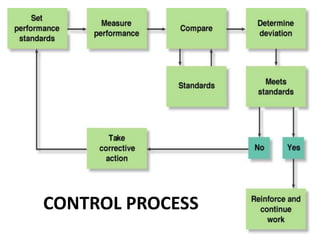
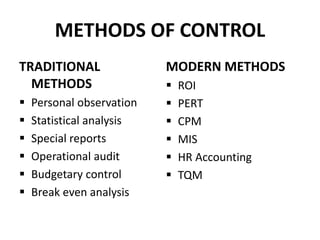
The document discusses the concept of controlling in management, defining it as the measurement and correction of subordinates' activities to ensure alignment with plans. It outlines the importance of control in achieving objectives, resource efficiency, decision making, and employee morale, and describes types and levels of control, as well as various control processes and methods. Essential features for effective control include focus on objectives, forward-looking strategies, flexibility, and motivation.