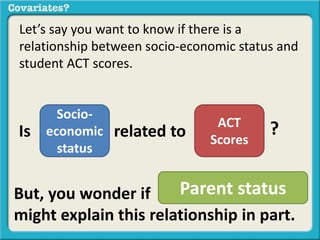
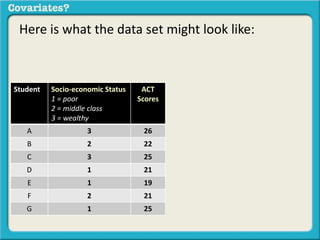
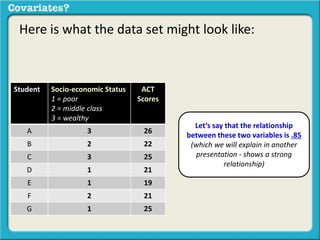
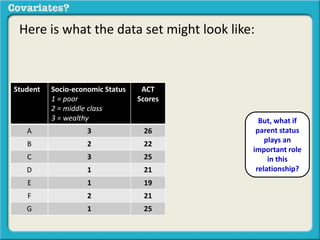
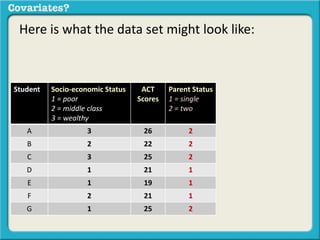
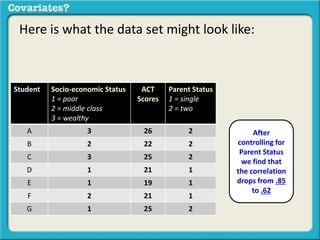
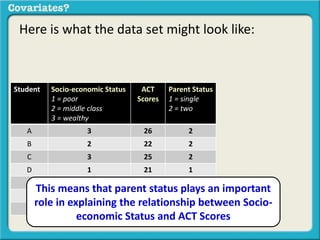
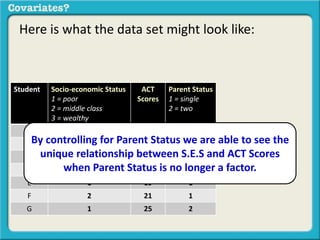
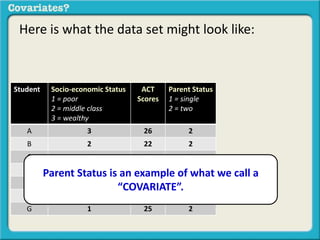
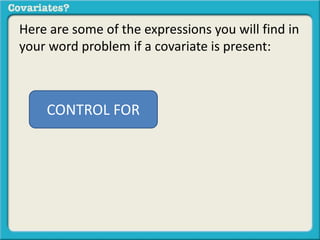
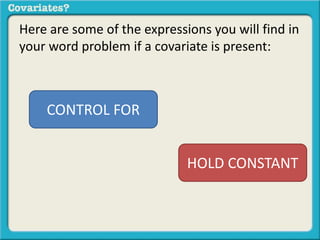
The document discusses covariates and how to determine if they are present in a problem. It uses an example of examining the relationship between socioeconomic status (SES) and student ACT scores, and whether parental status is a covariate. Adding parental status as a variable decreases the correlation between SES and ACT scores, showing it plays a role in explaining their relationship. Controlling for covariates allows viewing the unique relationship between variables when the covariate's effect is removed. Key terms that indicate a covariate is present include "control for", "hold constant", and "adjust for".