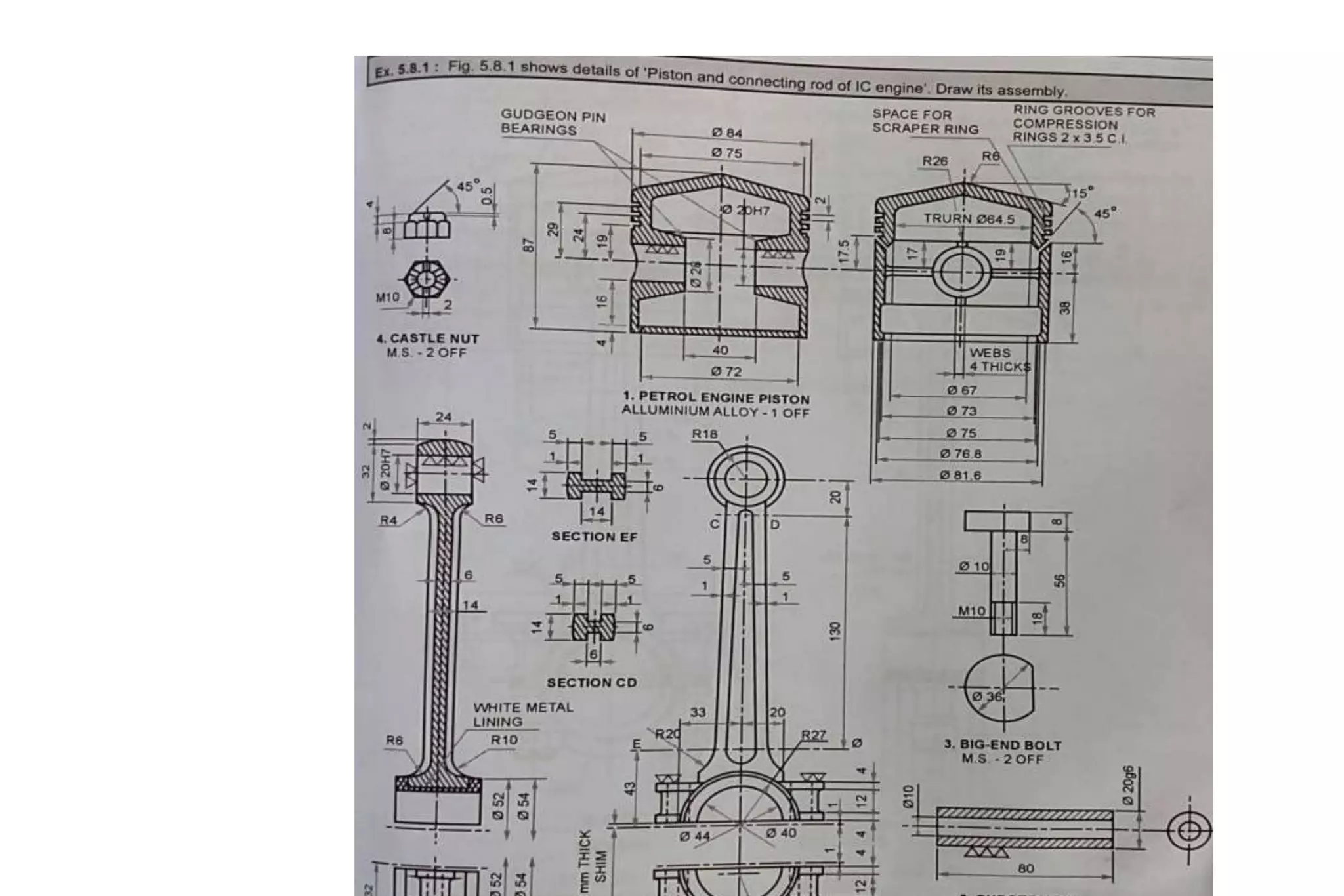
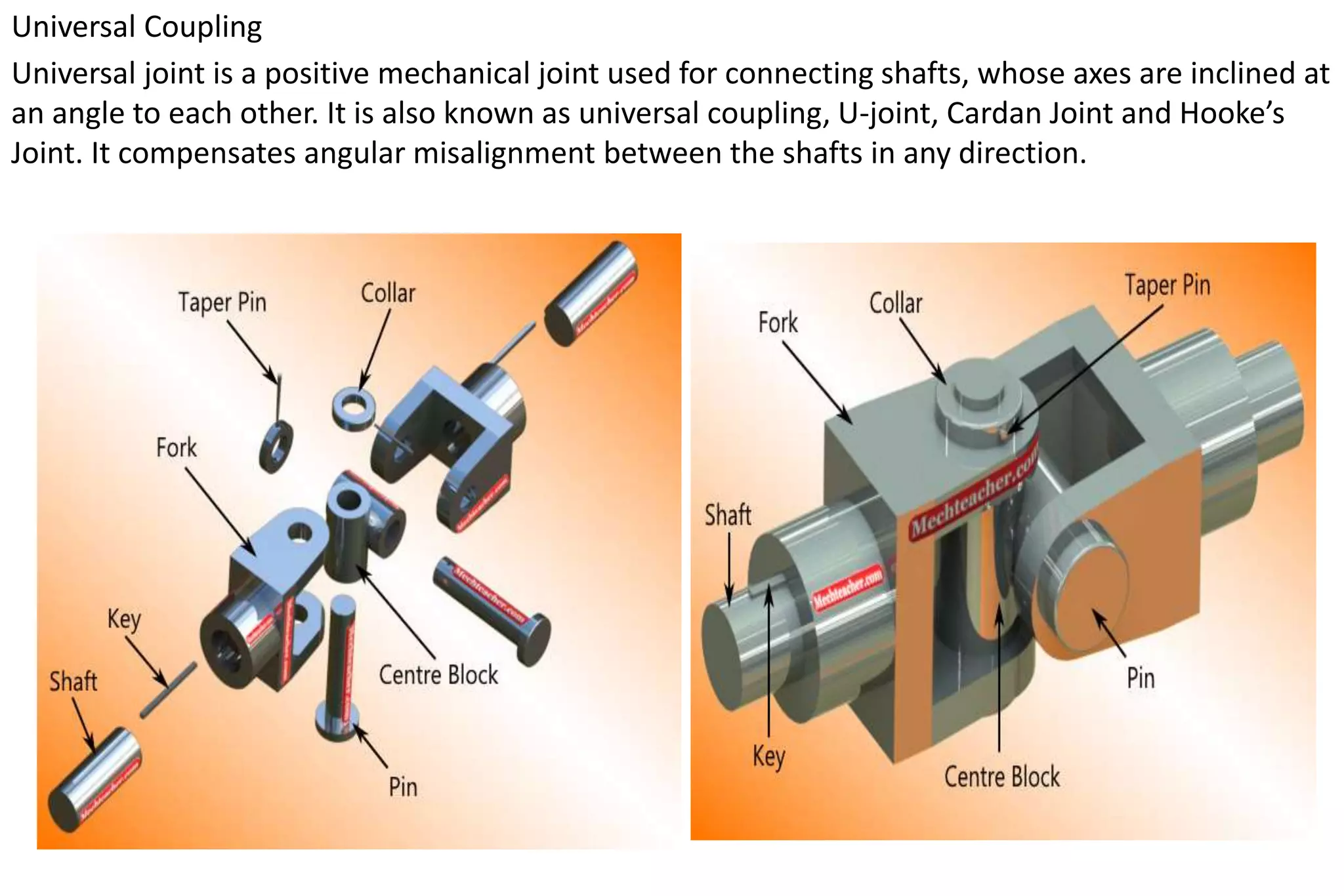
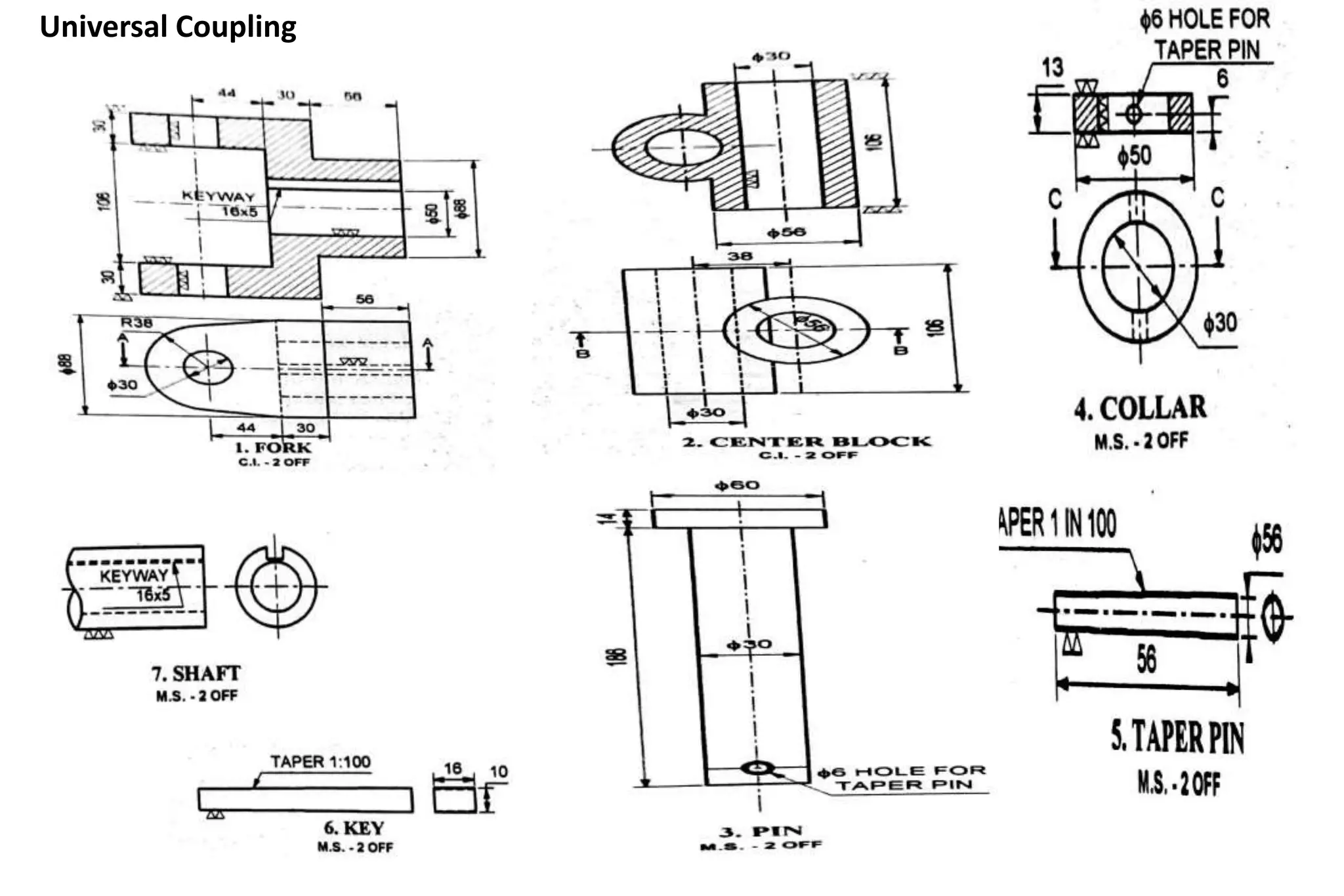
