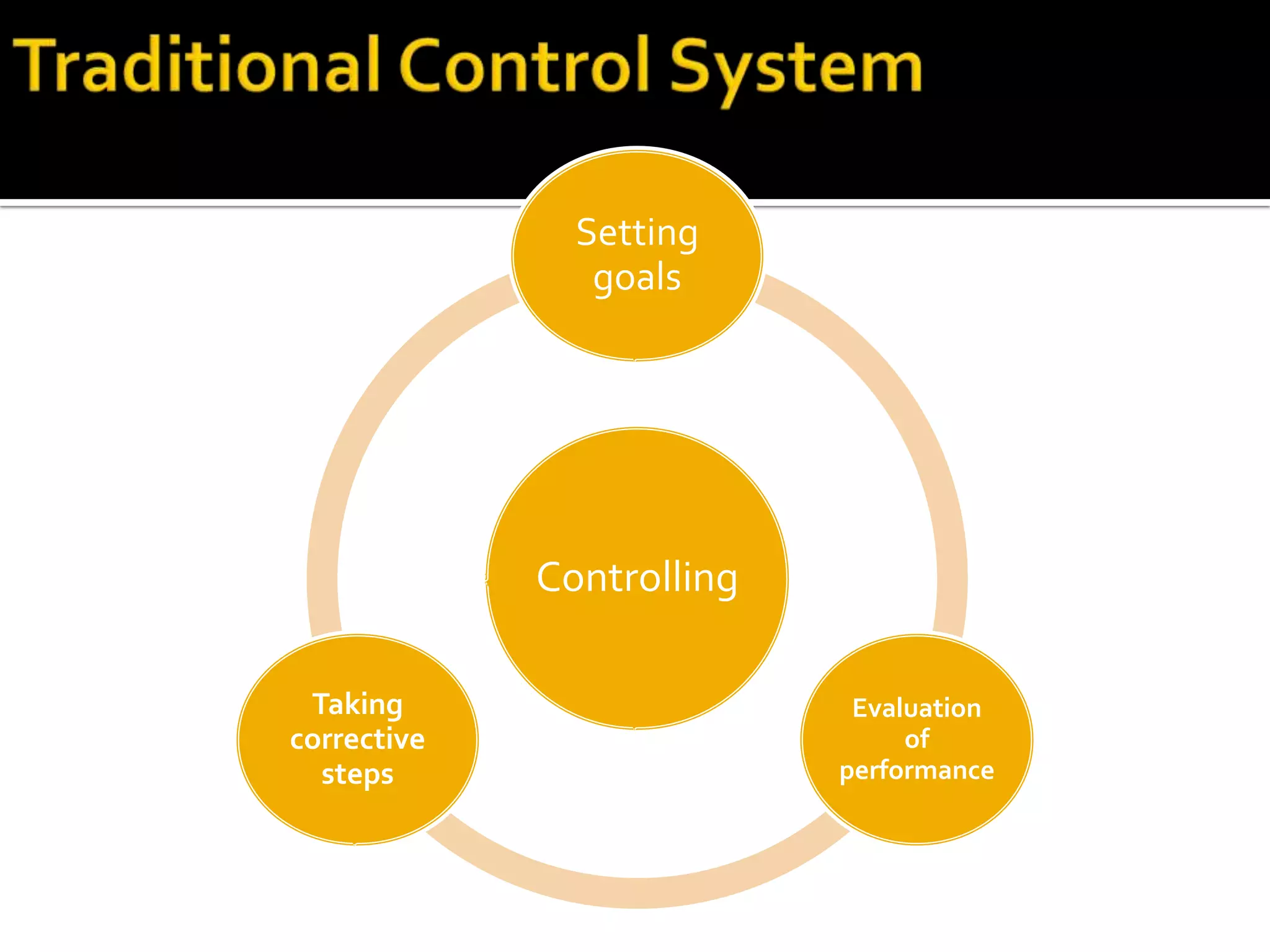
The document discusses traditional control processes used in business. It describes traditional control systems as involving setting standards and then monitoring performance. There are three main types of traditional controls: diagnostic controls which ensure goals are being met and issues can be explained, boundary controls which establish rules and identify actions to avoid, and interactive controls which allow for real-time strategic monitoring through face-to-face communication. Commitment-based controls rely on employee self-control and mutual understanding to keep things on track.