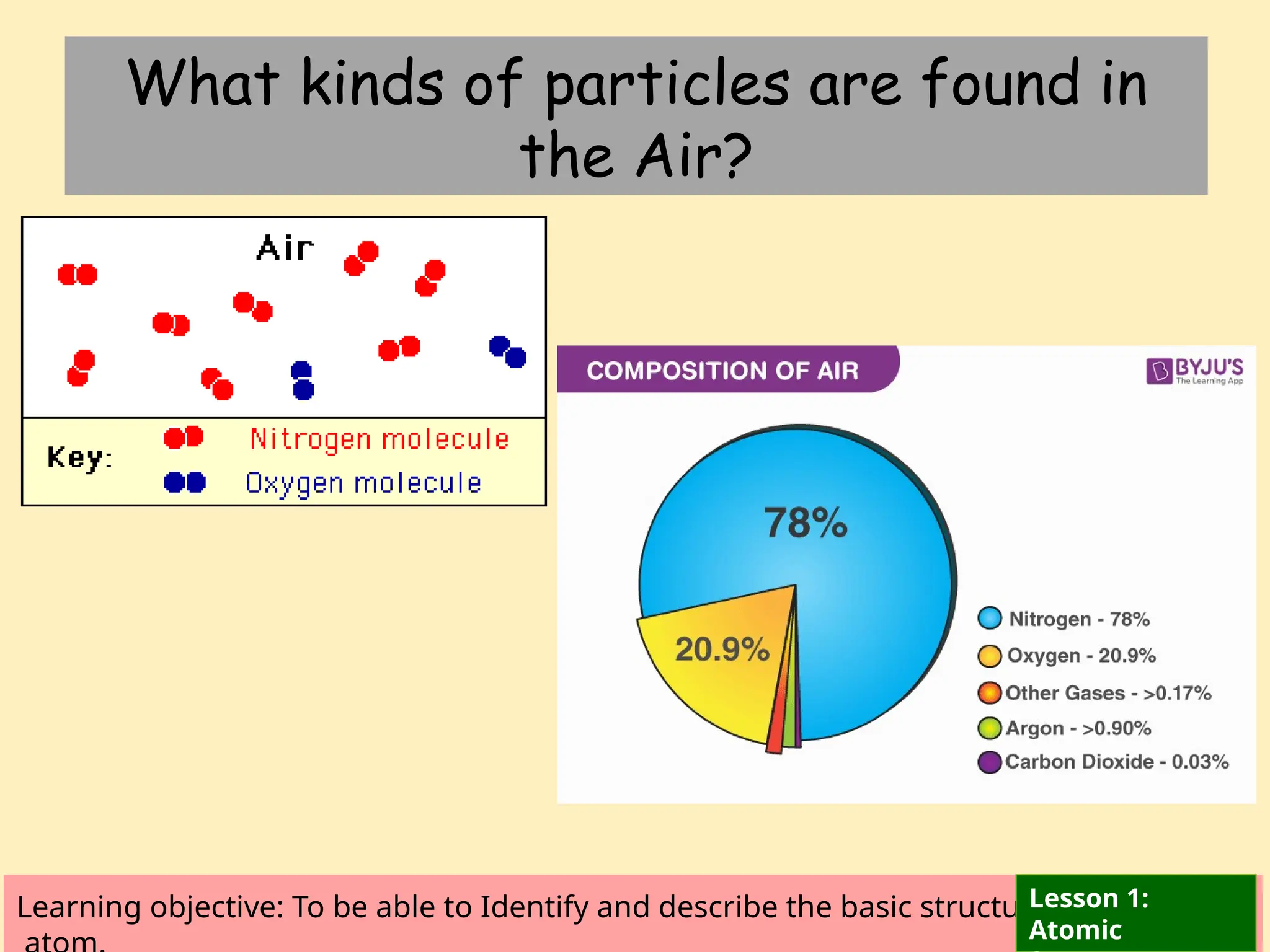
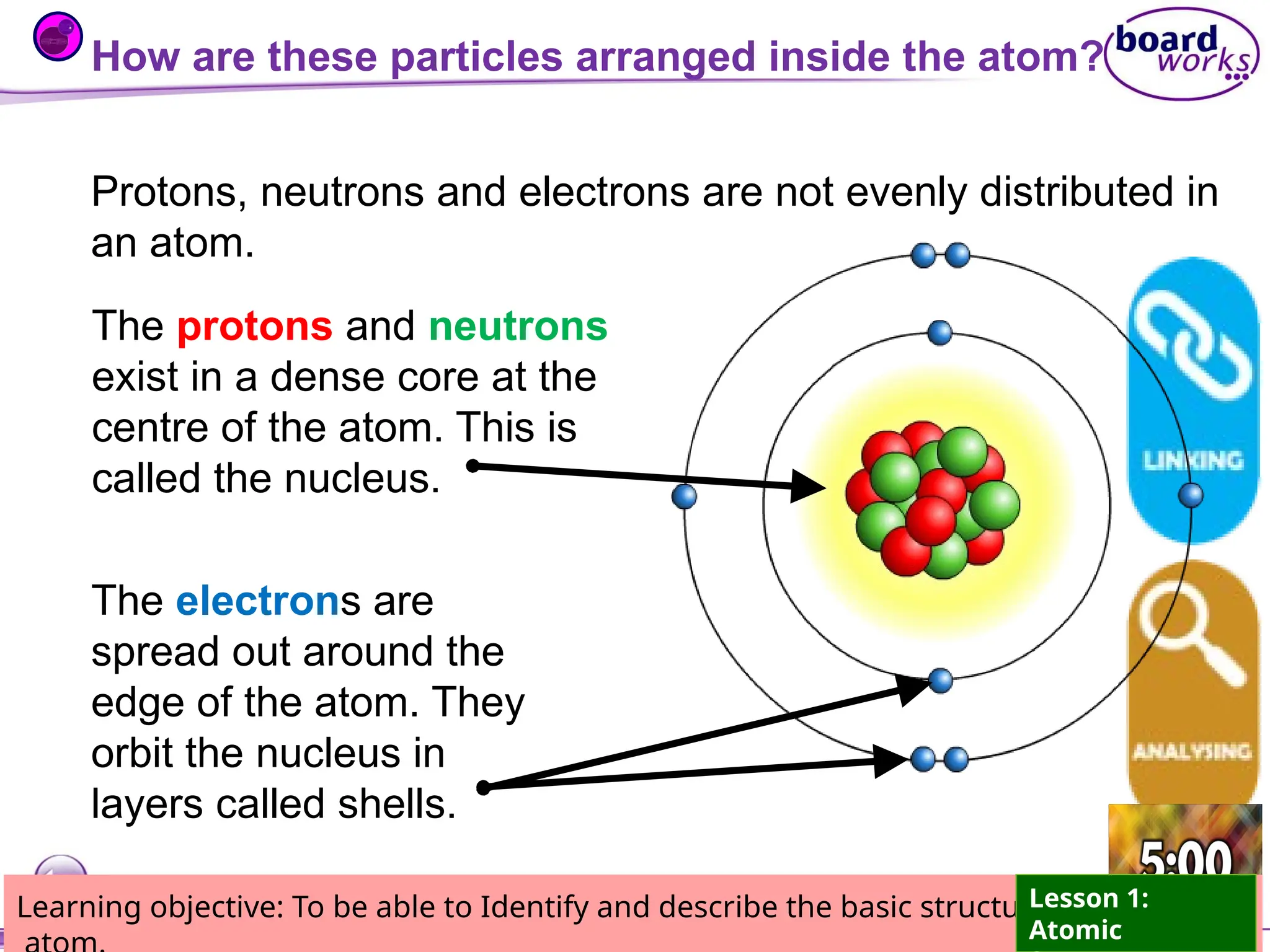
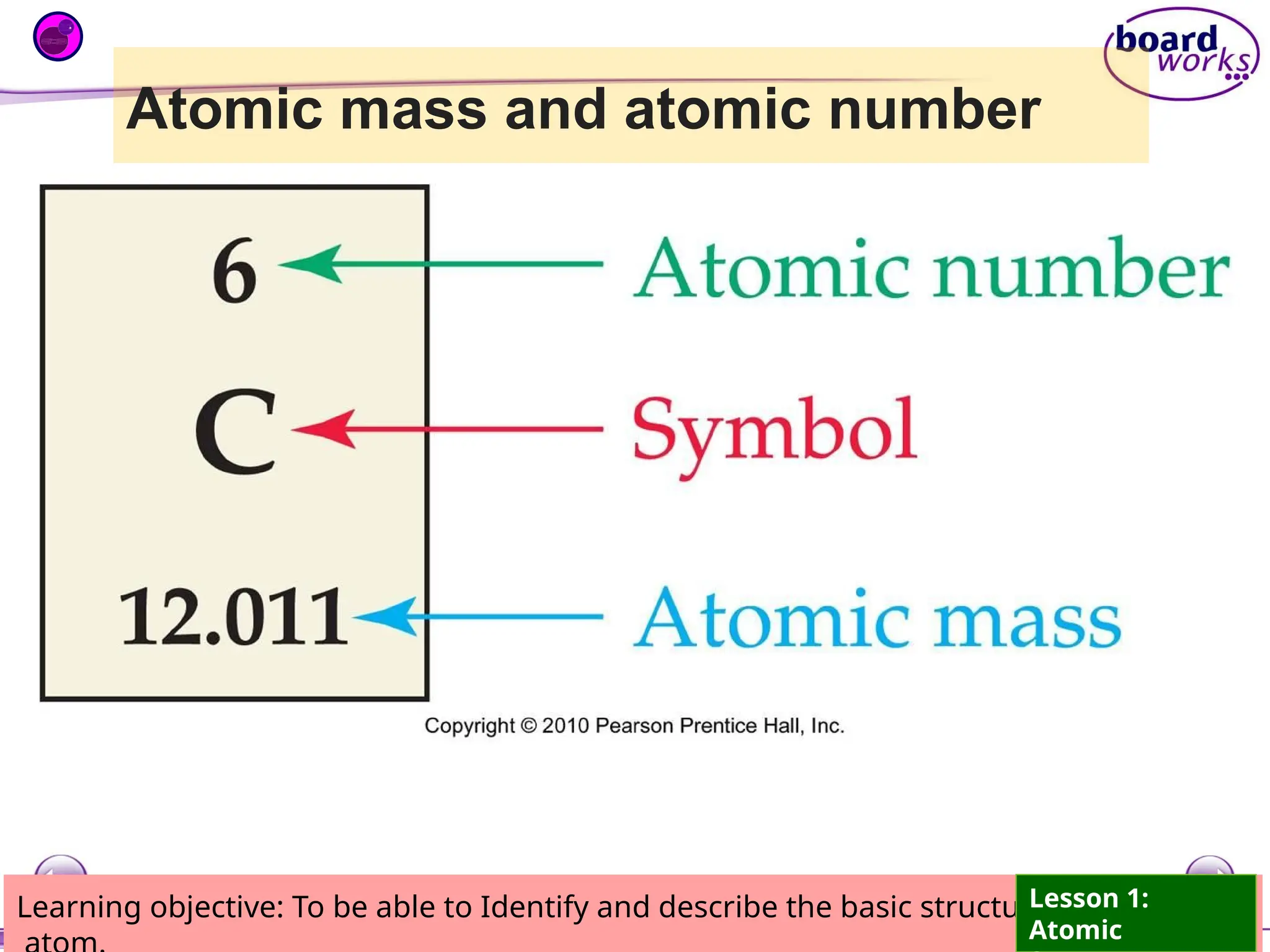