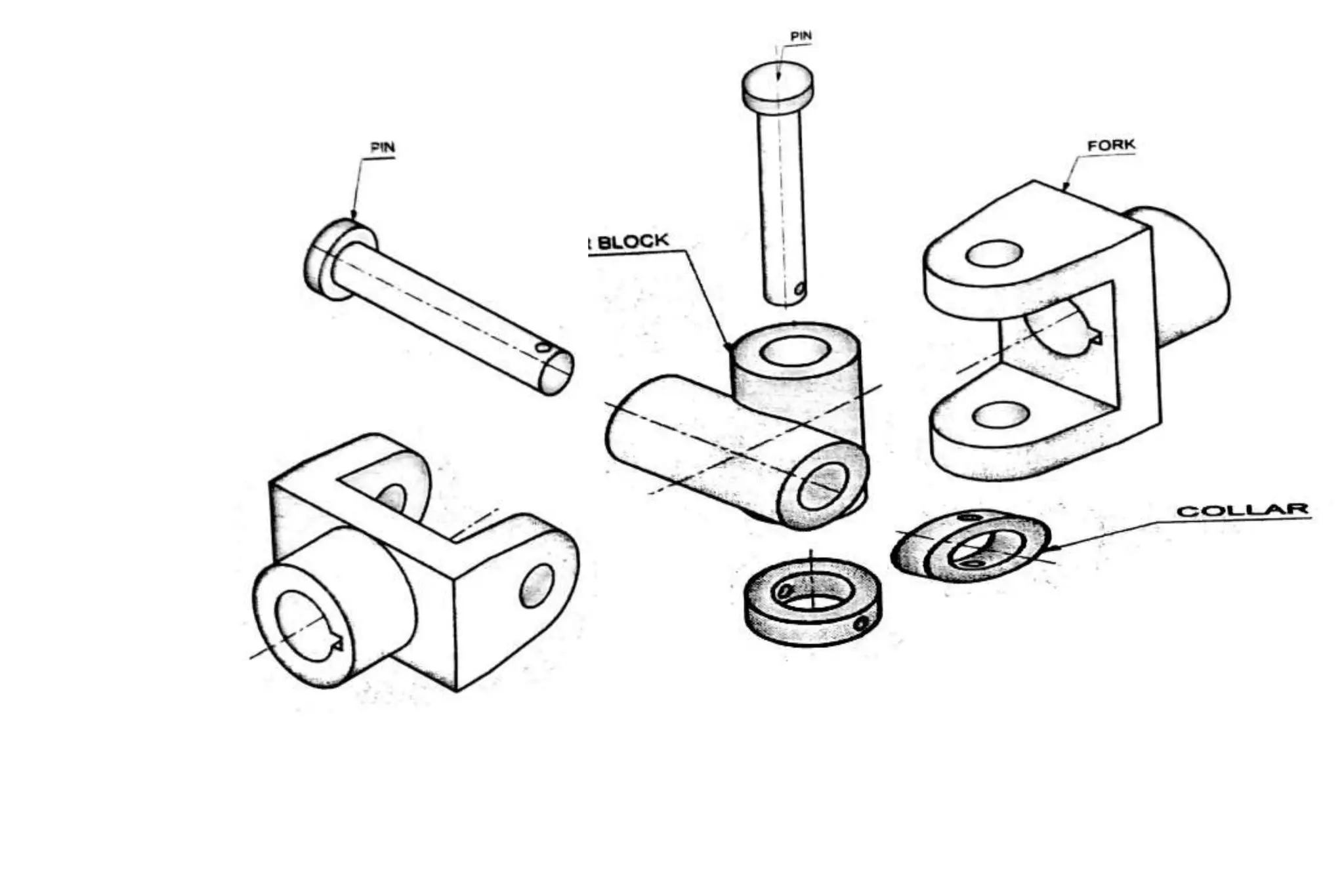
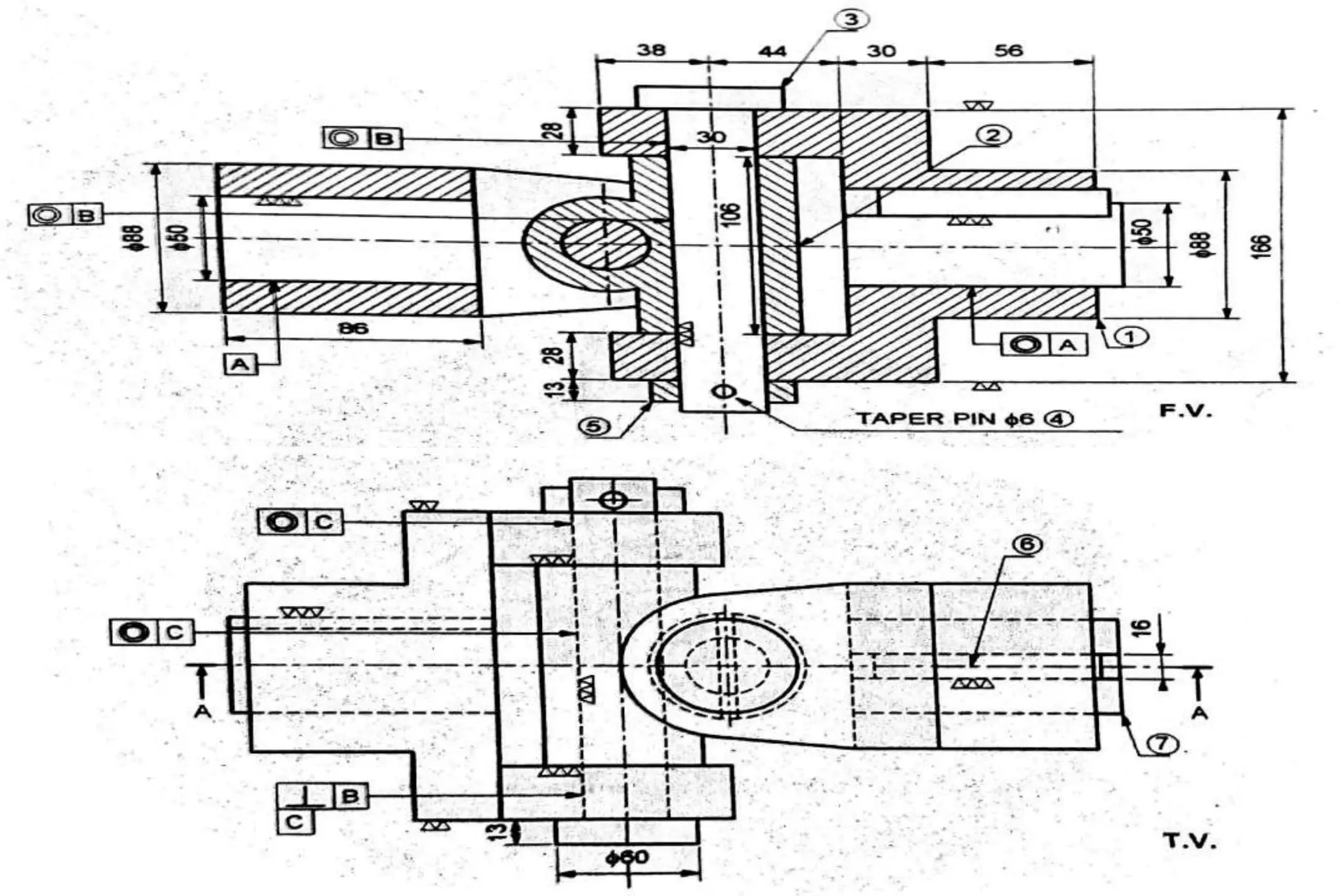
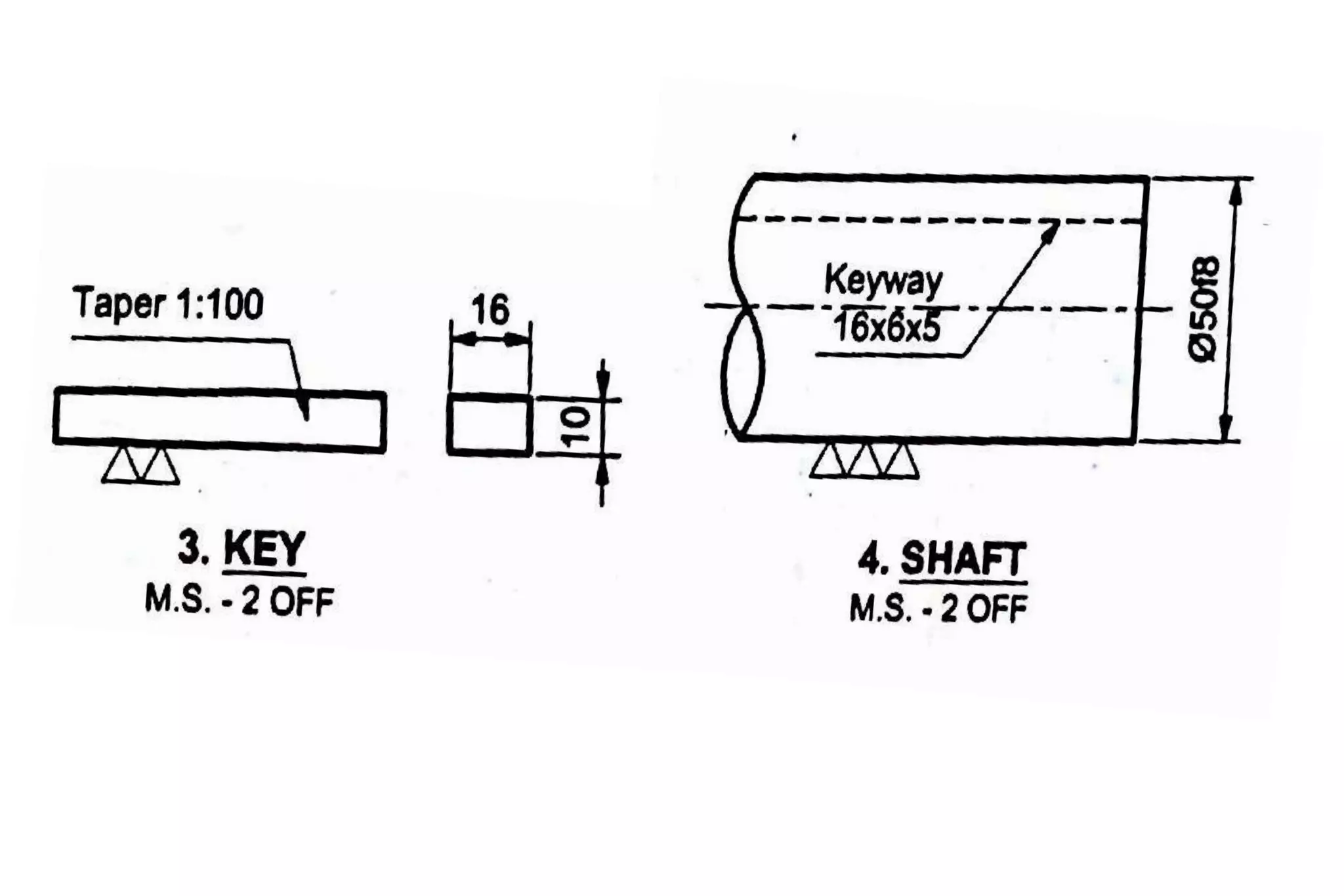
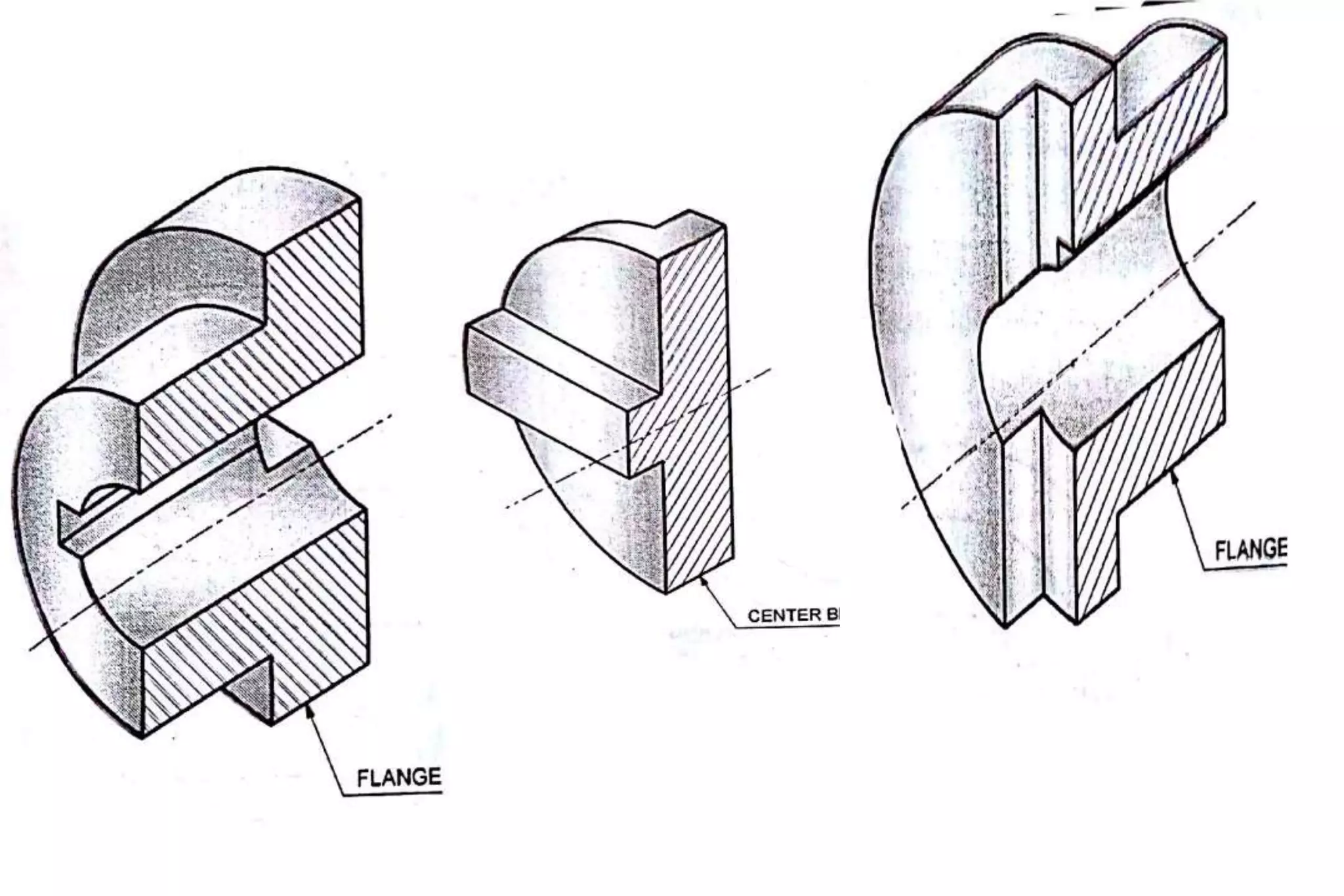
