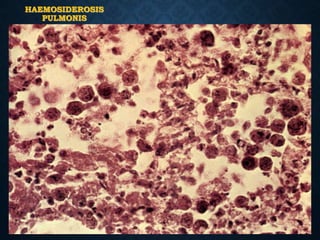
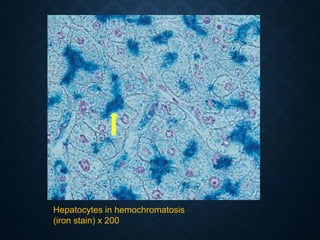
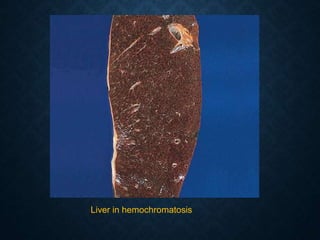
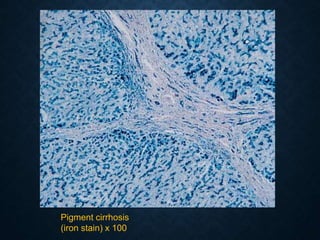
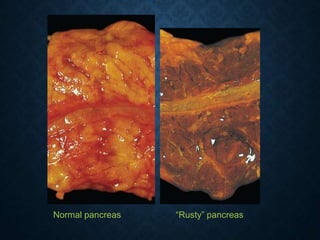
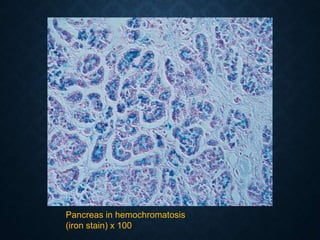
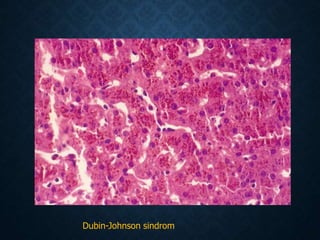
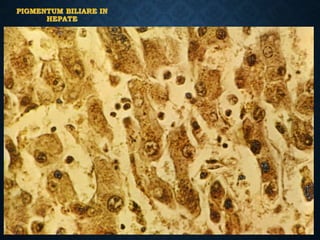
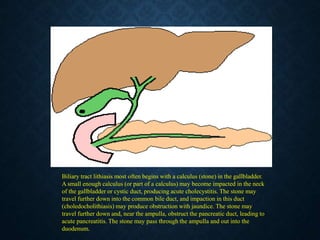
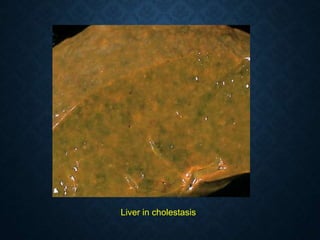
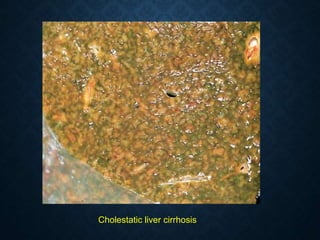
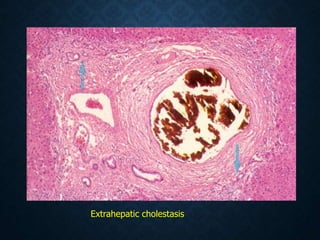
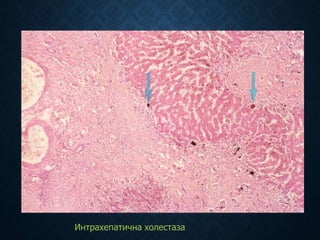
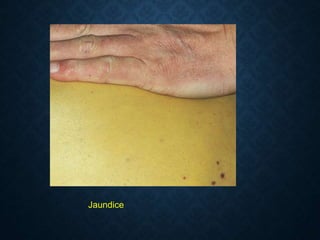
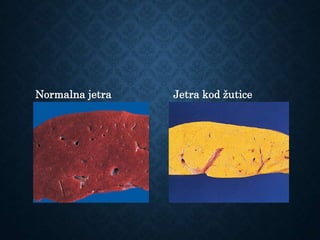
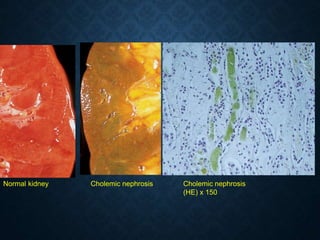
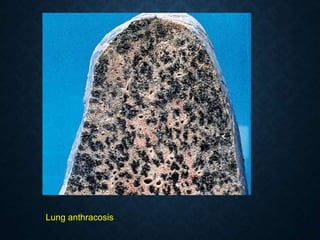
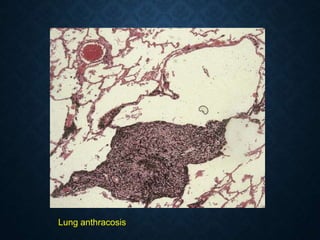
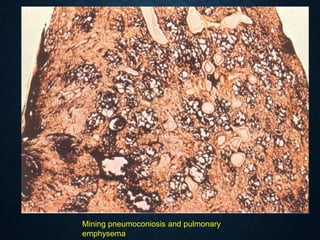
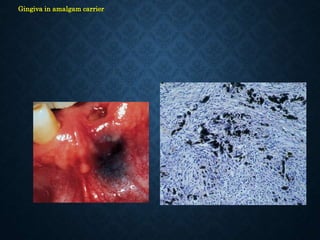
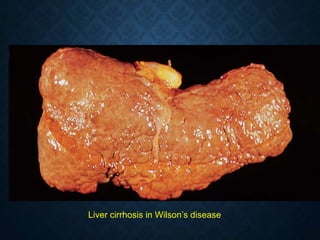
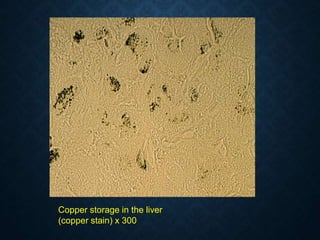
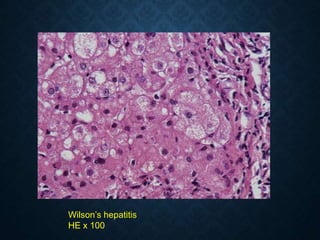
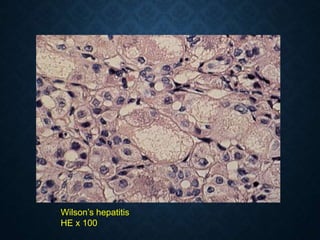
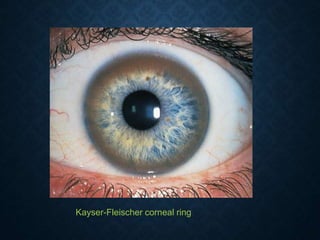
This document discusses atrophy and dystrophy. It defines atrophy as a decrease in size of a body part, organ, tissue or cell. Atrophy can be physiological, such as involution of organs over time, or pathological. Pathological atrophy has many causes including ischemia, inactivity, nerve damage, hormonal changes, malnutrition, pressure and decreased function. Dystrophy refers to morphological and functional damage to cells from intracellular or extracellular accumulation of substances. Common accumulations include water, lipids, and sphingolipids from genetic disorders. Specific diseases discussed include Gaucher disease, Niemann-Pick disease, and Tay-Sachs disease.