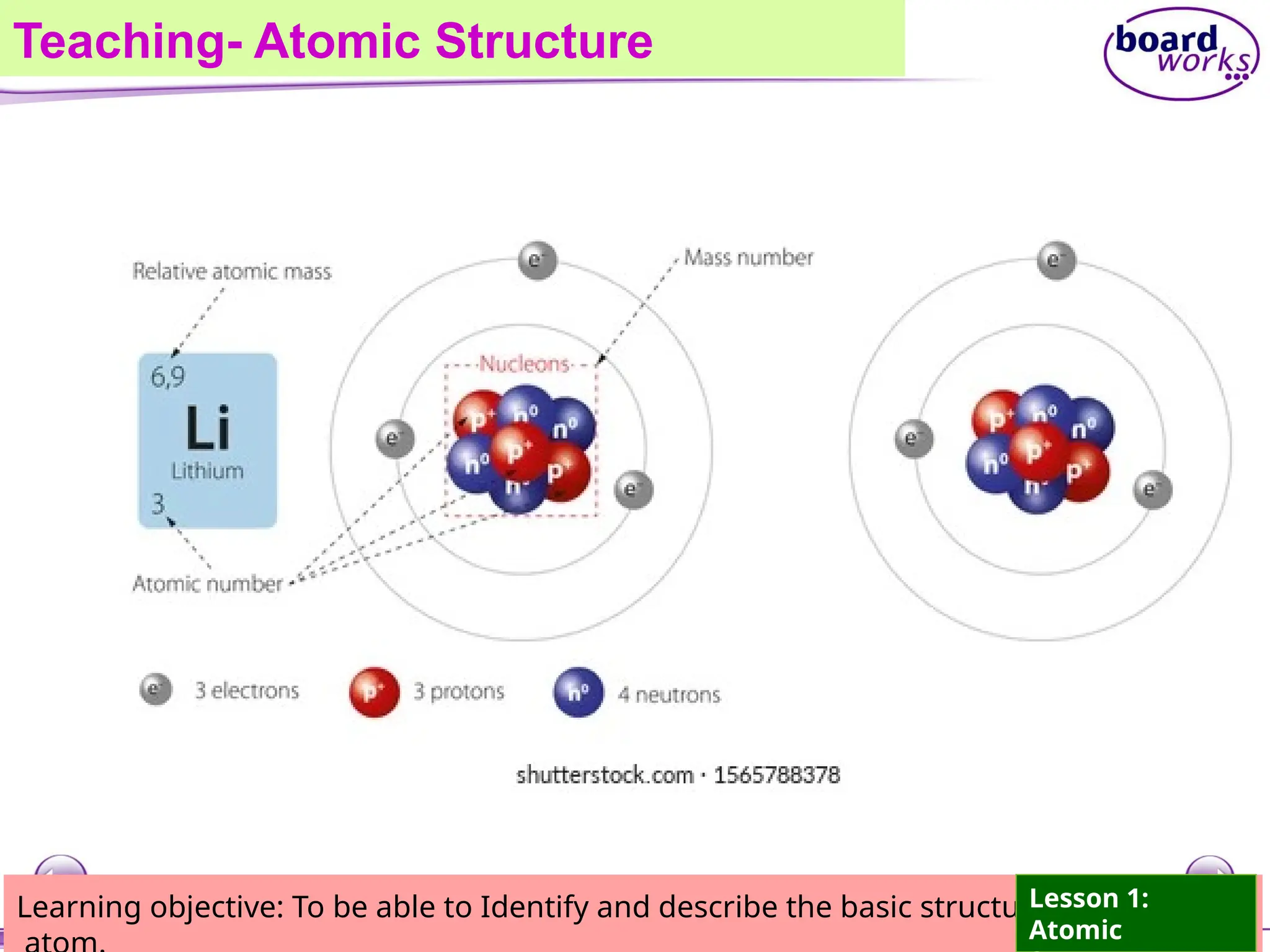
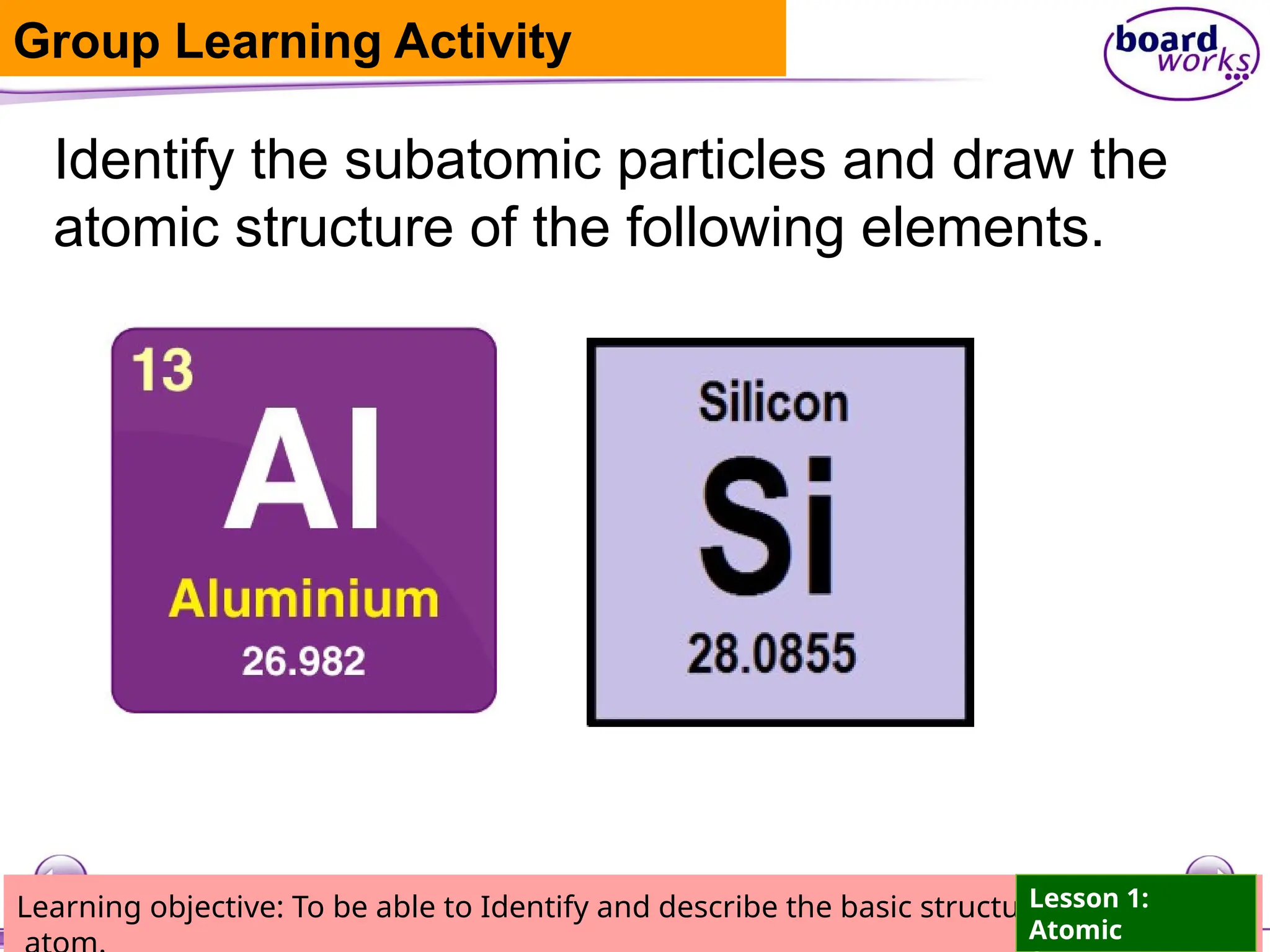
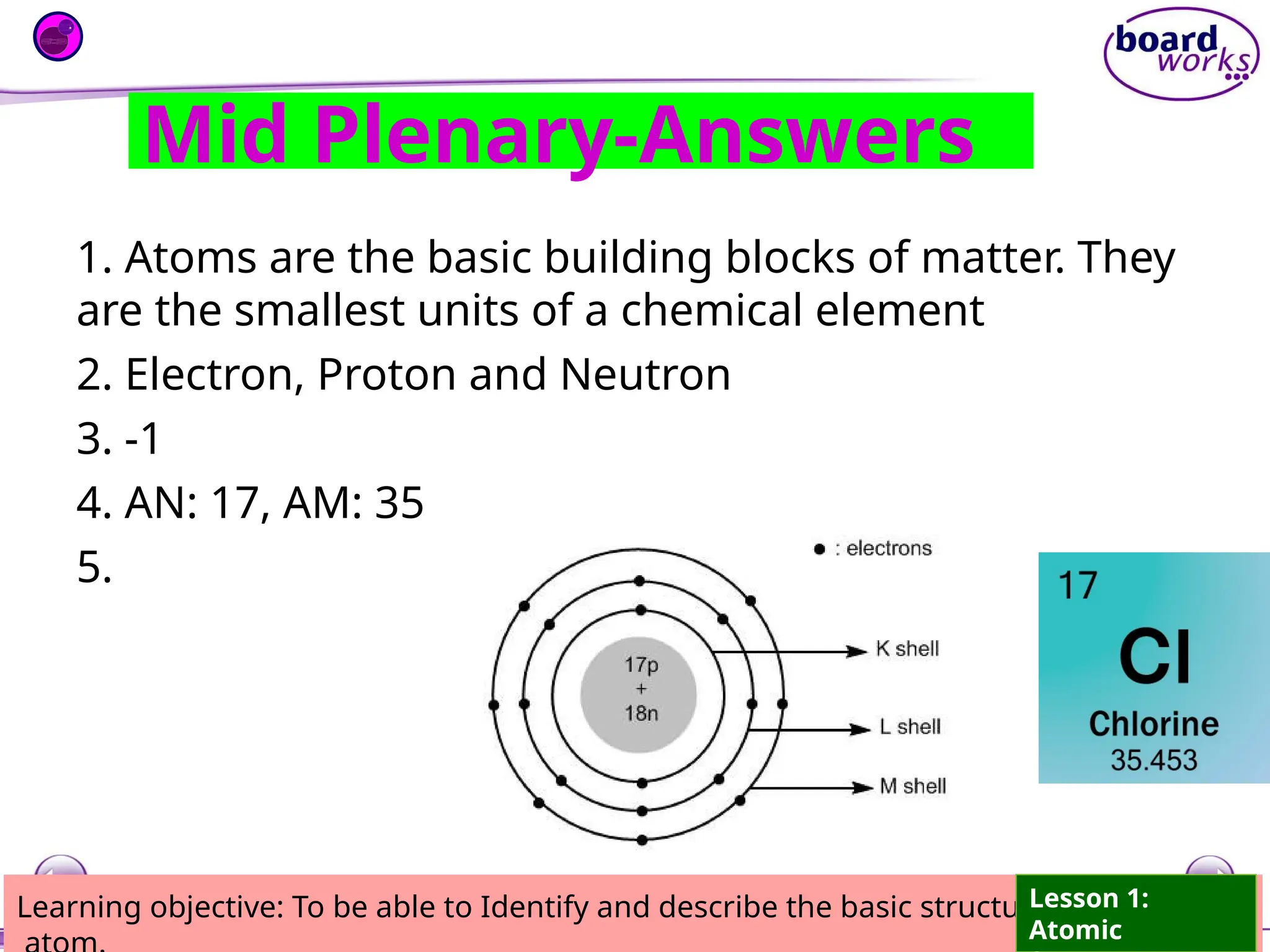
