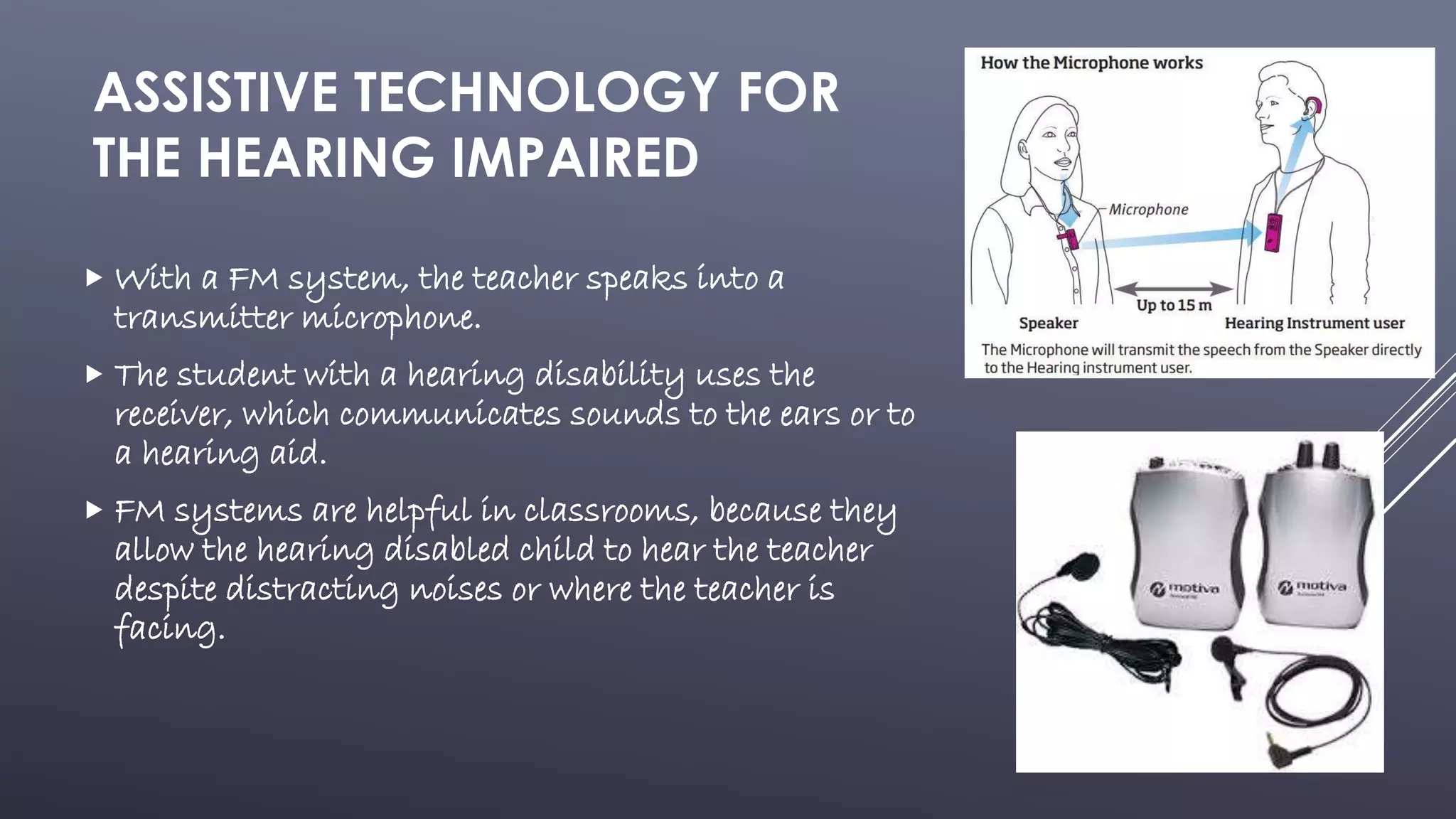
This document provides an overview of assistive technology (AT) including definitions, laws regarding AT, and examples of AT for students with different disabilities. AT is any tool or service that helps students with disabilities participate in class and achieve IEP goals. Laws like IDEA require schools to provide necessary AT. The document describes examples of AT for hearing impaired students like FM systems, seeing impaired students like video magnifiers, learning disabled students like speech recognition software, and physically disabled students like adjustable furniture and equipment.