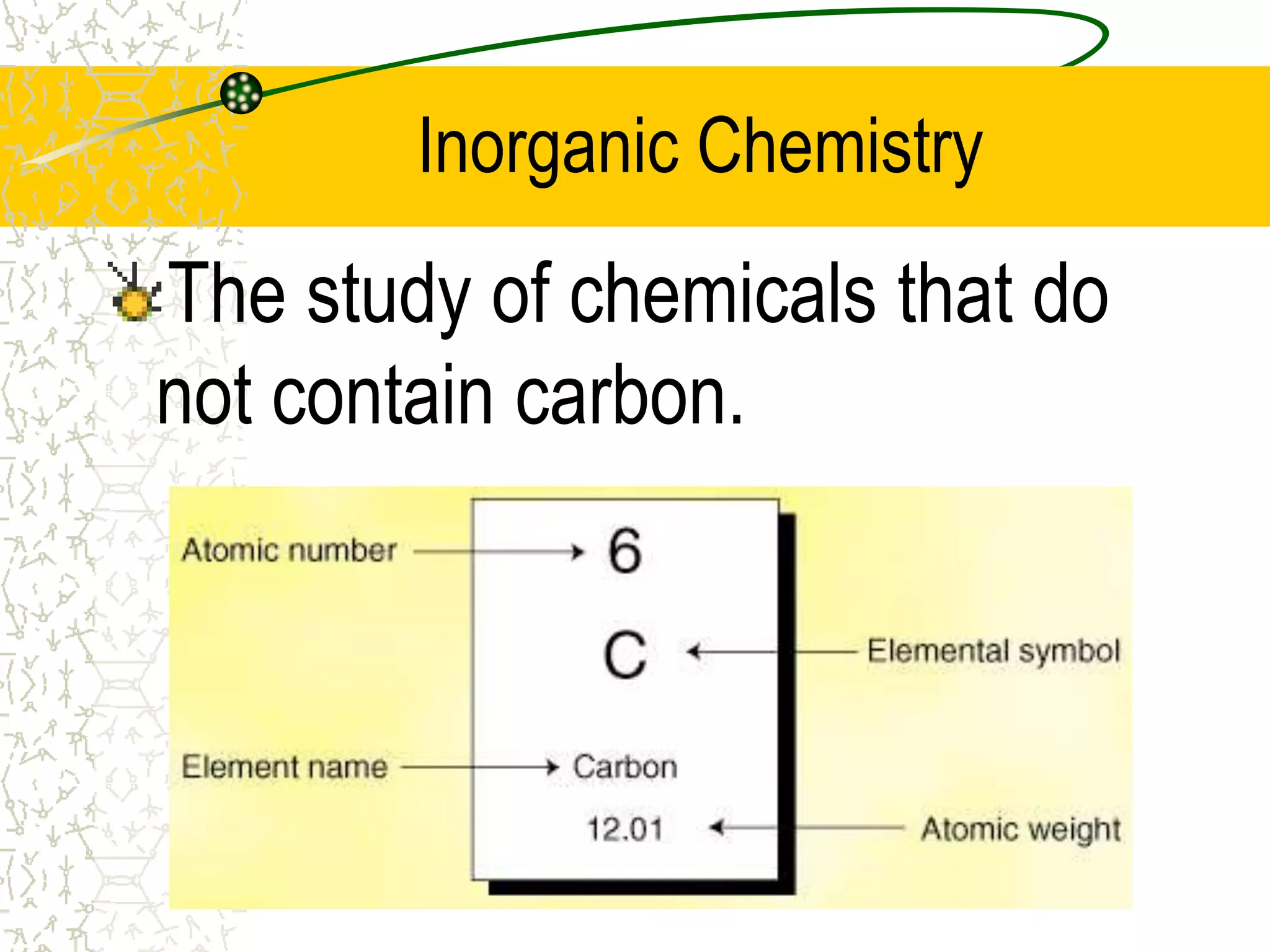
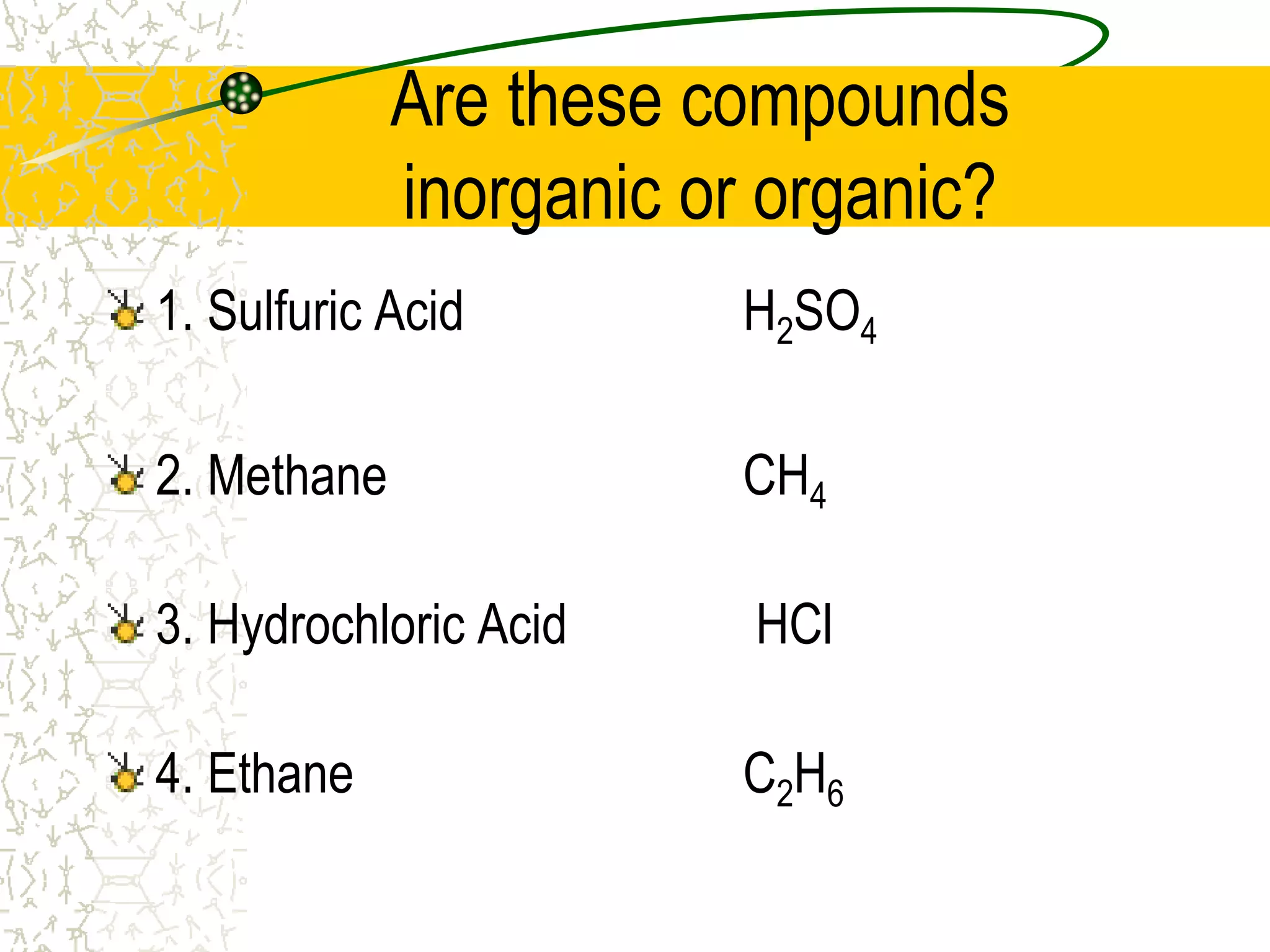
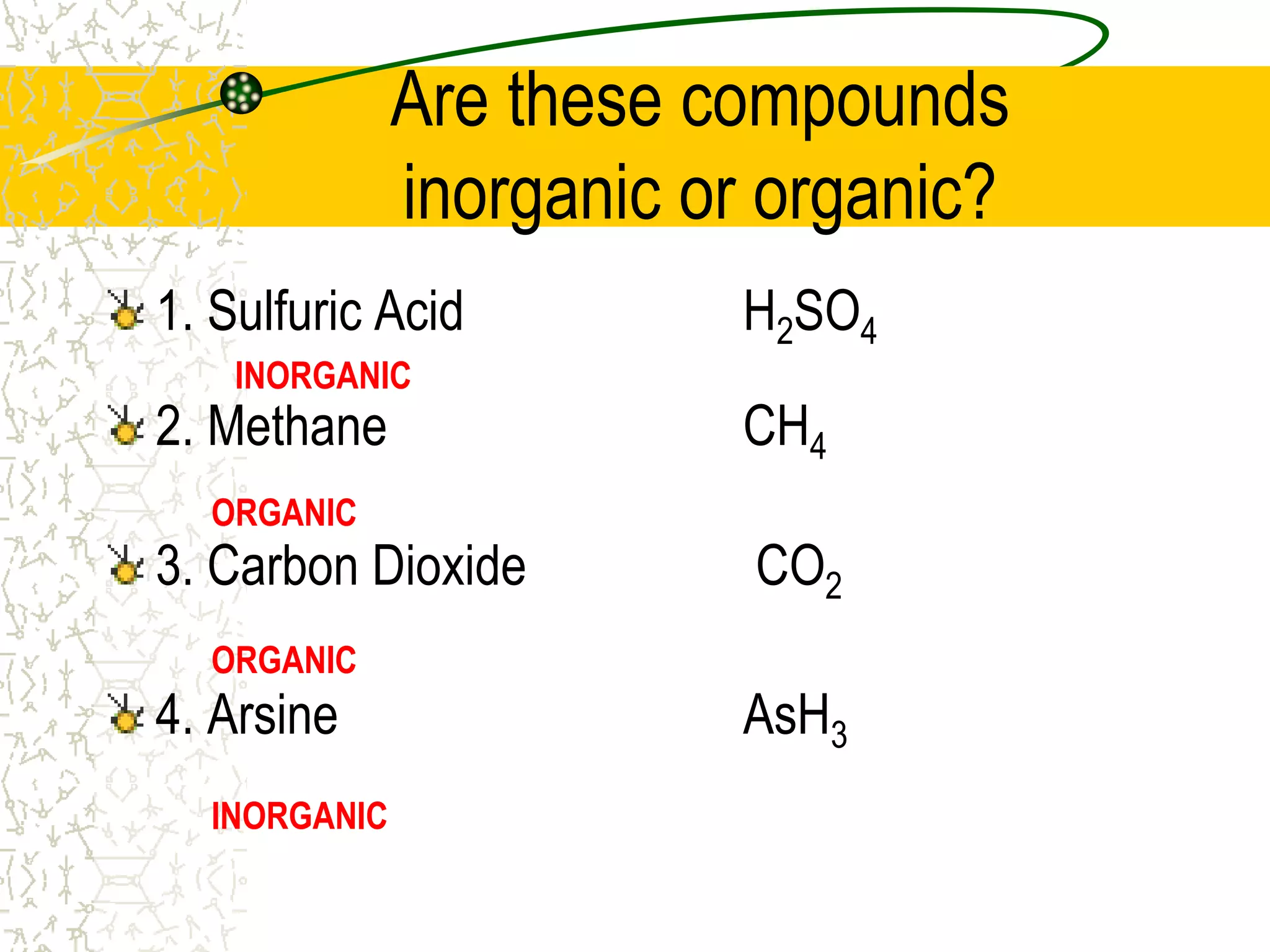
