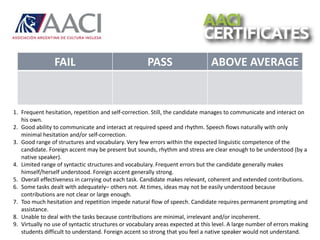
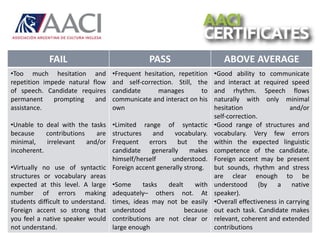
This document provides guidance for oral exam preparation. It discusses key aspects of student performance to focus on, including task achievement, fluency, and linguistic resources. Descriptors for different performance levels - fail, pass, and above average - are provided. Sample exam tasks like interviews, presentations, negotiations and discussions are shown. Suggestions are given for how to help students practice, including showing task types, scales, doing mock exams, and making practice fun and engaging. Strategies to teach students how to handle challenges in exams are also listed.