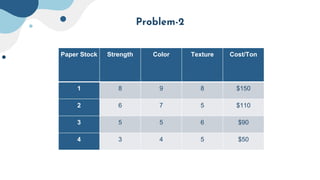
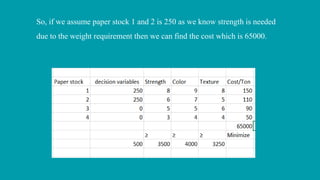
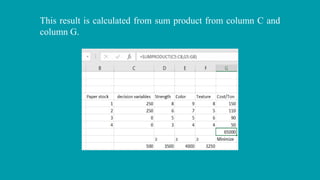
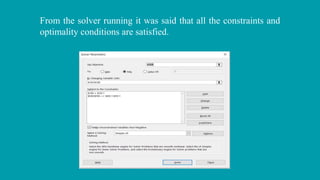
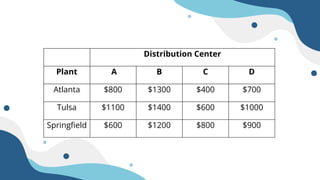
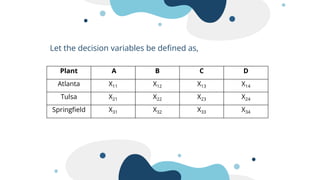
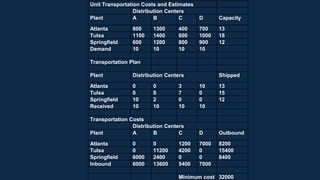
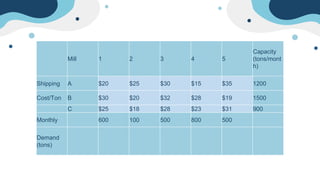
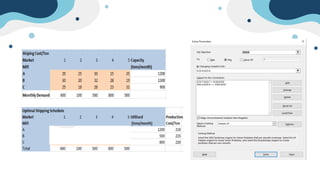
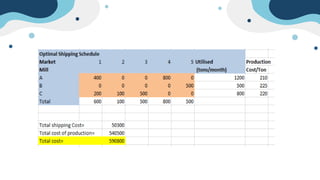
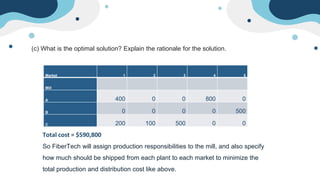
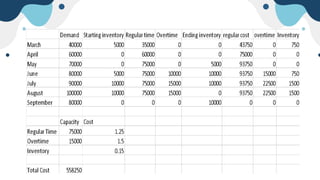
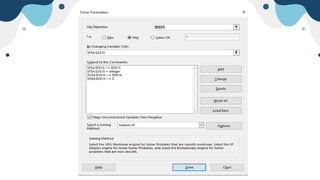
The document describes a linear programming problem to minimize costs for a pipe manufacturing company over 7 months. It provides production capacities, costs, demand forecasts, and inventory holding costs. The assistant formulates the LP with decision variables for regular and overtime production and inventory levels. The objective is to minimize total costs of production, inventory holding and meeting demand over the 7 months. The LP is set up and solved in a spreadsheet, finding the optimal solution that meets all constraints with a total minimum cost of $558,250.