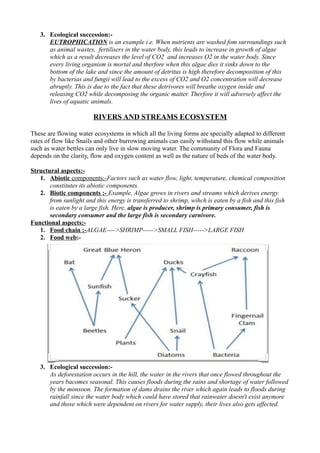
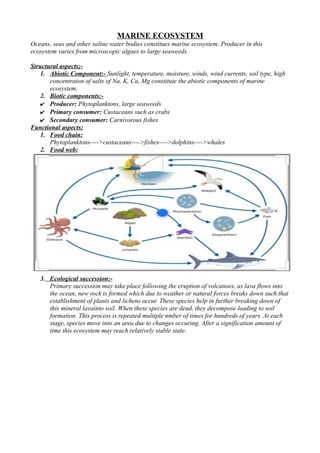
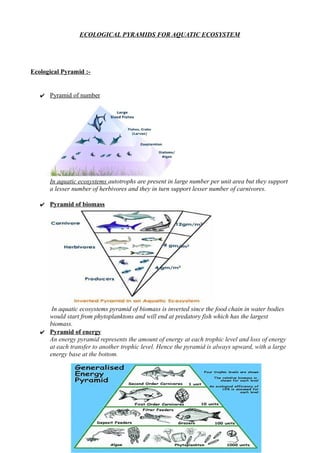
The document provides a comprehensive overview of aquatic ecosystems, including their definitions, components (abiotic and biotic), types (ponds, lakes, rivers, marine), and ecological interactions like food chains and webs. It highlights the importance and threats to these ecosystems, such as pollution, overfishing, and human interference, as well as the need for conservation measures. The conclusion emphasizes the significance of understanding and protecting aquatic ecosystems for biodiversity and human survival.