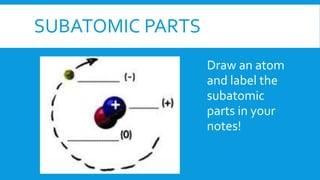
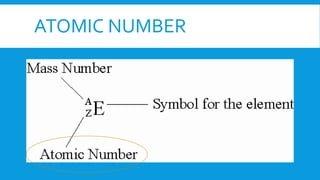
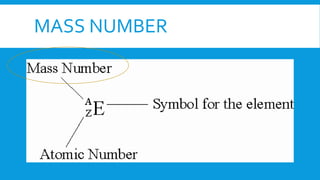
This document provides information on atomic structure including subatomic particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons. It defines these particles and their properties such as charge. It describes how atoms have no overall charge when the number of protons and electrons are equal. It also defines atomic number as the number of protons and mass number as the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Formulas are provided to calculate these values and the number of neutrons from the periodic table. Ions are also introduced as atoms that have gained or lost electrons, becoming positively or negatively charged.