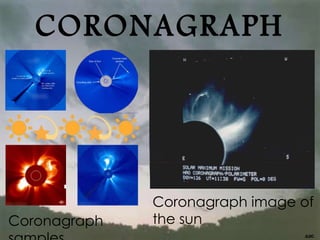
The document discusses several astronomical and measurement instruments, including coronagraphs, magnetometers, tellurions, and helioscopes. A coronagraph allows observation of solar phenomena by simulating an eclipse, while magnetometers measure magnetic fields and are used in various applications, including military contexts. Tellurions represent celestial movements and calendars, and helioscopes are designed for observing the sun and sunspots.