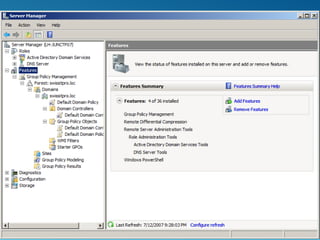
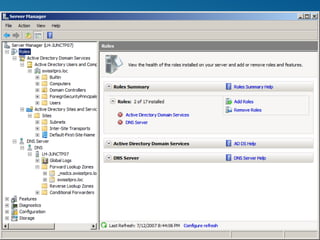
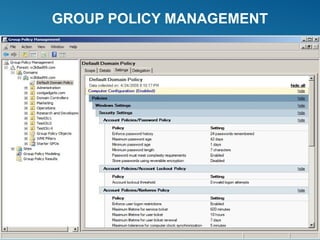
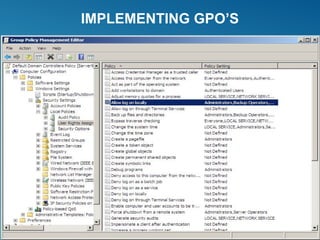
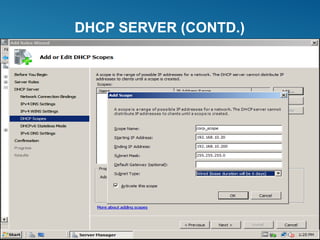
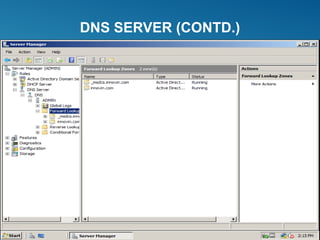
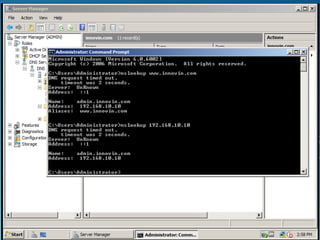
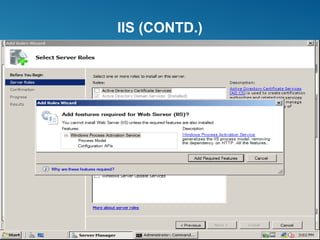
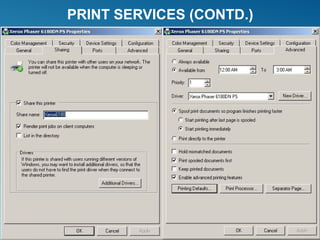
Windows Server 2008 can fulfill various server roles like file/print sharing, web server, DNS, DHCP, and Active Directory. It is available in Standard, Enterprise, and Datacenter editions. The presentation discusses the roles, editions, new features like Server Core, and technologies like Active Directory, DNS, DHCP, and file services.