This document provides an overview of Earth's atmosphere, including its composition, structure, and importance. It discusses the following key points:
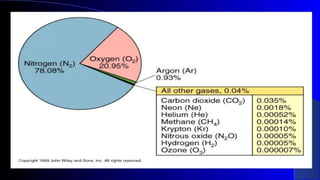
- The atmosphere is composed primarily of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace amounts of other gases. It also contains water vapor and aerosol particles.
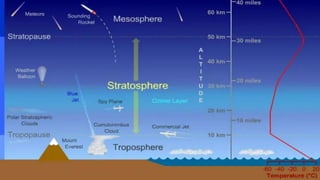
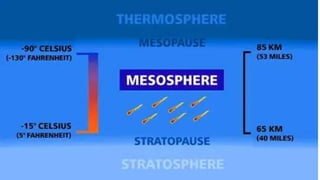
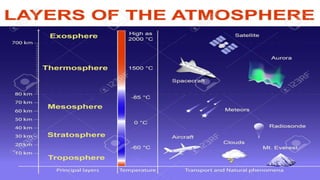
- The atmosphere is divided into five main layers based on temperature - the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Each layer has distinguishing temperature and chemical characteristics.
- The different layers play important roles. The troposphere contains most weather phenomena. The stratosphere absorbs ultraviolet radiation via the ozone layer. The thermosphere facilitates radio communication.
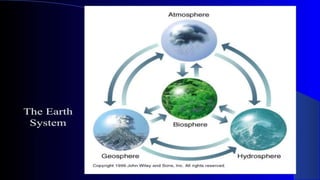
- Together,