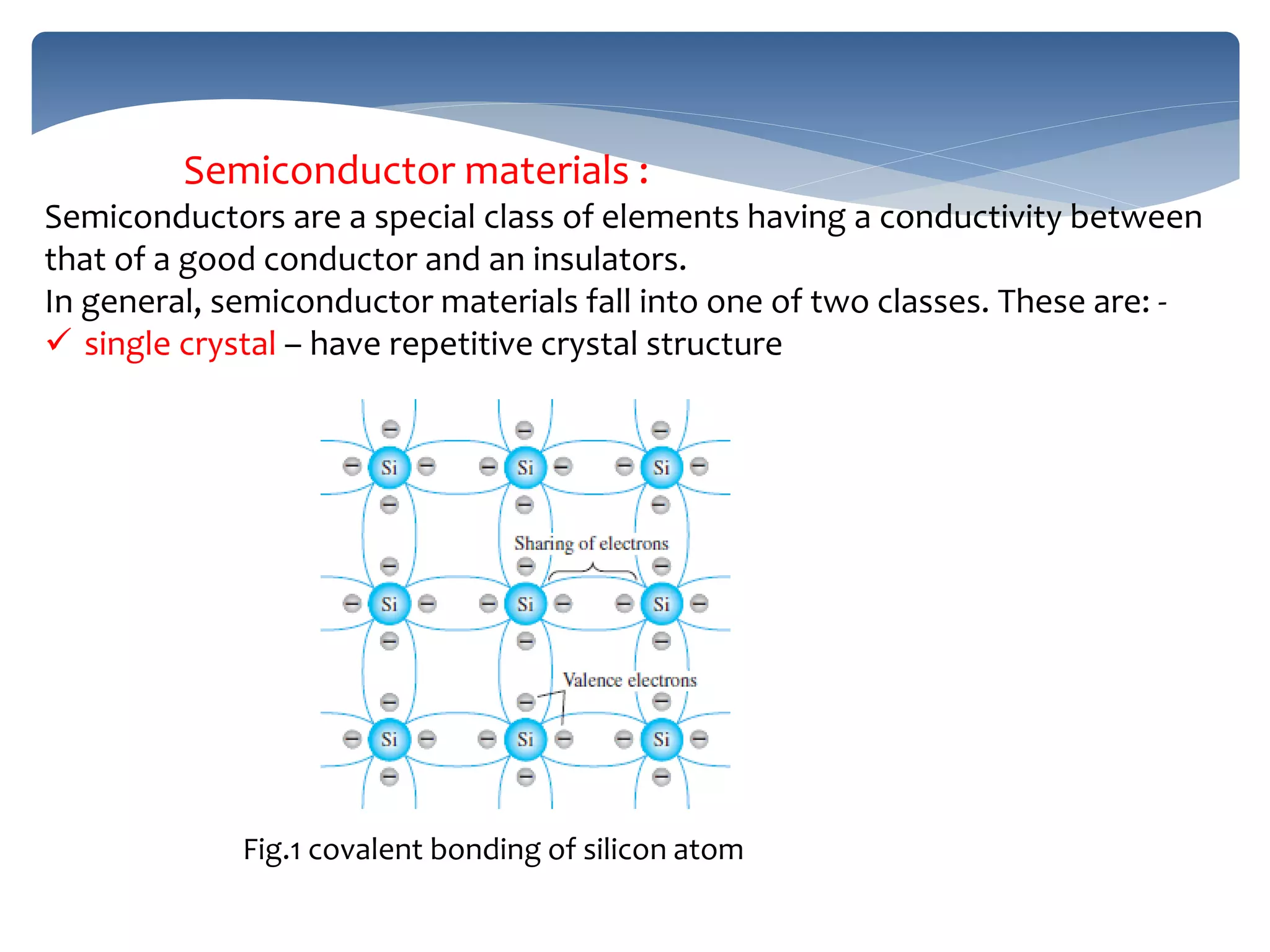
This document discusses basic semiconductor theory, including:
1. Semiconductors have conductivity between conductors and insulators and include materials like silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide.
2. Doping semiconductors with impurities creates n-type or p-type materials by introducing excess electrons or holes.
3. The atomic structure of semiconductors includes valence and conduction energy bands separated by a bandgap through which electrons can jump with sufficient energy.