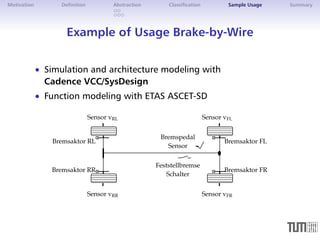
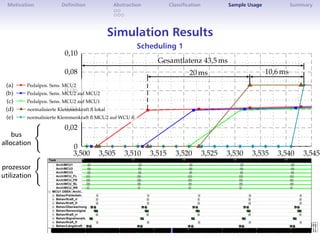
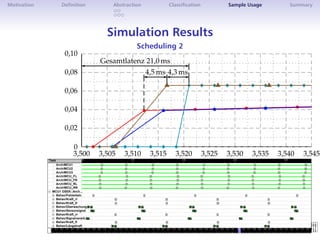
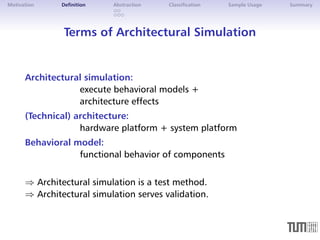
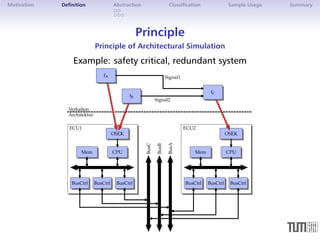
The document discusses architectural simulation as a method for validating distributed automotive systems. It defines architectural simulation and related terms, then presents a taxonomy for classifying model abstraction. The document also examines dependencies between abstraction levels and model types. As an example, it applies architectural simulation to a brake-by-wire system, showing scheduling analyses and results. Advantages are better test coverage and depth than other methods, though disadvantages include effort required and limited accuracy.




![Motivation Definition Abstraction Classification Sample Usage Summary
Notation
Simplification
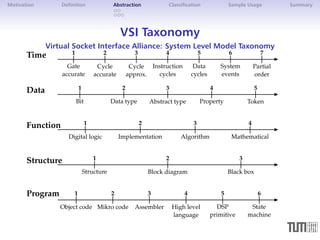
VSI Taxonomy, displayed as vector:
a =
aZ
aD
aF
aS
aP
! Time
Data
Function
Structure
ProgrammingModel
!
disuse of axis expressed by ?
abstraction ranges written as intervalls, e. g.
aV =
0
@
[4;7]
[2;4]
22?
1
A](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-141127103649-conversion-gate01/85/Architectural-Simulation-of-Distributed-ECU-Systems-8-320.jpg)
![Motivation Definition Abstraction Classification Sample Usage Summary
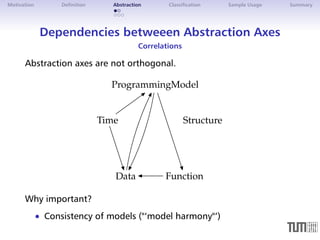
Dependencies betweeen Abstraction Axes
Sample Relation, Sample Usage
Sample: RZP = Time ProgrammingModel
Time 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Program 2 2 3 3 4 5 6
Sample usage:
CPU modell for run time estimation
Estimates generated C code (level P = [4; 6])
To deliver instruction cycles (level Z = 4)
Relation states: RZP(4) = 3
) Model cannot meet requirements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-141127103649-conversion-gate01/85/Architectural-Simulation-of-Distributed-ECU-Systems-10-320.jpg)
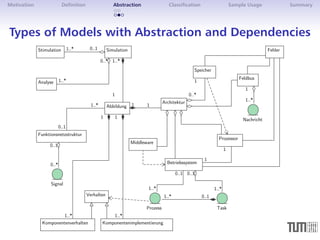
![Motivation Definition Abstraction Classification Sample Usage Summary
Types of Models with Abstraction and Dependencies
1
CA
Betriebssystem
Prozessor
Nachricht
1
1
0..1
0..1
0
B@
1
[2;5]
2
[2;3]
3
[1;4]
CA
0
B@
[4;6]
[2;4]
33 [1;5]
0
@
1
A
22112](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-141127103649-conversion-gate01/85/Architectural-Simulation-of-Distributed-ECU-Systems-13-320.jpg)
![Motivation Definition Abstraction Classification Sample Usage Summary
Types of Models with Abstraction and Dependencies
P0ostulation:
@
1
A
[4;6]
[2;4]
33
[1;5]
22112
+
0
@
1
A
[2;5]
2
[2;3]
3
[1;4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-141127103649-conversion-gate01/85/Architectural-Simulation-of-Distributed-ECU-Systems-14-320.jpg)