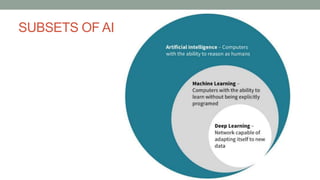
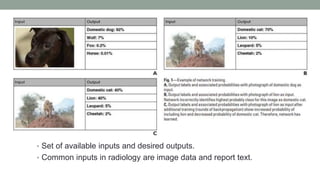
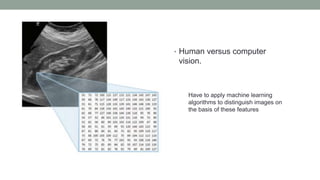
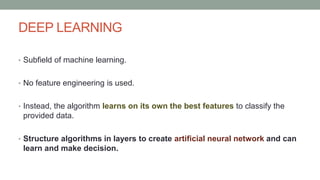
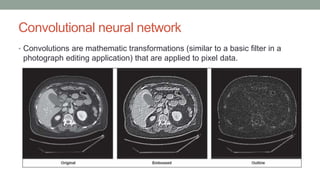
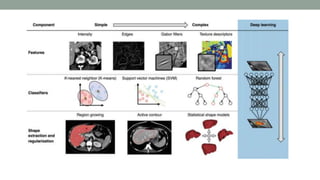
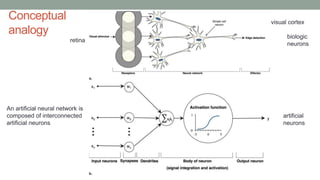
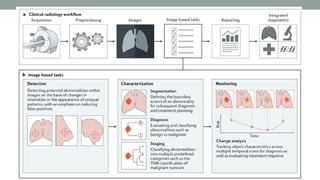
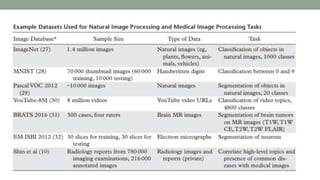
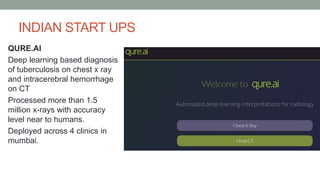
This document discusses artificial intelligence and its applications in radiology. It begins with definitions of artificial intelligence and its subsets of machine learning and deep learning. It then discusses how machine learning and deep learning are being used in medical imaging for tasks like cancer diagnosis and detection of findings in images. The document outlines how large amounts of medical image and patient data are being used to train AI models to perform tasks like segmentation and anomaly detection. It provides examples of startups and projects applying AI to problems in radiology. It concludes by discussing views on AI in radiology, noting that AI can increase radiologist efficiency and consistency if integrated into the workflow, rather than replacing radiologists.