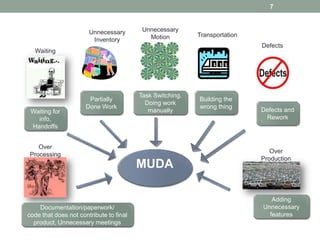
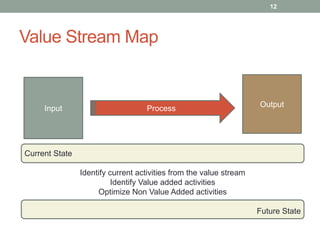
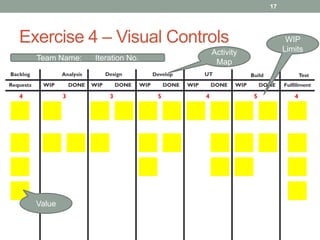
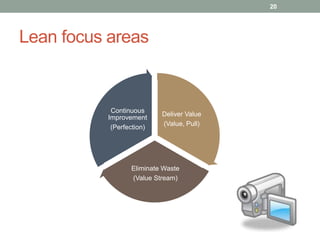
The document discusses applying lean techniques in software development. It begins with an overview of lean origins in Toyota's production system and the lean philosophy of removing waste to get more from less. Several lean techniques are then described, including value stream mapping to identify value-added and non-value added activities, the dependency structure matrix to visualize task dependencies, and visual controls and poka-yoke for process transparency and mistake-proofing. Examples and exercises are provided to illustrate how to apply these techniques. The presentation emphasizes the lean focus areas of continuous improvement, delivering value, and eliminating waste from value streams.