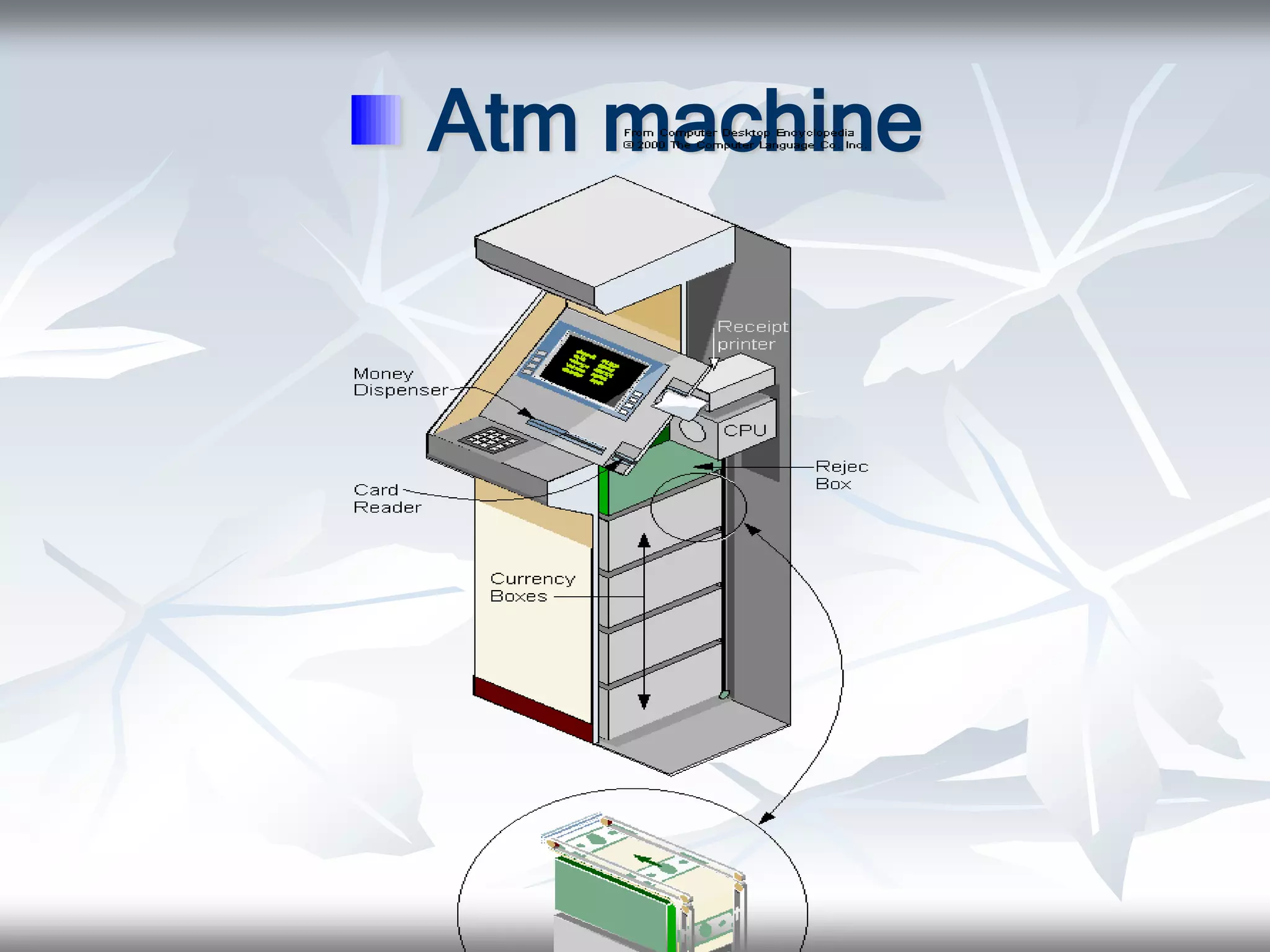
This document discusses the use of facial recognition technology at ATMs. It begins with an introduction and outline. It then provides background on the history of ATMs, including their invention in the late 1960s. It discusses the need for facial recognition at ATMs to reduce fraud. The document explains how facial recognition works by analyzing nodal points on the face and creating a unique faceprint. It describes the identification process and advantages of using this technology, such as reduced fraud and convenience. Potential disadvantages include recognition not being unique enough and the need for time to match images. In conclusion, the document argues that additional security like facial recognition is needed due to increasing ATM fraud.