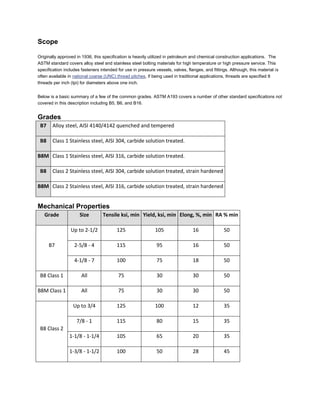
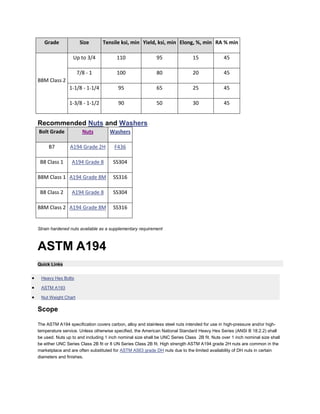
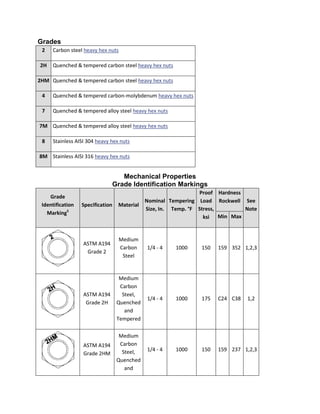
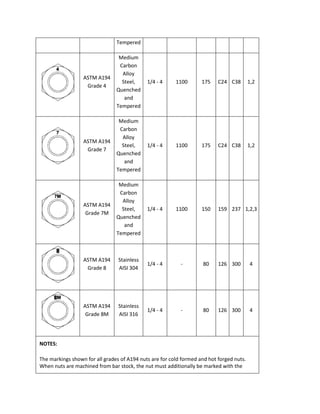
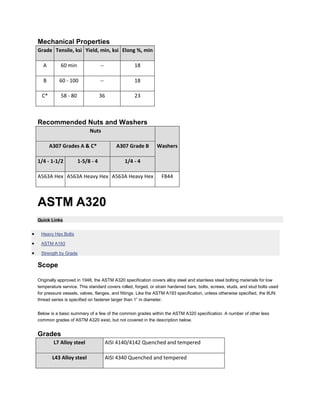
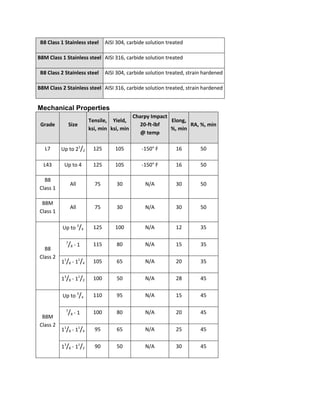
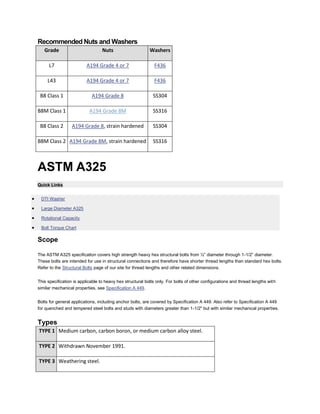
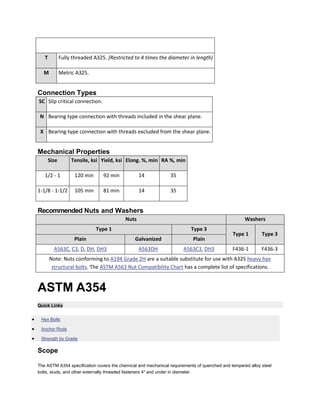
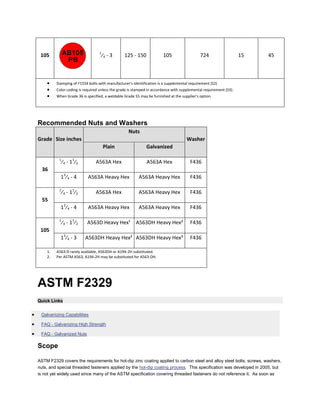
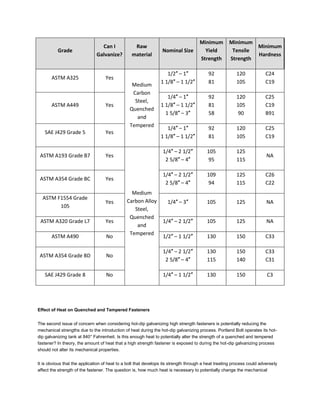
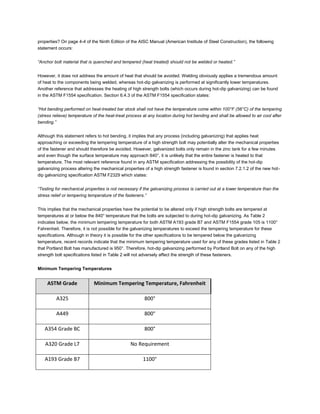
The document discusses various ASTM bolt specifications. It provides details on specifications for bolts made of different materials, intended for different applications and temperature ranges. Specifications cover bolts made of steel, alloy steel and stainless steel. Each specification lists the grades of bolts it covers along with the minimum mechanical properties requirements for each grade.