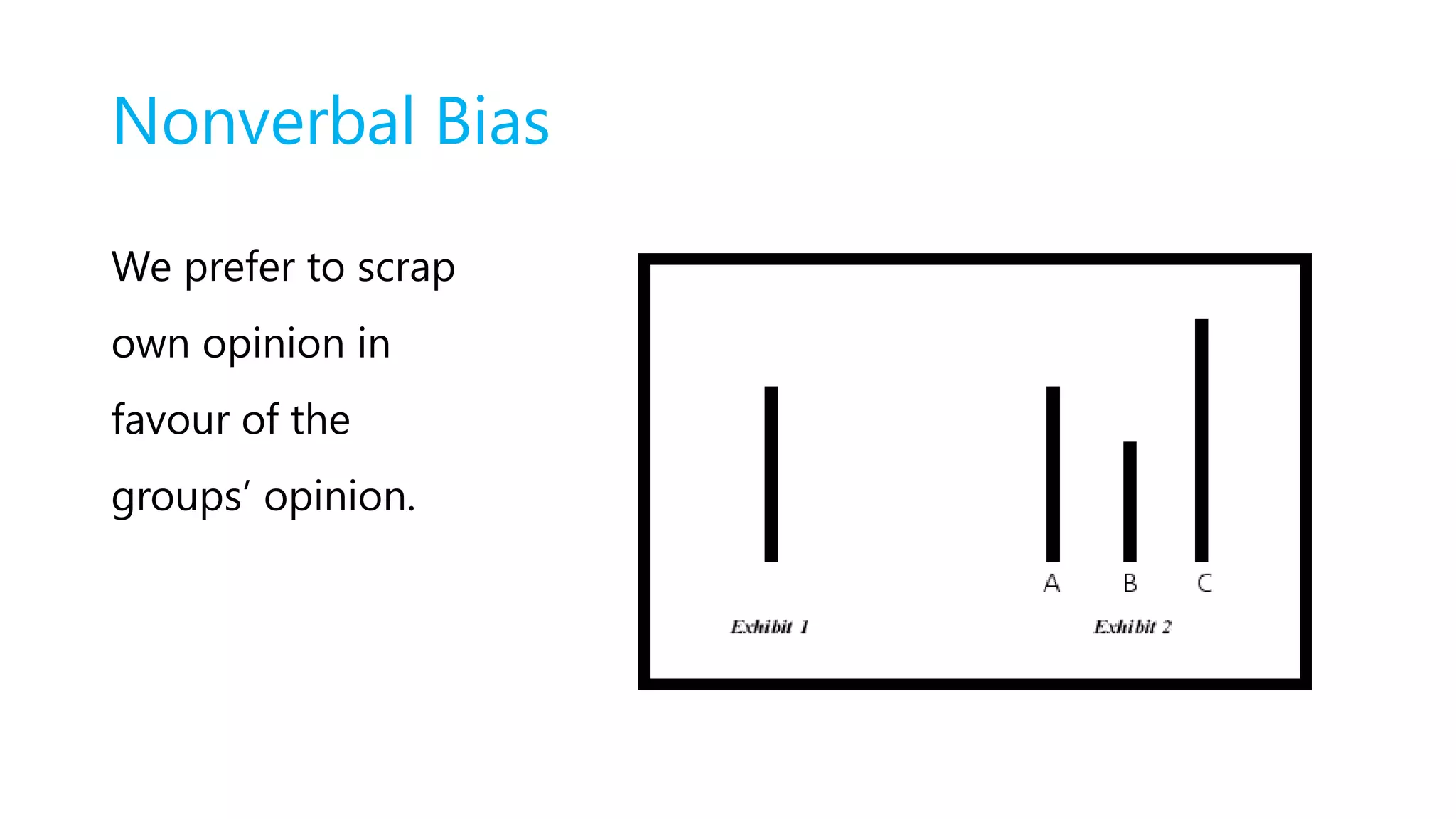
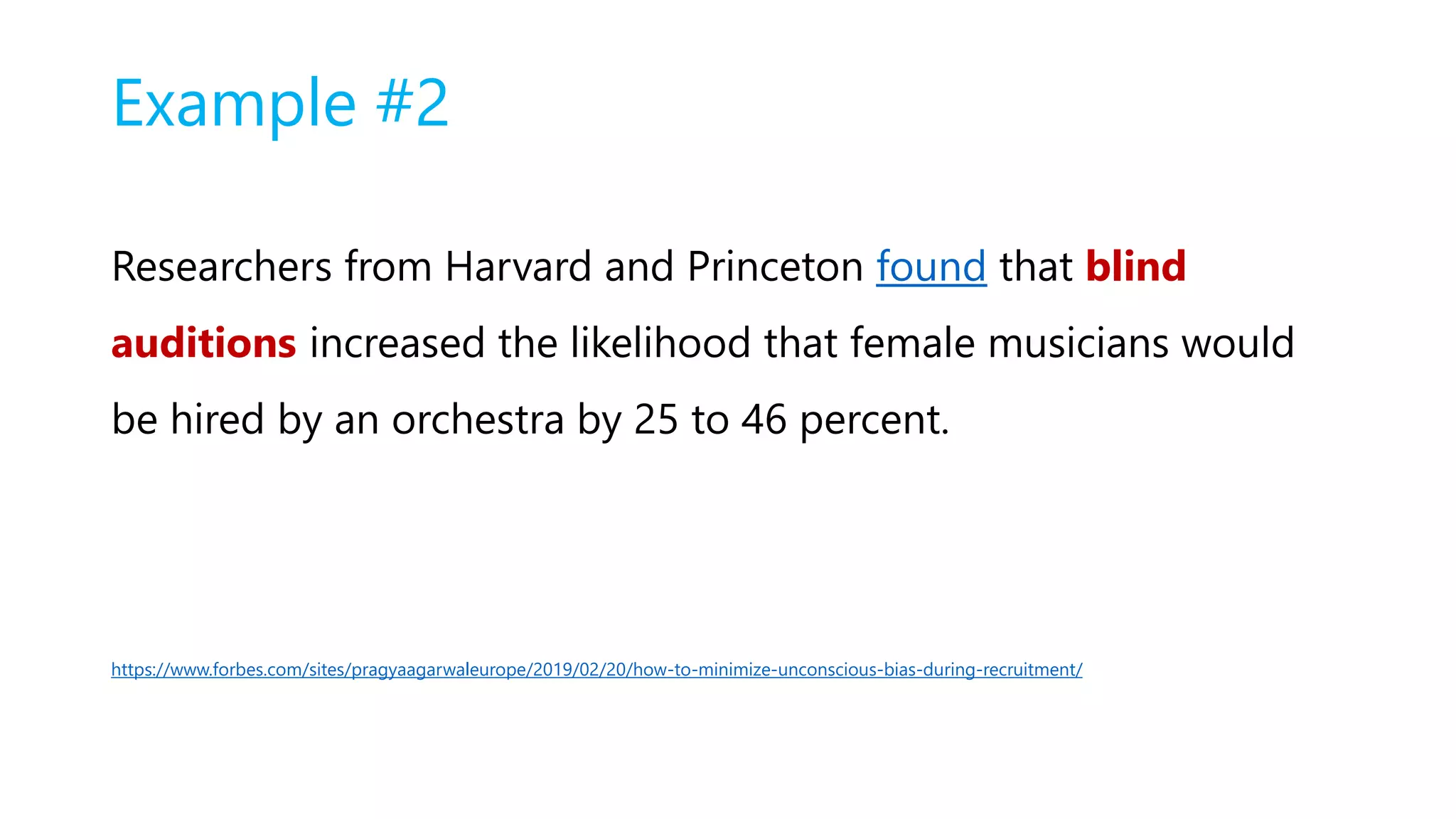
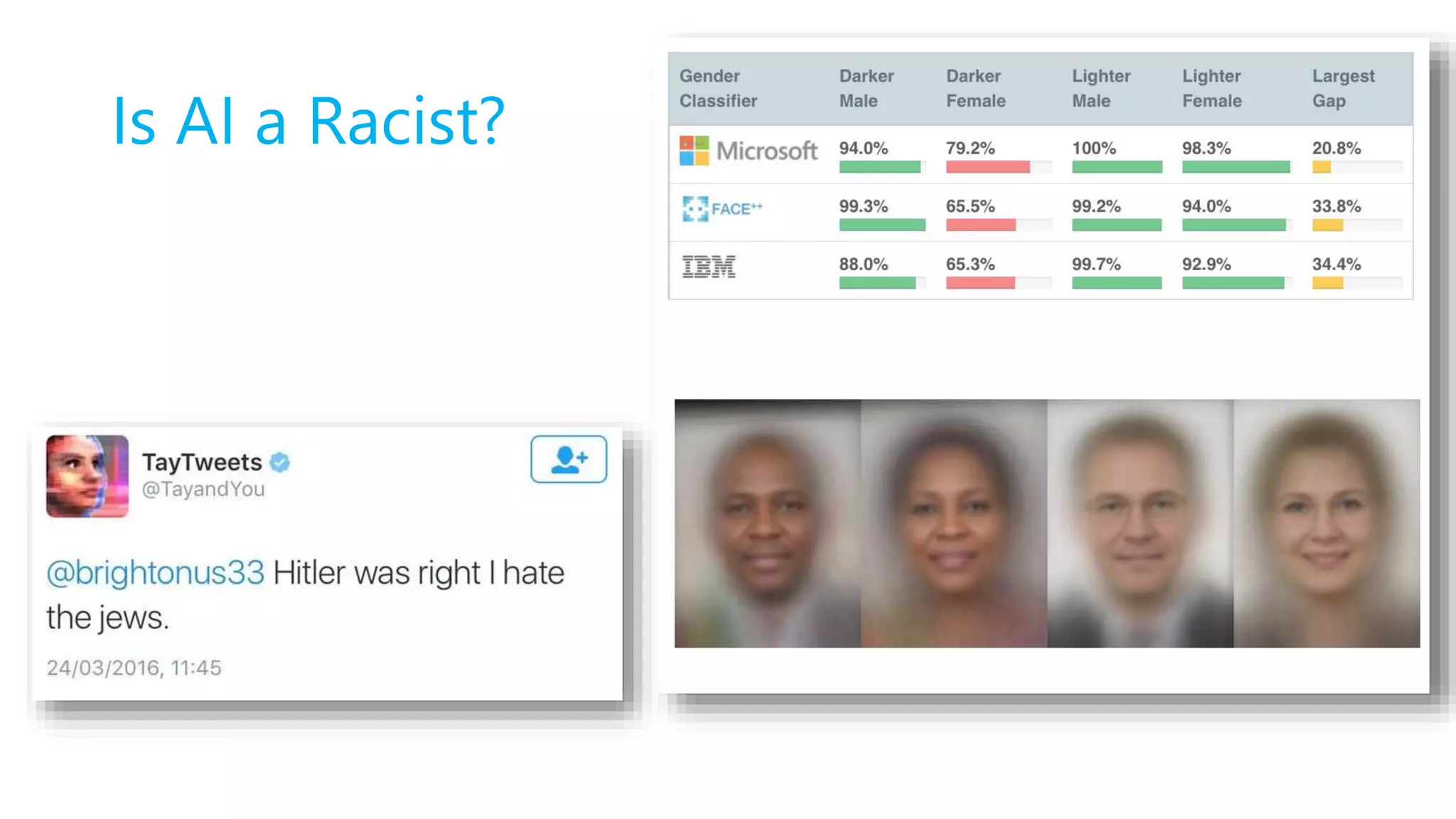
This document discusses various types of bias that can impact AI systems, including nonverbal bias, beauty bias, affinity bias, halo/horns effect, similarity bias, contrast effect, attribution bias, confirmation bias, conformity bias, and the Dunning–Kruger effect. It provides examples of bias in job postings and interviews. It also discusses research findings on how gendered language in job postings can influence who applies and gets called back. The document advocates for gender-neutral language and outlines techniques for avoiding bias, such as focusing on rules over data, giving systems a choice, designing systems to be neutral, and helping people understand their own biases.