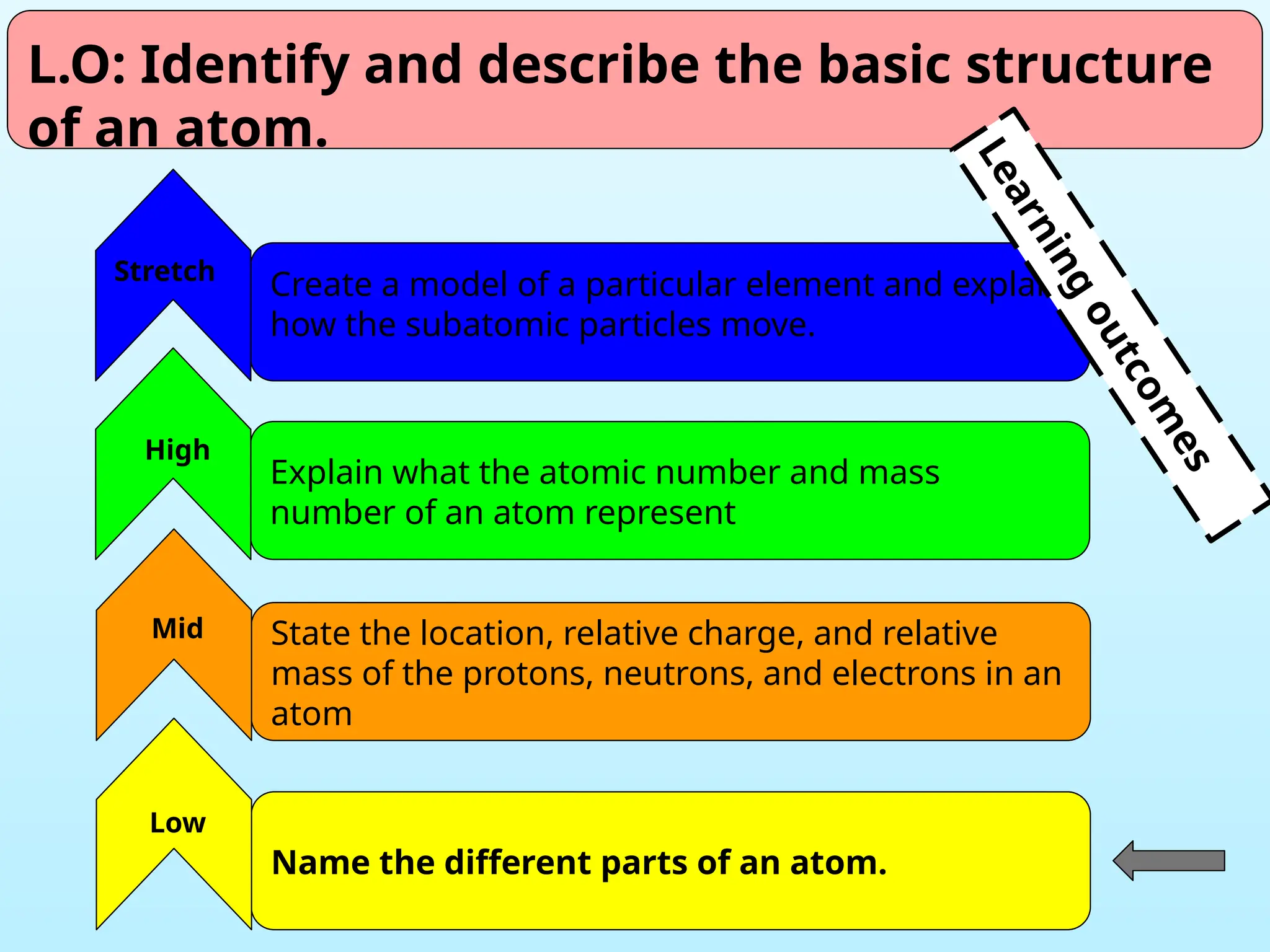
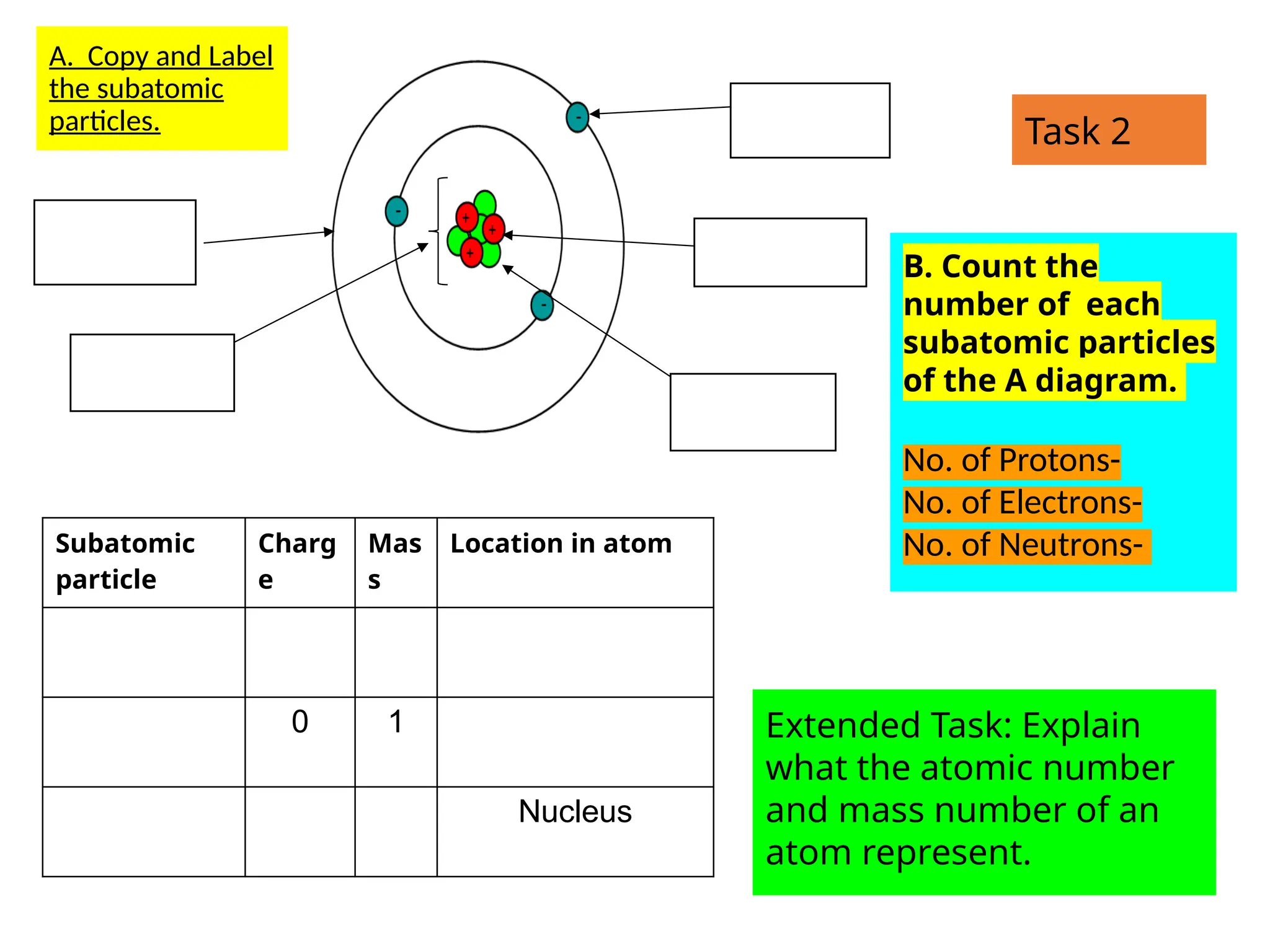
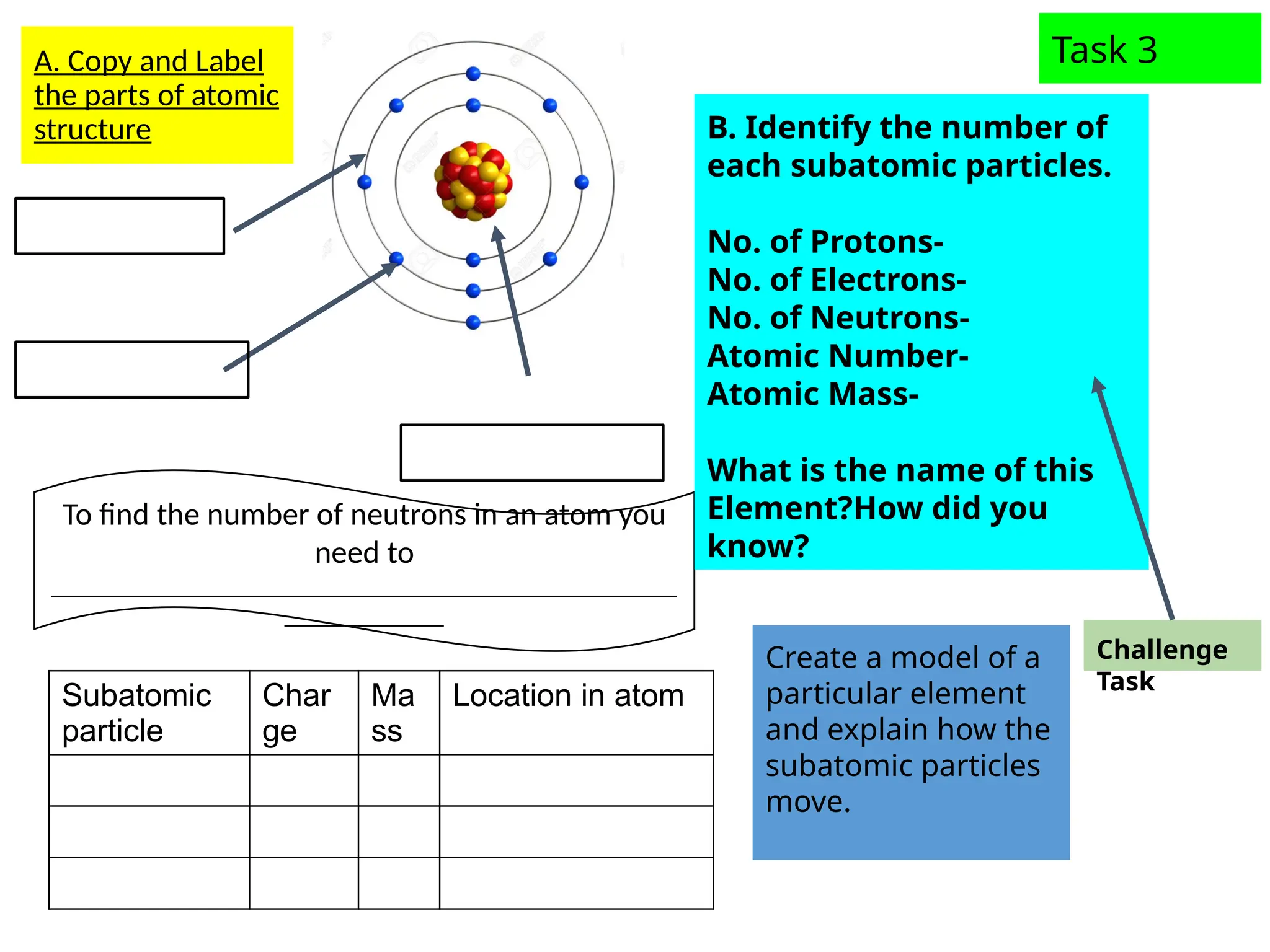
