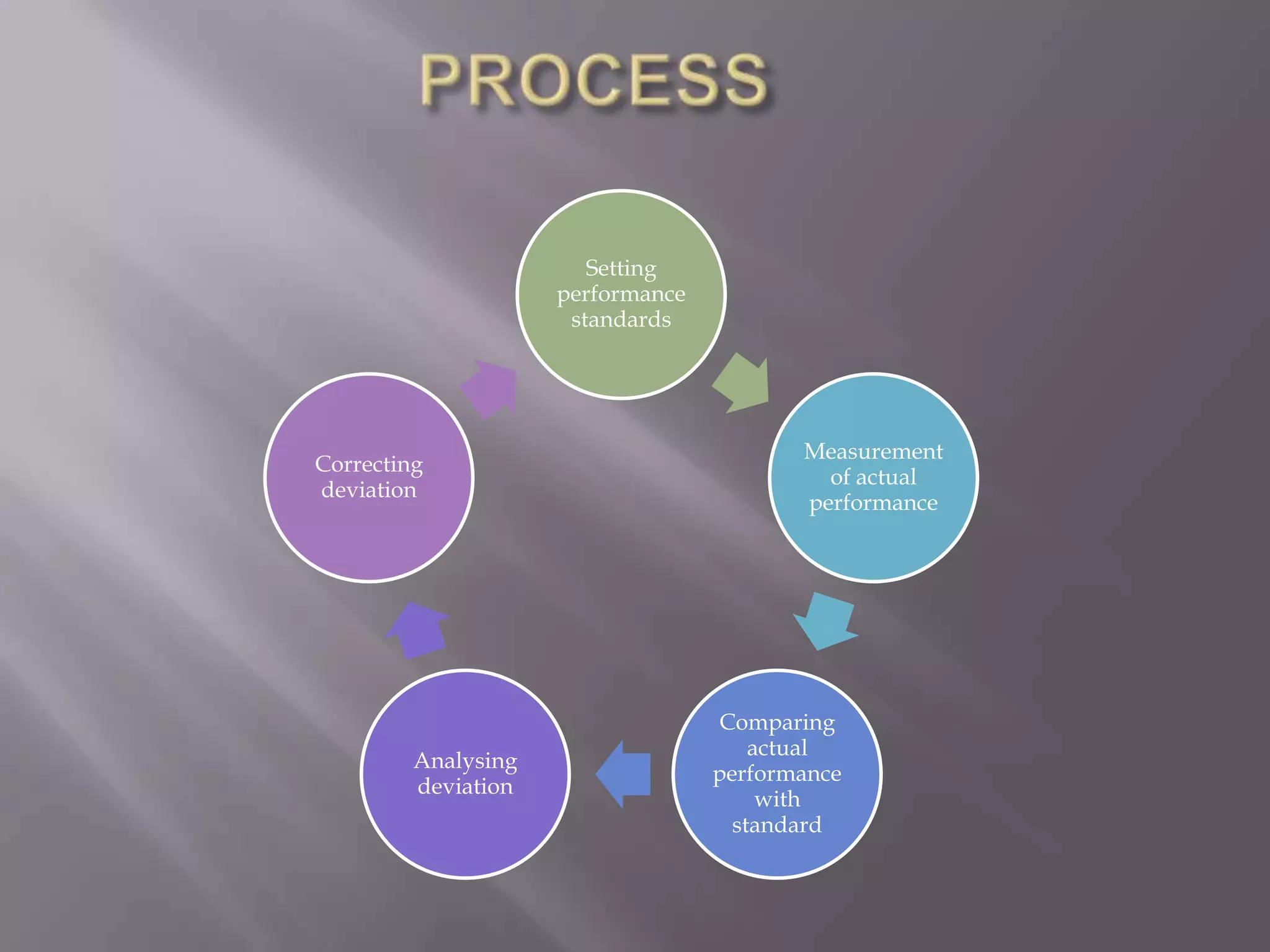
Control management involves setting standards, measuring actual performance against those standards, and taking corrective action when needed. It is an important function that helps check for errors and minimize deviations from goals. The key purposes of control management are to maximize resource use, ensure purposeful organizational behavior, and improve efficiency and effectiveness. Control aids decision-making and makes plans more effective by allowing organizations to measure performance and take steps to stay on track.