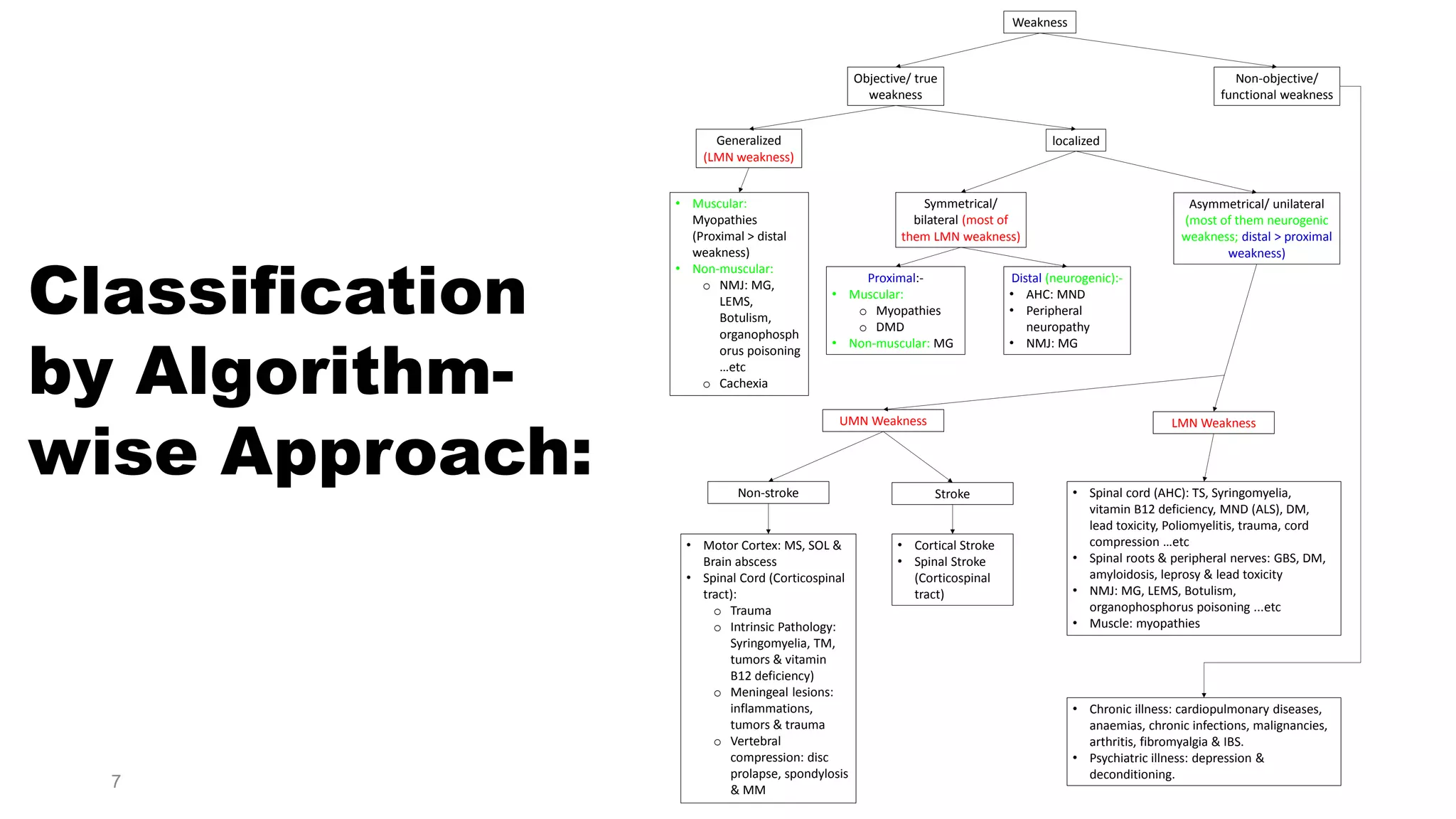
1) The document discusses an approach to evaluating muscle weakness by differentiating between true muscle weakness and fatigue or functional weakness. It provides a classification and diagnostic algorithm.
2) Key points in the evaluation include determining if weakness is objective or subjective, localized or generalized, and distinguishing patterns that suggest neurological causes versus muscular causes.
