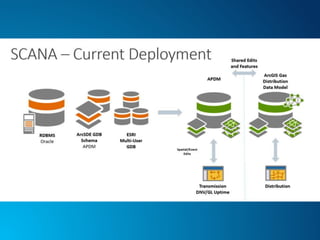
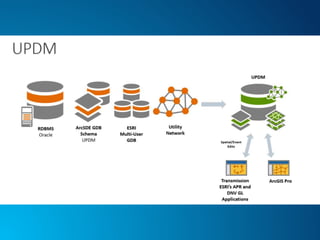
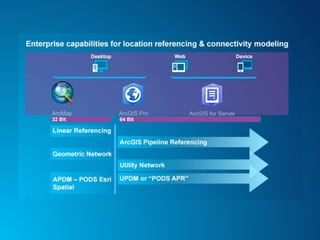
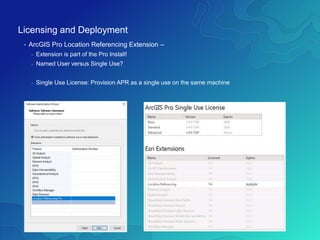
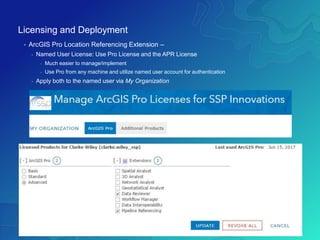
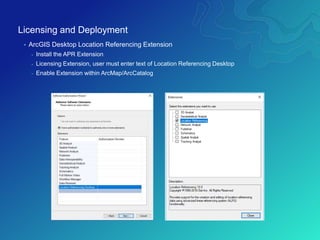
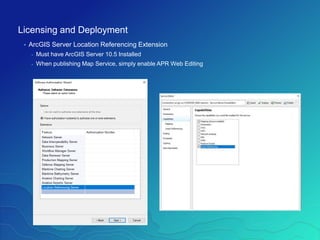
The document outlines the implementation of a Utility Pipeline Data Model (UPDM) for gas asset management by SCANA and PSNC, detailing the consolidation of GIS environments and the benefits of a centralized data model for improved analytics and regulatory reporting. It covers lessons learned in the project, including the integration of data across different platforms, addressing historical data management, and establishing user-friendly workflows for pipeline management. Key considerations include architectural setup, licensing for software extensions, and tips for data loading and management throughout the project.