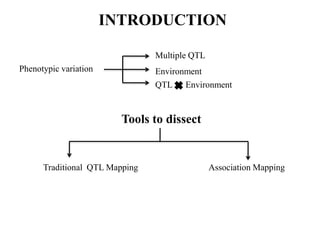
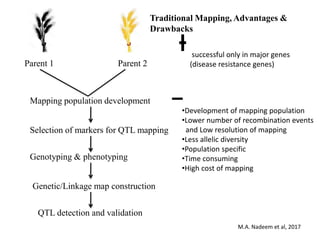
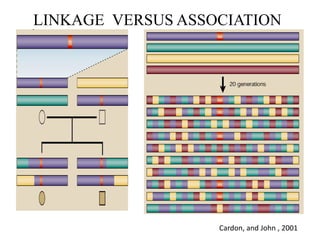
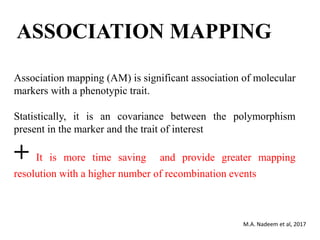
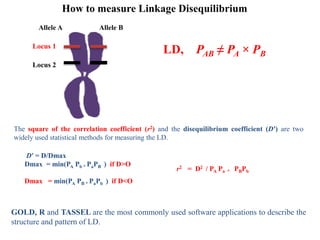
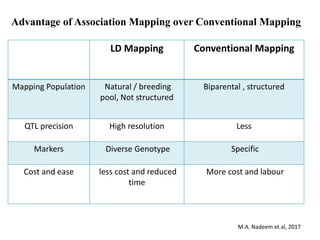
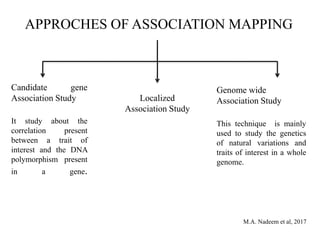
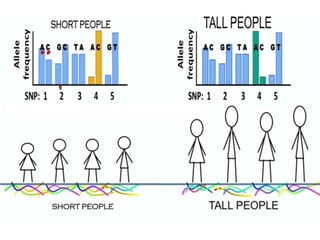
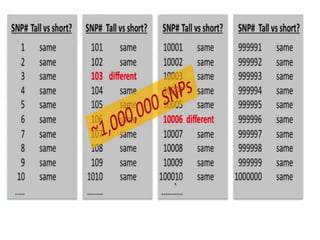
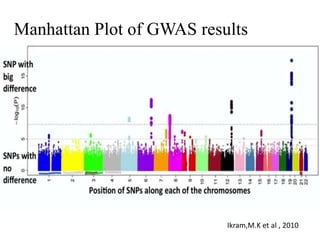
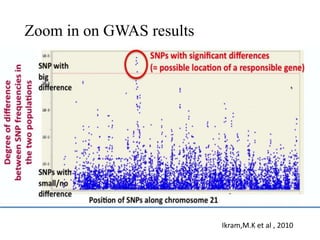
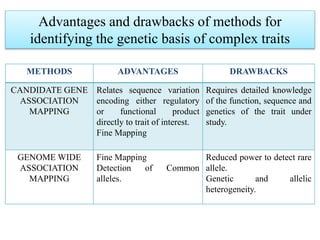
This document provides an overview of association mapping as a tool for dissecting phenotypic variation and mapping quantitative trait loci (QTLs). It discusses the differences between traditional QTL mapping using biparental mapping populations versus association mapping using natural populations. Association mapping offers higher mapping resolution, uses more diverse germplasm, and is less time-consuming and costly than traditional QTL mapping. It then describes linkage disequilibrium-based association mapping and factors that influence linkage disequilibrium. The document also discusses different approaches to association mapping, including candidate gene association studies, genome-wide association studies, and localized association studies.