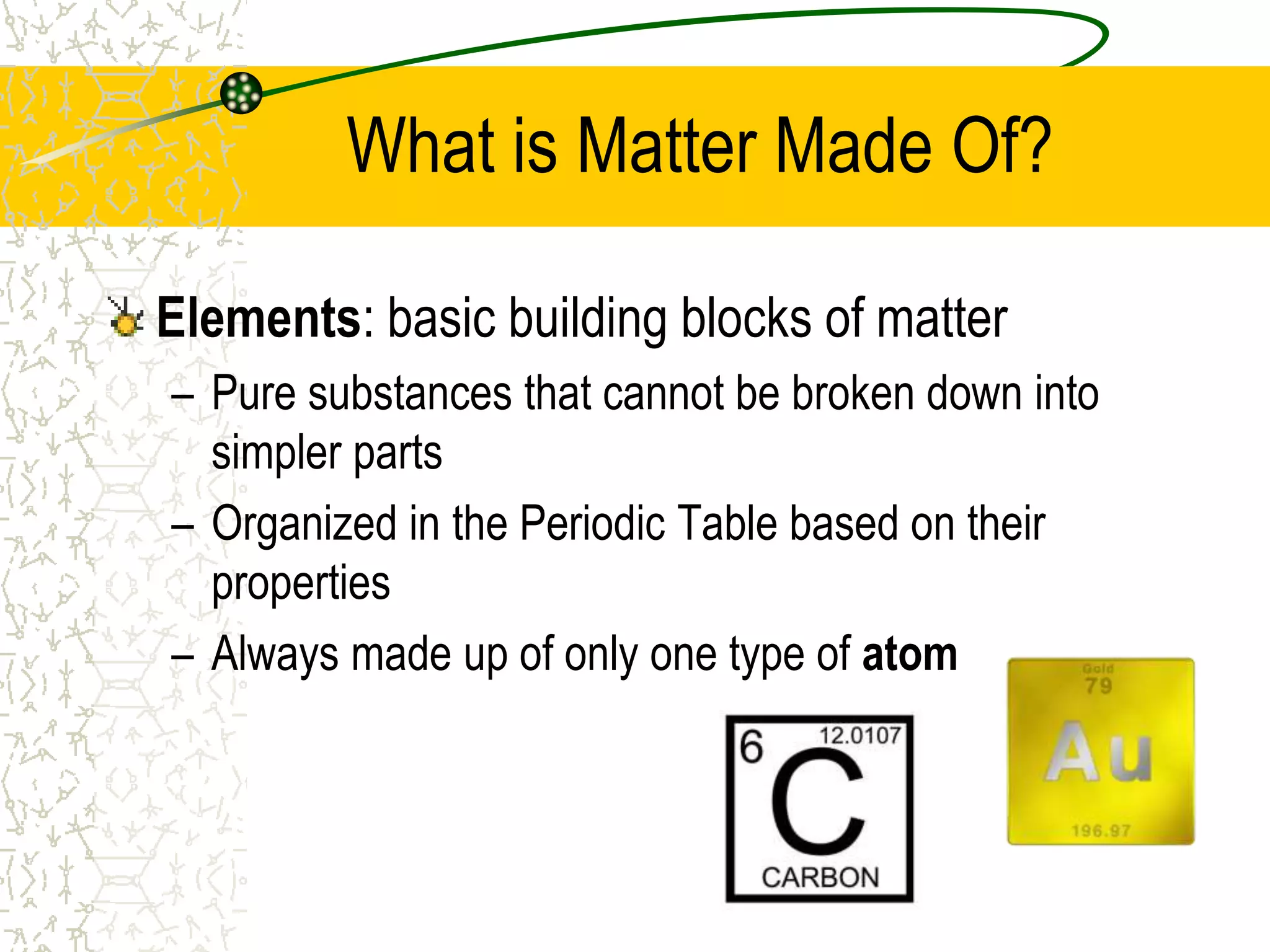
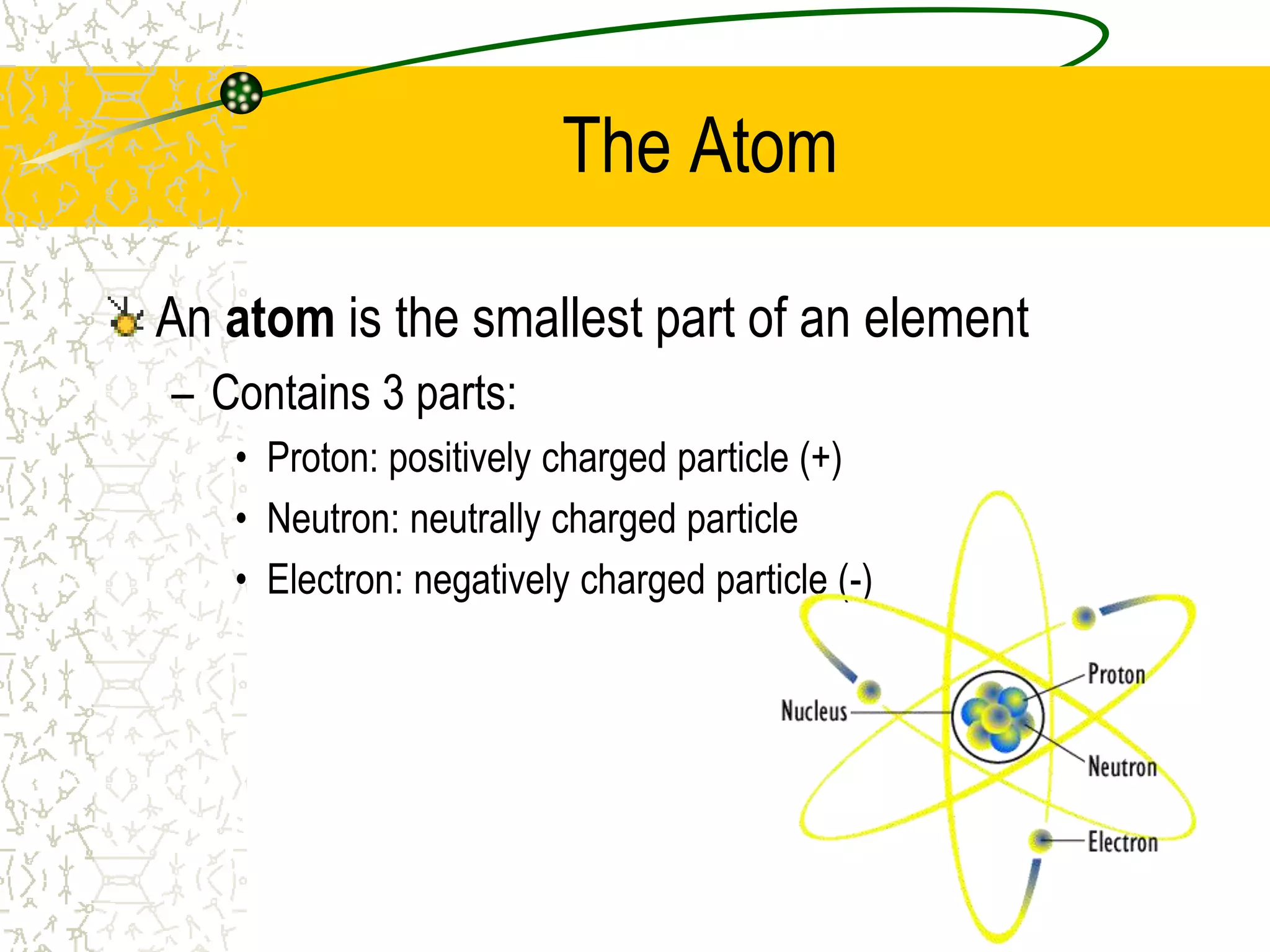
