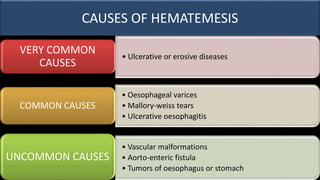
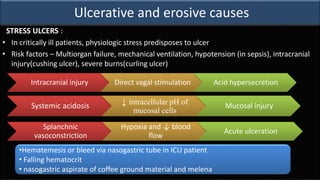
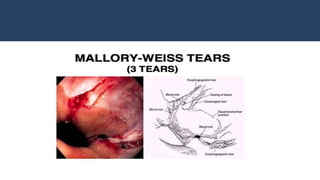
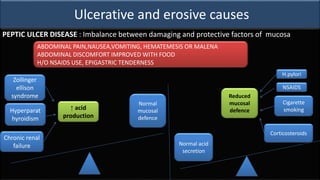
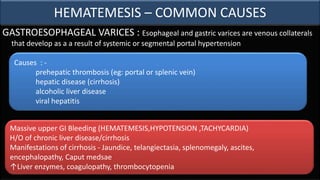
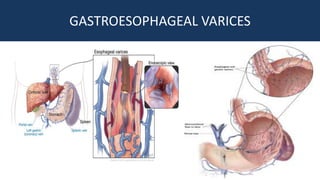
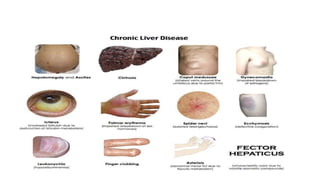
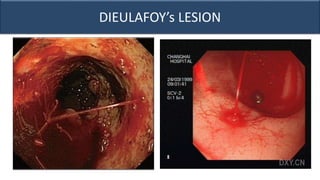
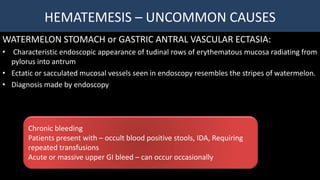
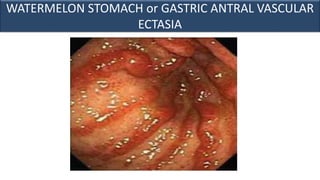
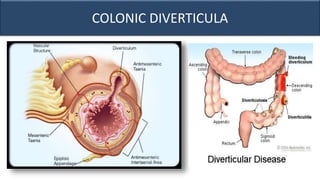
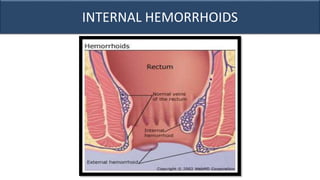
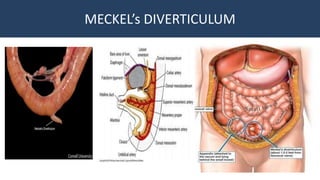
This document provides an overview of approaches to gastrointestinal bleeding. It discusses the common clinical presentations including hematemesis, melena, hematochezia, and occult bleeding. For hematemesis, the most common causes are discussed such as stress ulcers, Mallory-Weiss tears, peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal varices, and Dieulafoy's lesion. For hematochezia, common causes include colonic diverticula, internal hemorrhoids, colon cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease. The document provides details on evaluating each potential cause and characteristics to consider in the clinical history and examination.