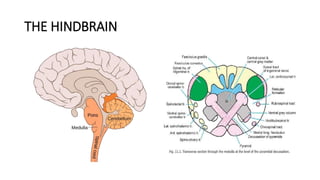
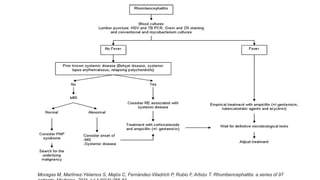
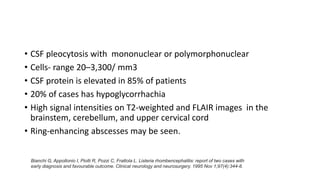
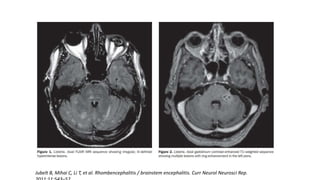
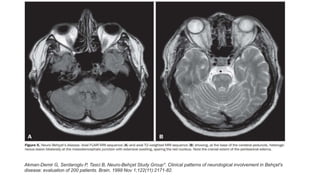
This document provides an overview of rhombencephalitis (inflammation of the hindbrain). It discusses the etiology, which can be infectious (bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic), autoimmune, paraneoplastic, or demyelinating. Common infectious causes include Listeria monocytogenes, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, enteroviruses like EV71, and herpes viruses. Clinical presentation often involves fever, headache, cranial nerve palsies, ataxia, and altered mental status. Diagnosis involves CSF analysis and brain imaging. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but often involves antibiotics and antivirals. Prognosis can vary from complete recovery to significant neurologic sequelae or death