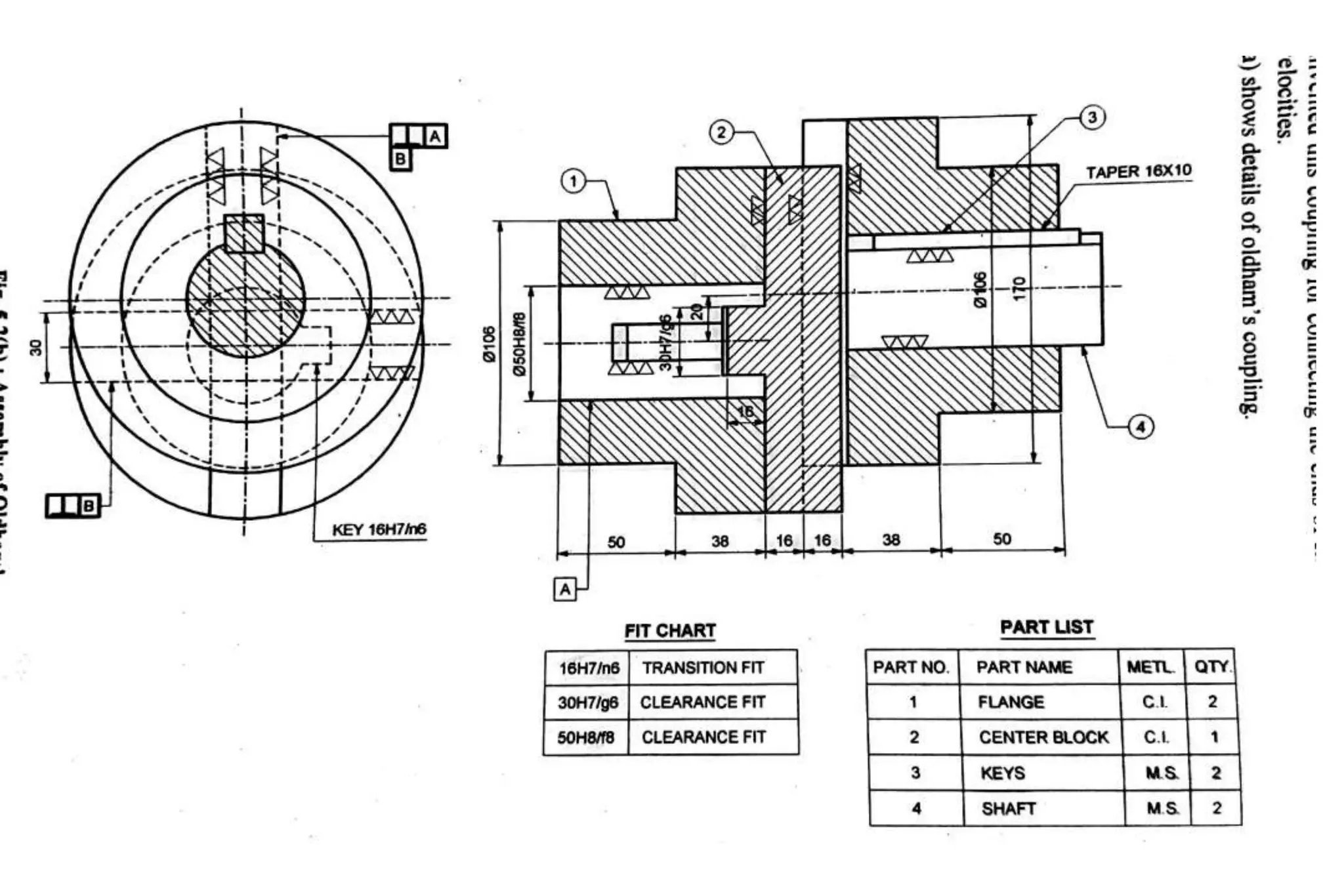
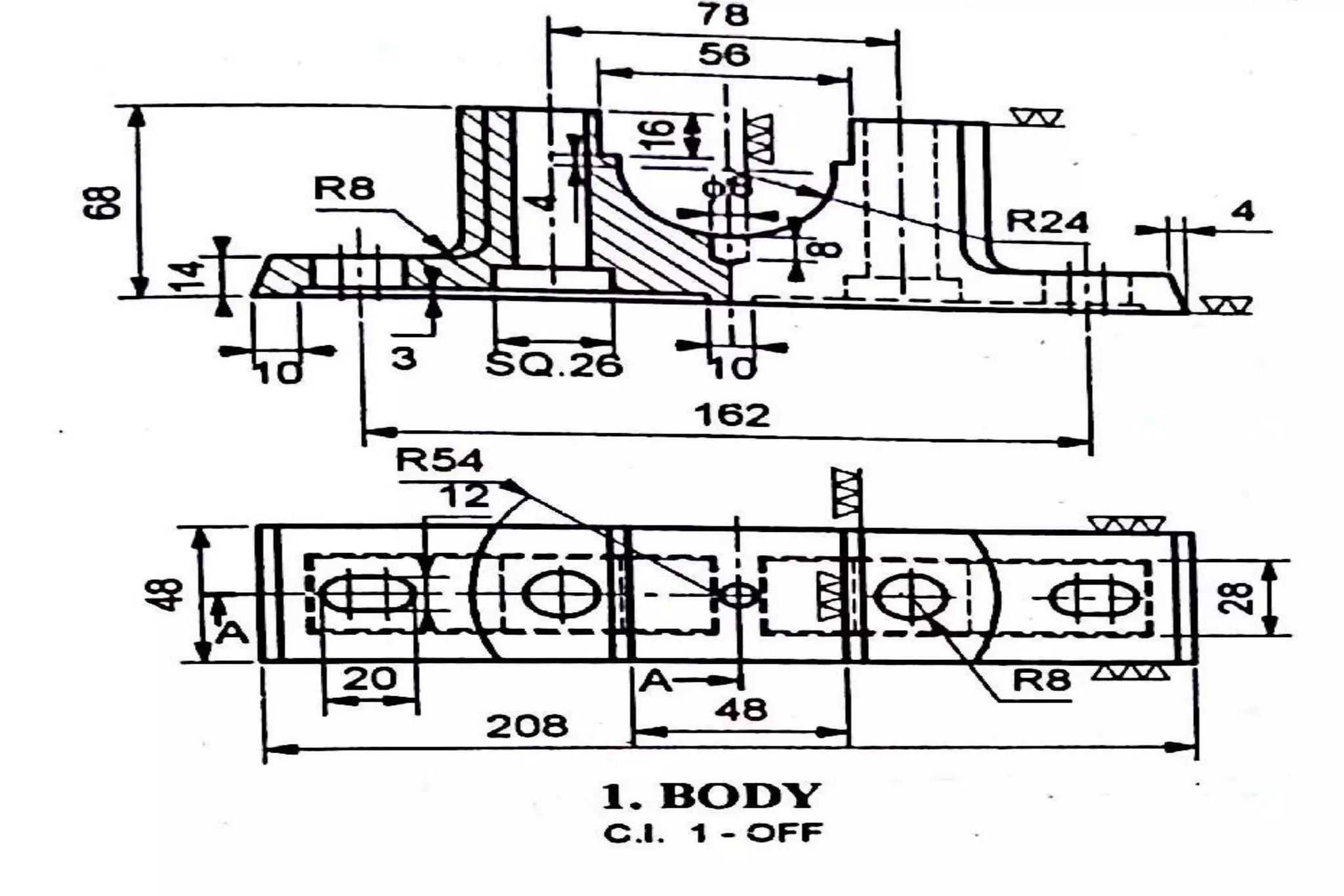
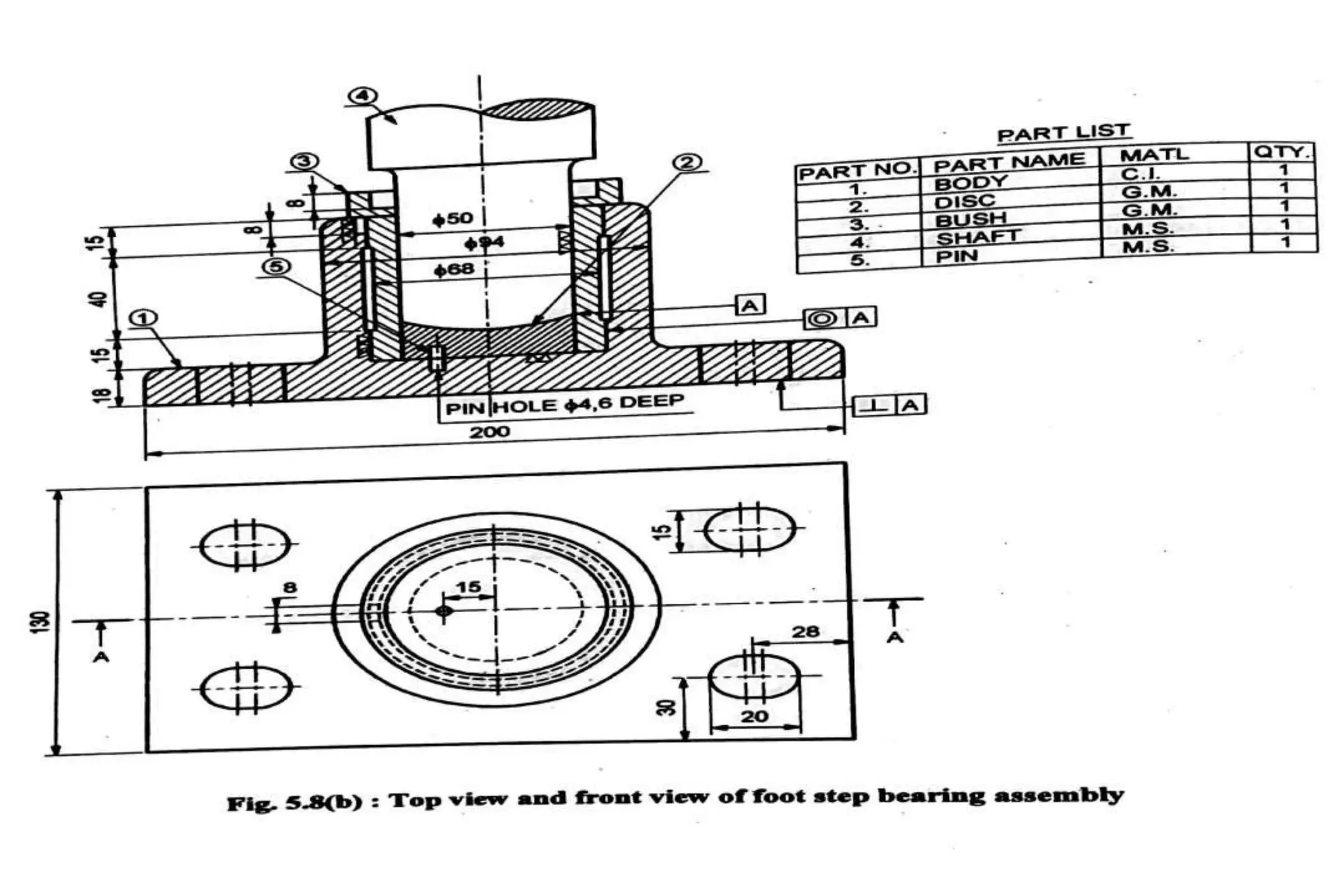
