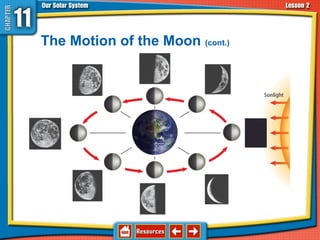
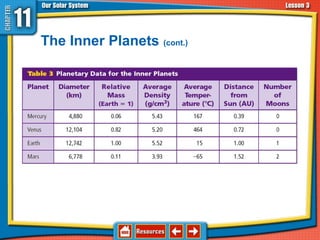
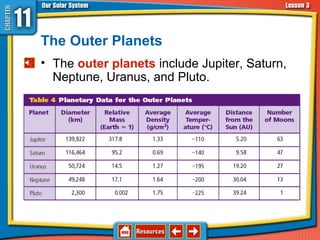
The document discusses topics relating to the Sun-Earth-Moon system and planetary motion. It describes how Earth orbits the Sun in an elliptical path, rotating on its tilted axis to cause day and night. The Moon orbits Earth, reflecting sunlight and exhibiting phases as its illuminated portion changes. Eclipses can occur when the Sun, Earth, and Moon align, blocking light. The planets are divided into inner rocky planets and outer gas giants, with characteristics like composition and moons described for each. Asteroids, comets, and meteoroids are also discussed, along with their origins and interactions with planets.