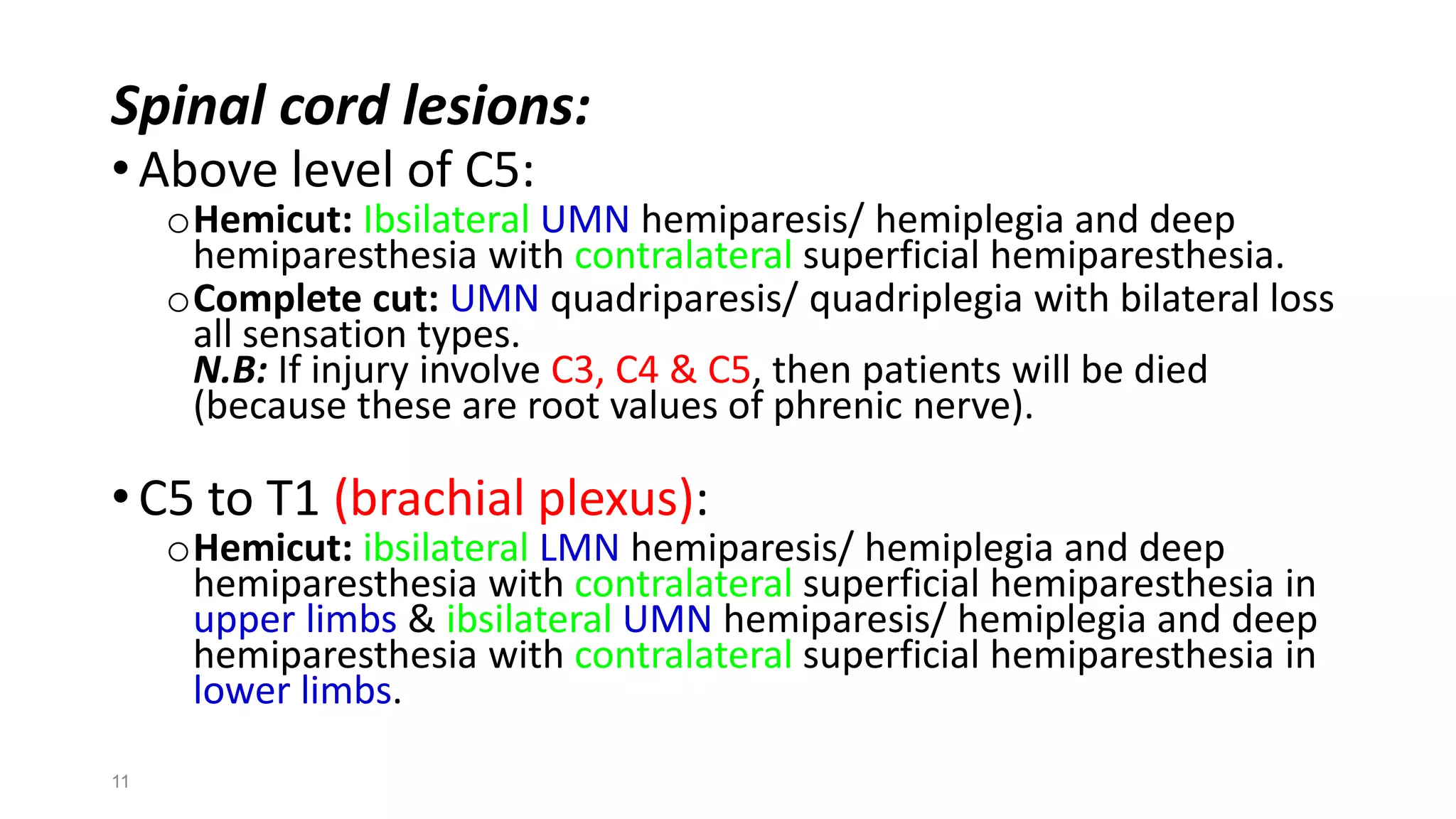
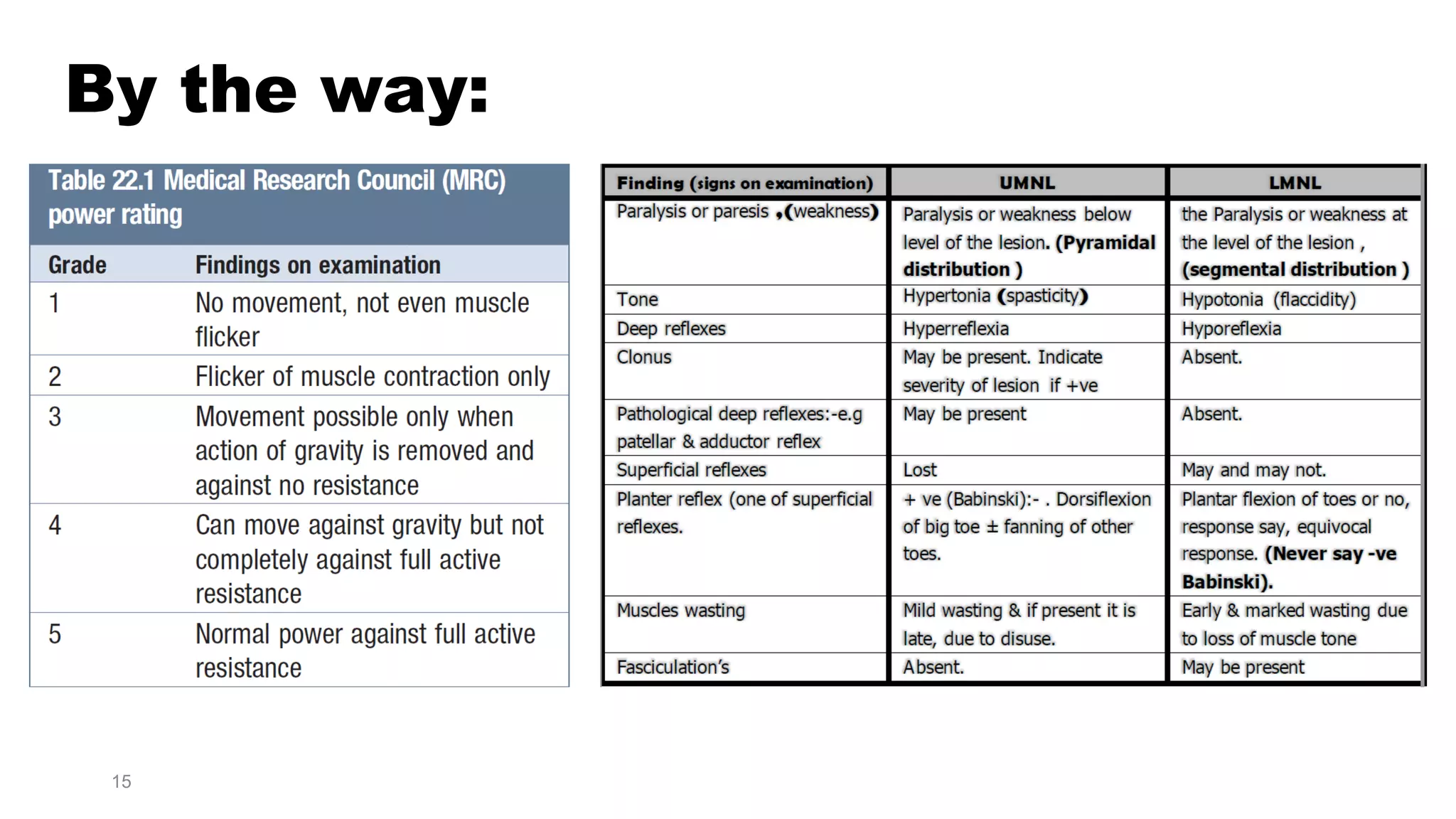
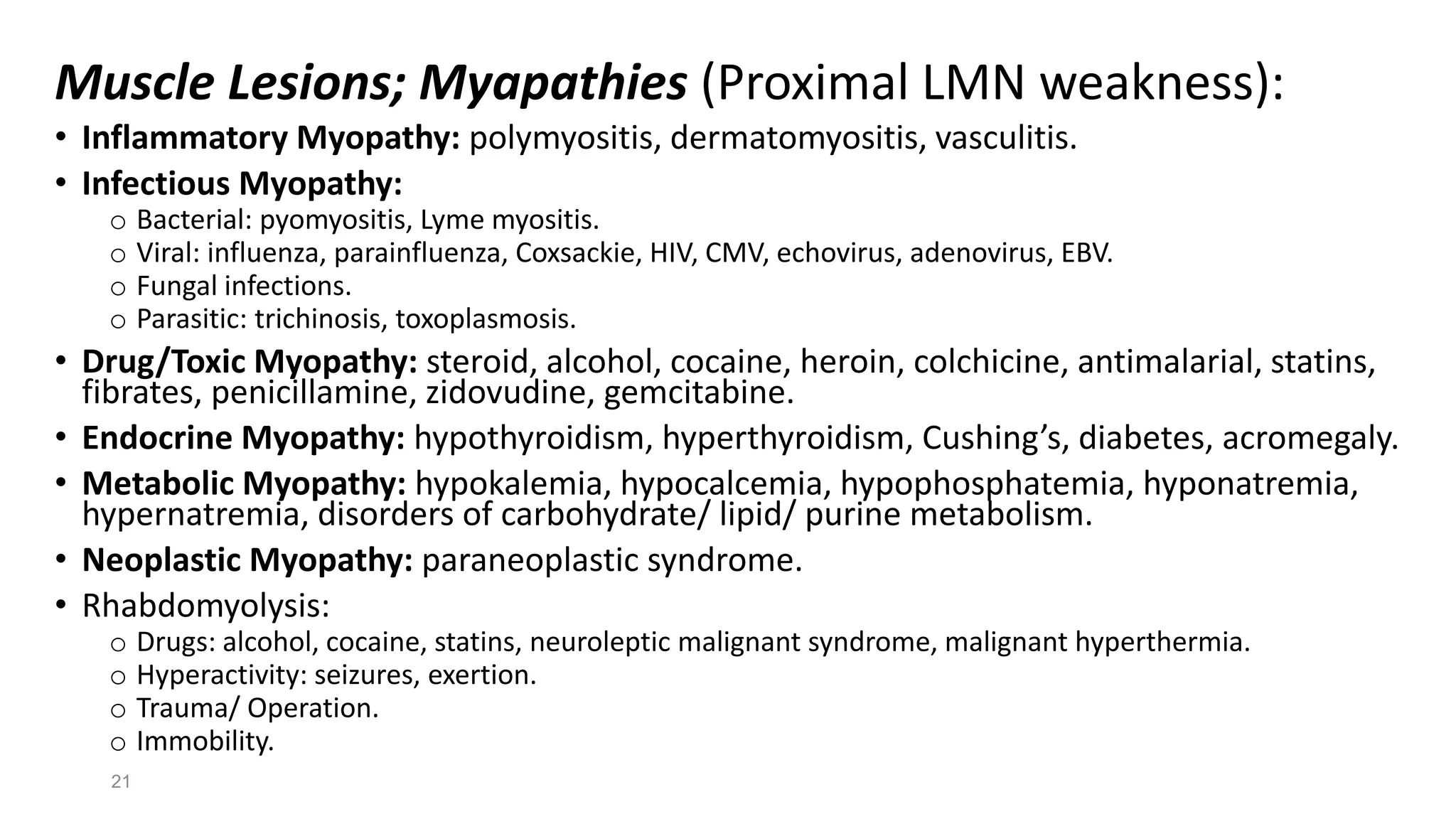
3) Common etiologies discussed that can cause true muscle weakness include stroke, spinal cord lesions, peripheral neuropathies, myasthenia gravis, and myopathies. Fatigue may be caused by medical illnesses, drugs/alcohol, or psychiatric conditions.


![• Fatigue is subjective term reported by patient as weakness-like
complain felt after exercise but actually muscle power is normal, i.e:
no pathology in muscle or in its nerve supply. So fatigue is non-
objective muscle weakness, non-neuromuscular weakness,
functional muscle weakness or false muscle weakness.
Motor Nerve Supply
True Muscle Weakness
Wrong neither in
muscle nor in its
nerve supply
Functional
Muscle
weakness
[Myopathy]Muscle
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtomuscleweakness-181006153906/75/Approach-to-muscle-weakness-3-2048.jpg)