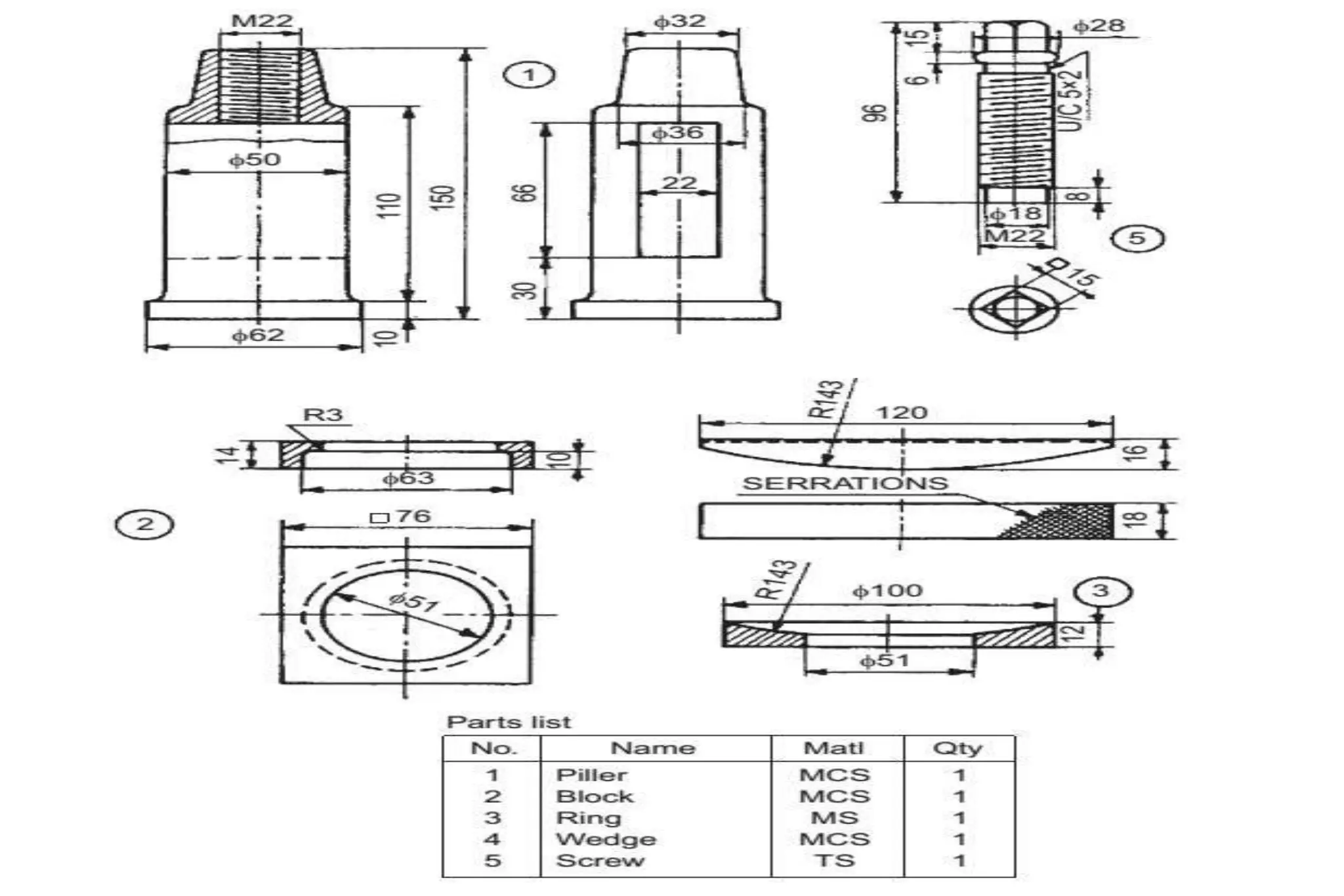
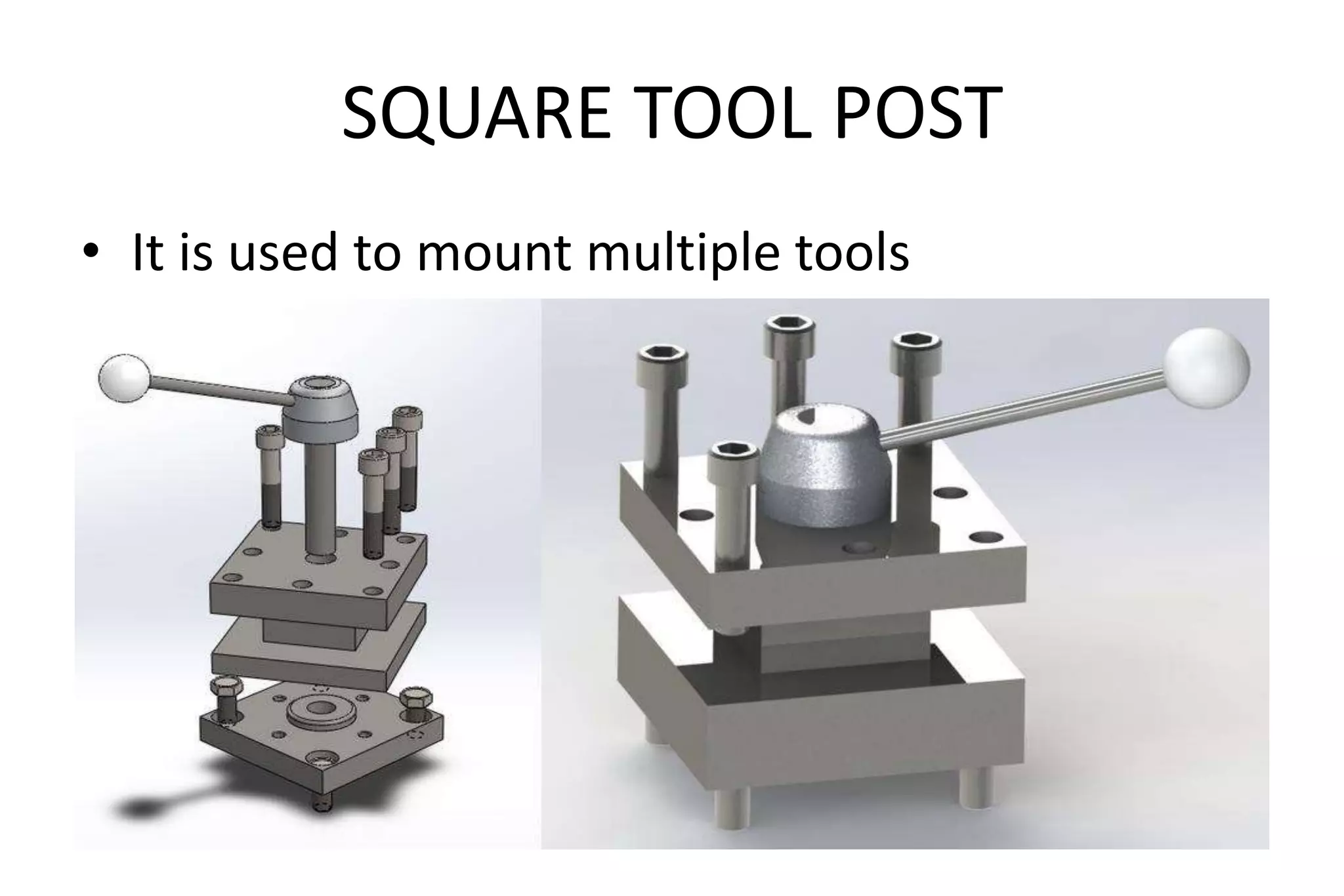
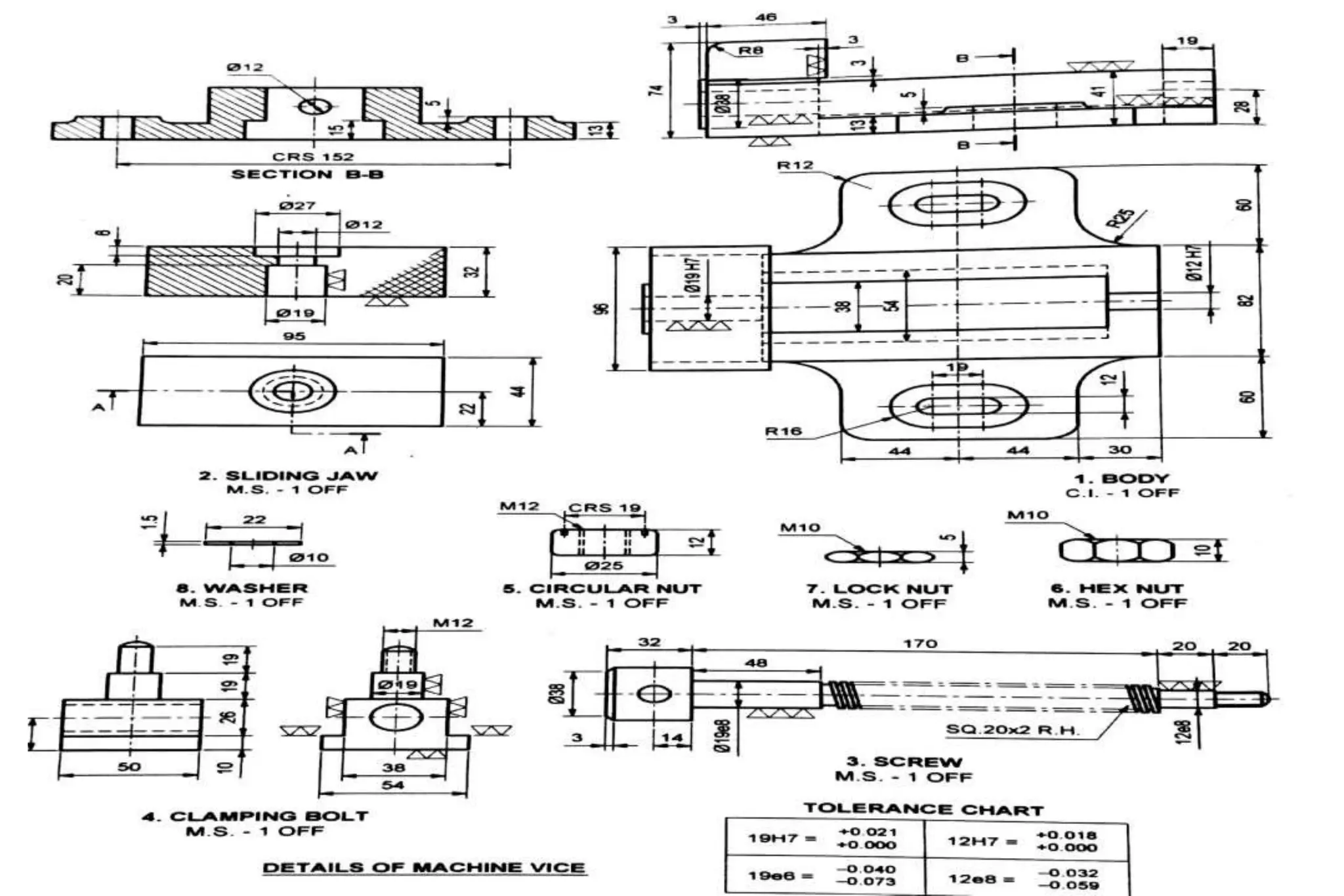
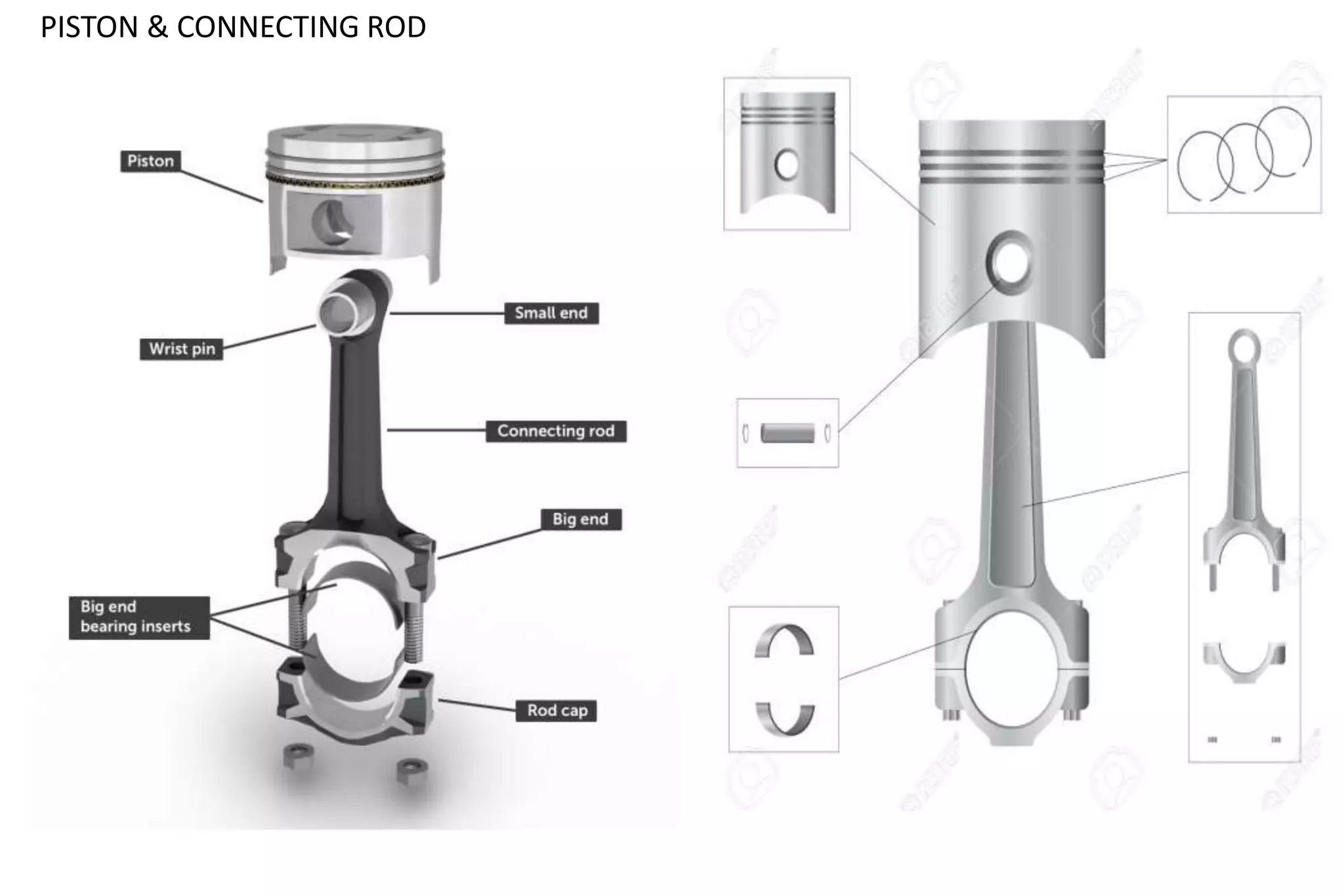
