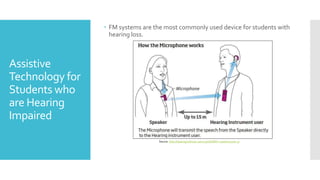
The presentation discusses assistive technology (AT) that supports students with disabilities in achieving their educational goals across various needs, including hearing, visual, learning, and physical disabilities. It explains the legal requirements outlined by the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) for schools to provide appropriate AT services and devices to eligible students. The document also details specific assistive technologies and tools available for each type of disability, along with resources for further information.