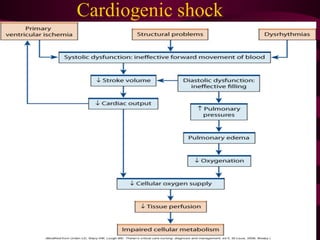
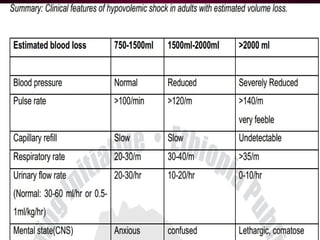
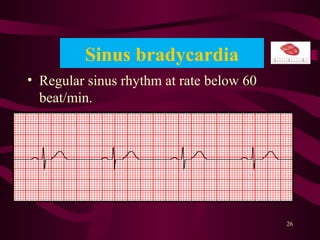
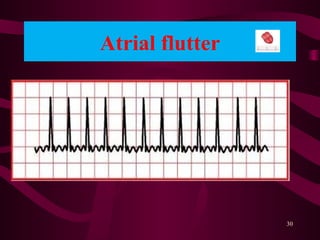
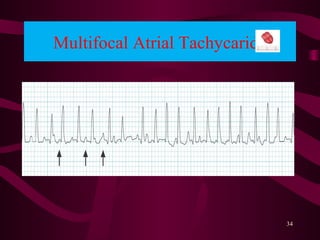
This document discusses circulatory failure, shock, and arrhythmias. It defines shock as a state where oxygen delivery to tissues is inadequate to meet demands. Shock is classified into hypovolemic, cardiogenic, and distributive types. Management of shock involves fluid resuscitation, treating the underlying cause, and supportive care. Arrhythmias are disorders of heart rate and rhythm that can be bradycardic or tachycardic in nature. Common arrhythmias discussed include sinus bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, and ventricular tachycardia. Treatment involves use of anti-arrhythmic agents.