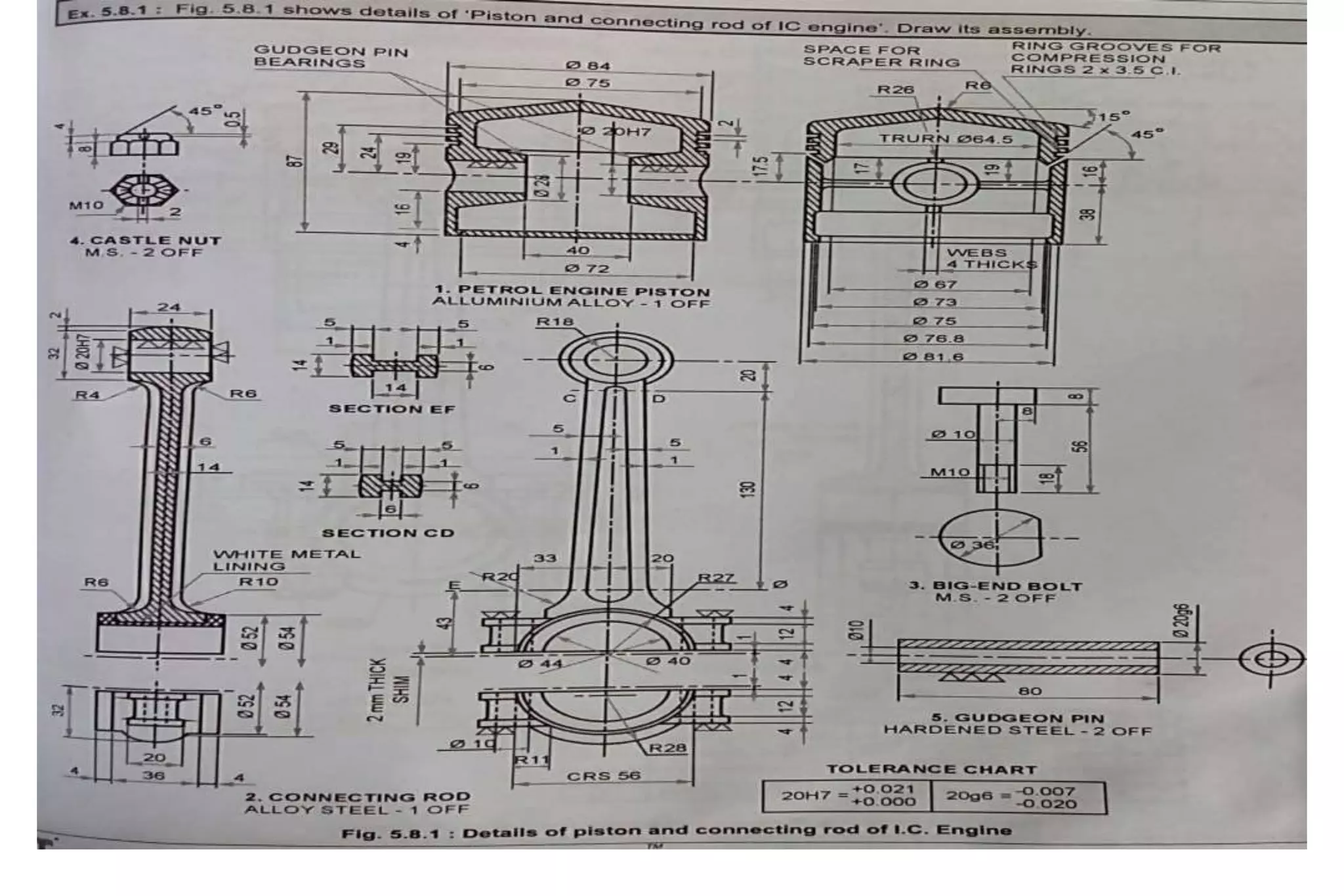
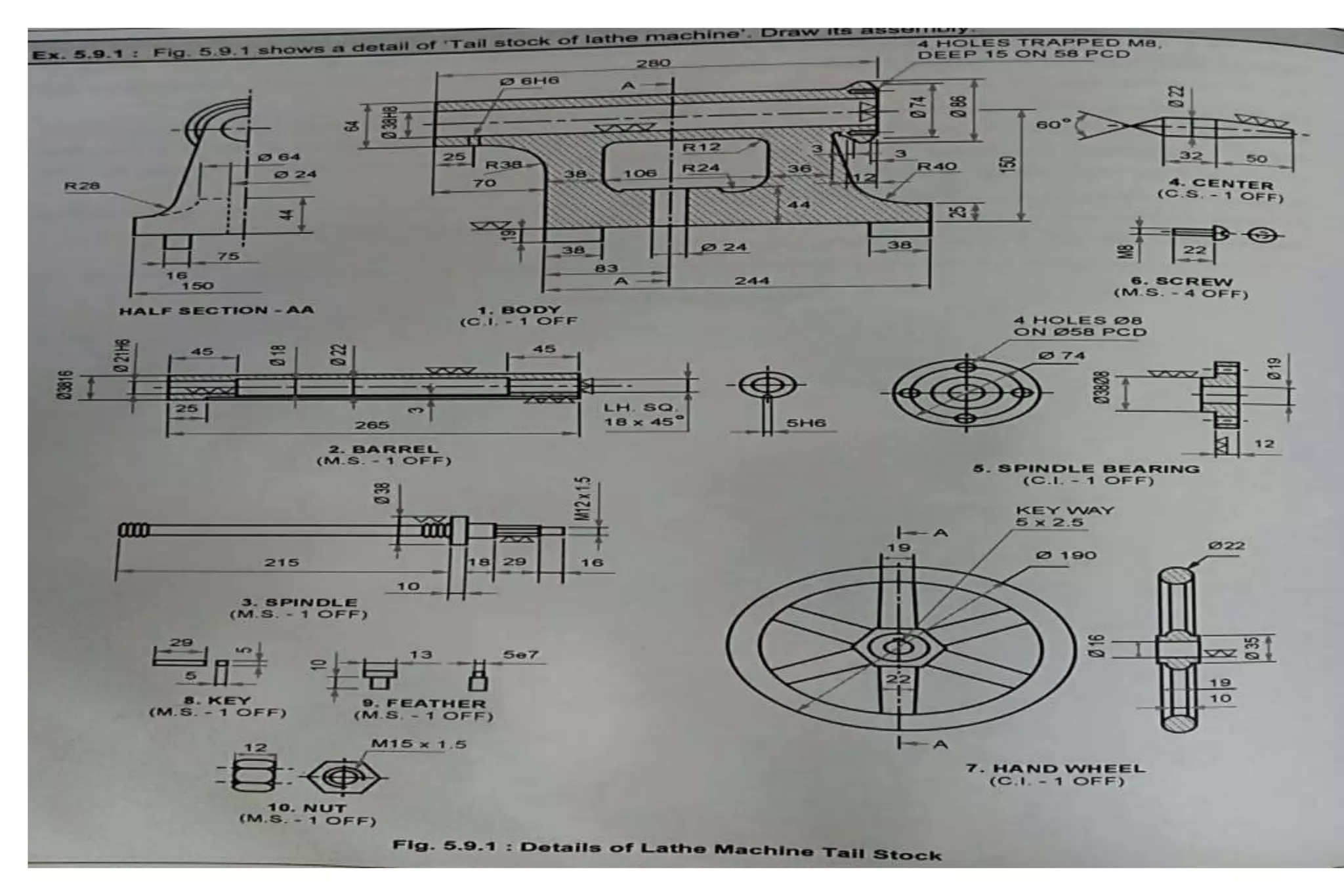
The document outlines the procedure for creating assembly and detailed drawings for mechanical components, particularly focusing on the piston and connecting rod assembly. It details steps for drawing assembly and detail drawings, highlighting the importance of understanding machine functionality, scale selection, and ensuring accurate dimensions. Additionally, it describes various types of coupling and tool holders used in mechanical engineering applications.