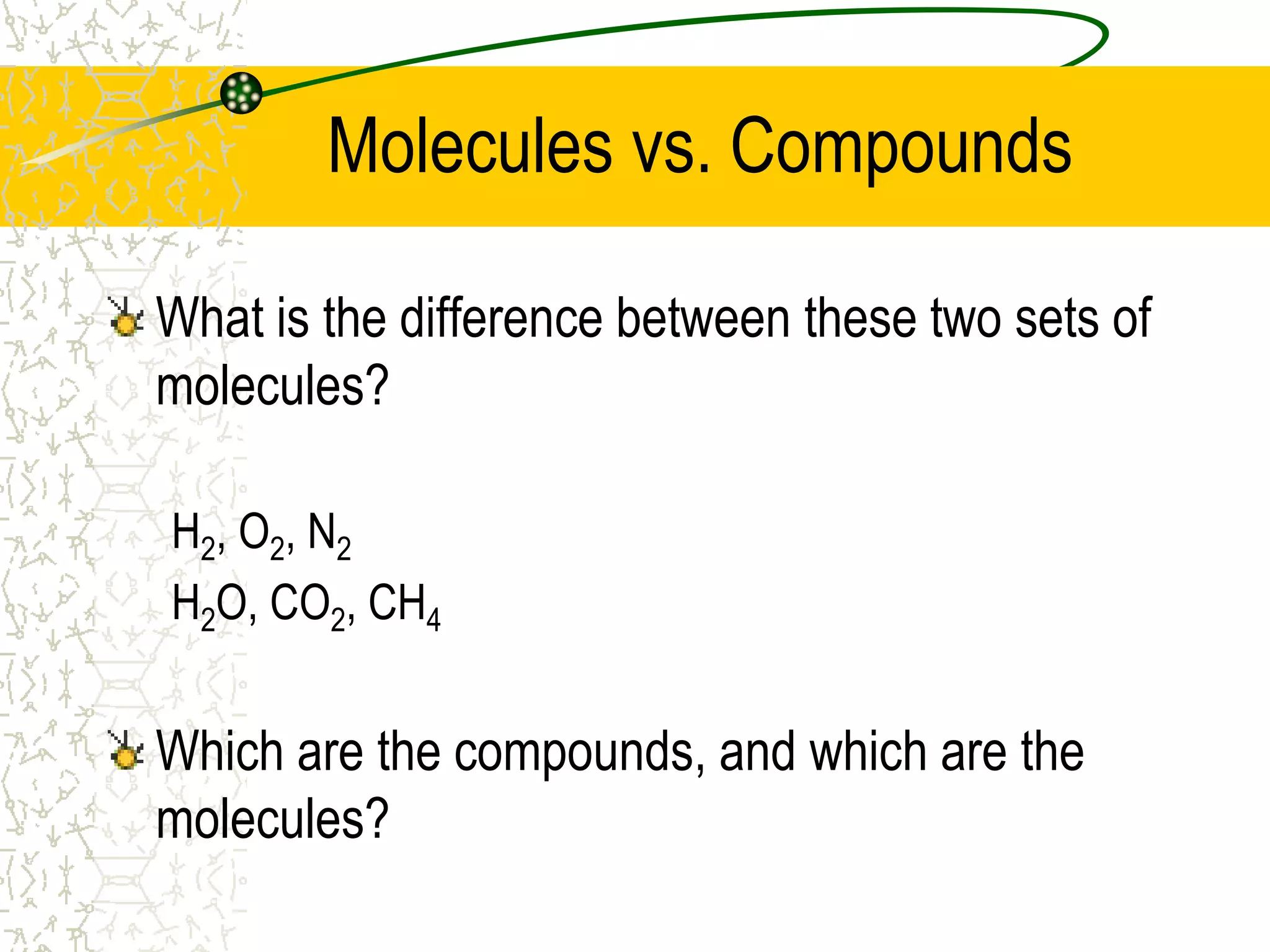
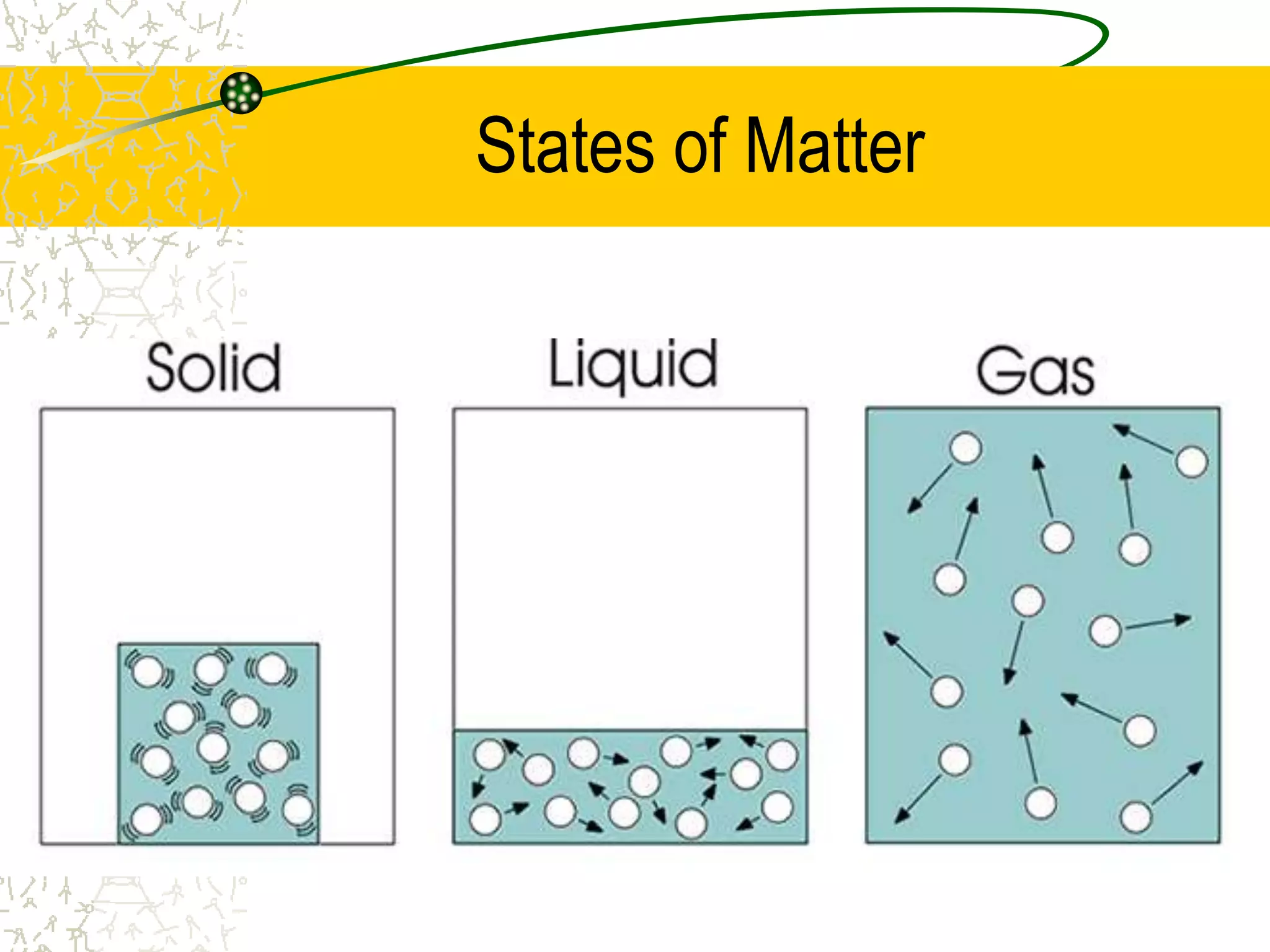
This document provides an introduction to chemistry, including what chemistry is, the five main branches of chemistry, and some key concepts about matter. It defines chemistry as the study of matter and its properties. The five branches are inorganic, organic, analytical, physical, and biochemistry. Matter is defined as anything that has mass and takes up space, and can exist in solid, liquid, or gas states. Chemical and physical properties are also introduced.