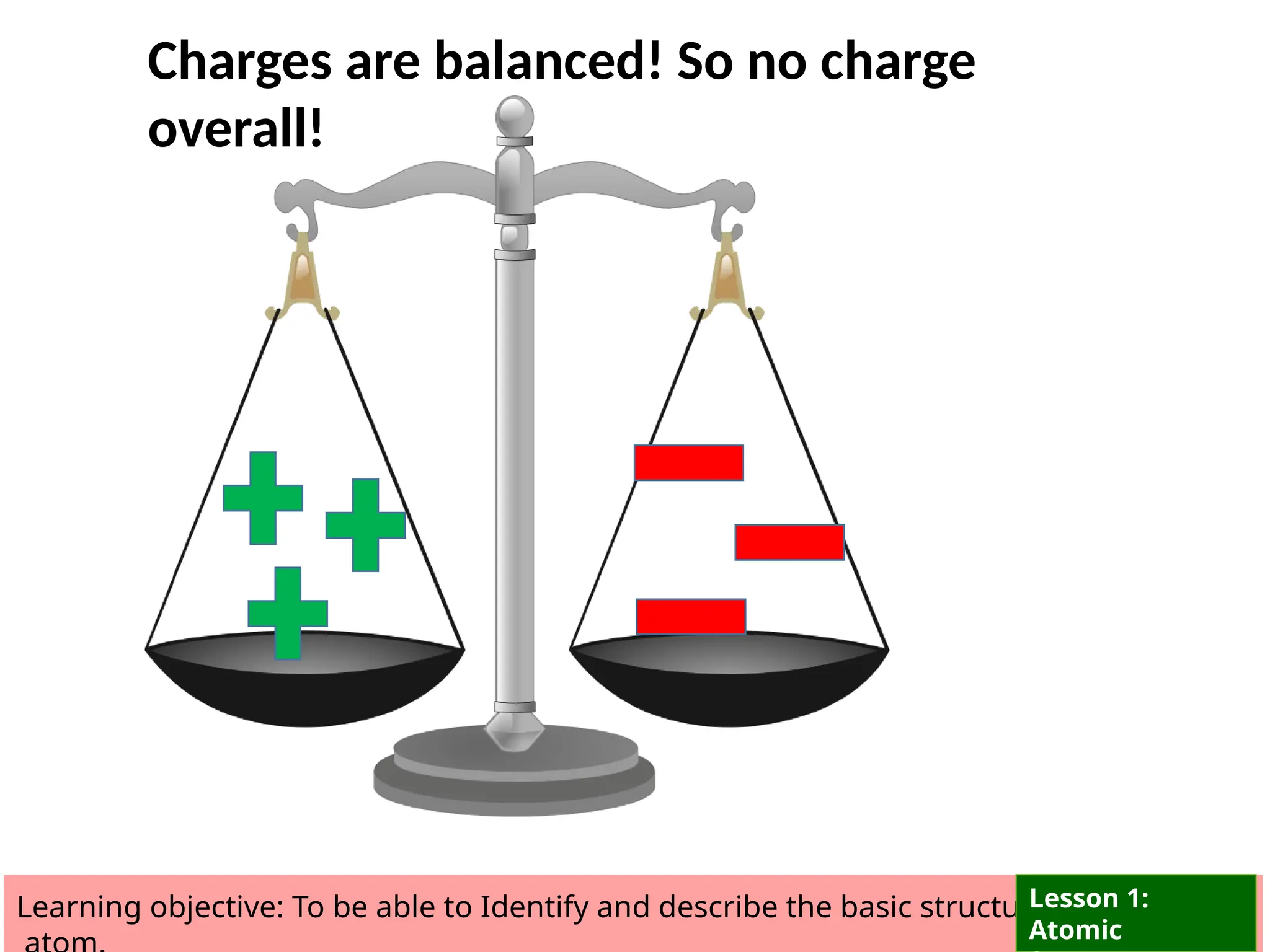
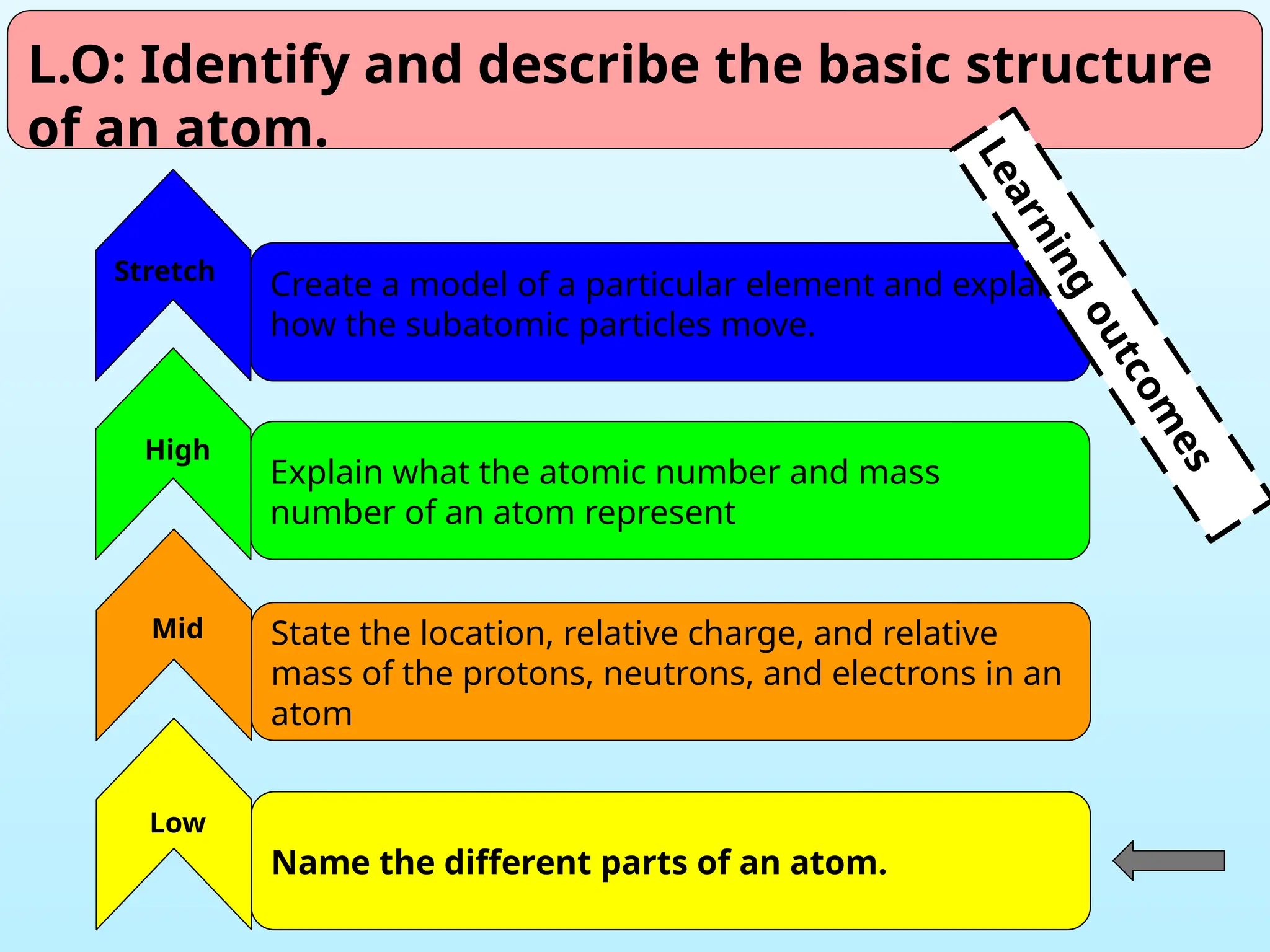
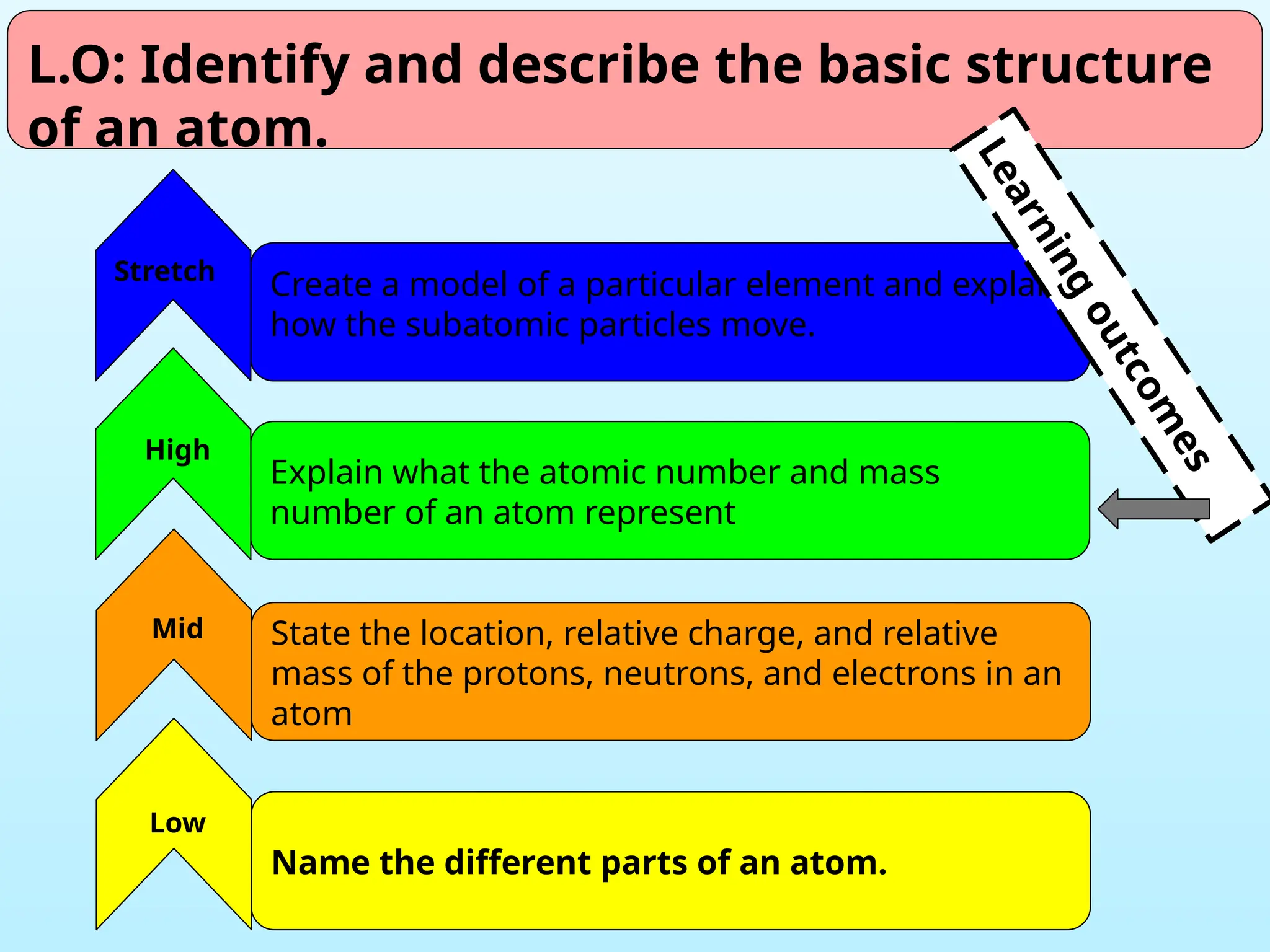
The document outlines learning objectives for identifying and describing the basic structure of an atom, including the types and characteristics of subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons). It discusses their arrangement within the atom, the concept of atomic number and mass number, and the principle that atoms are electrically neutral due to equal numbers of protons and electrons. Various activities and questions are provided to assess understanding and reinforce the material presented.