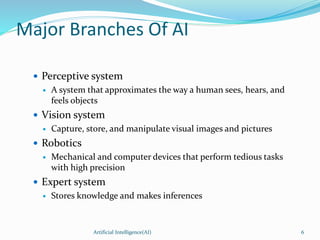
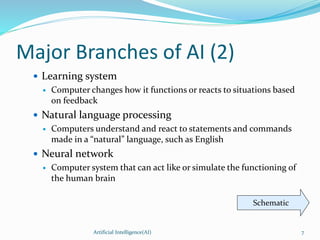
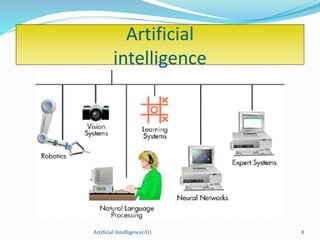
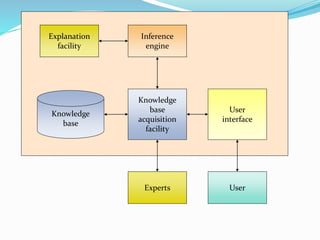
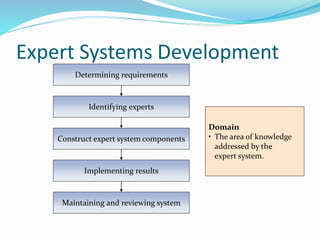
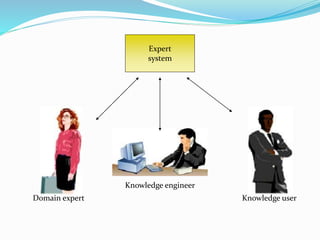
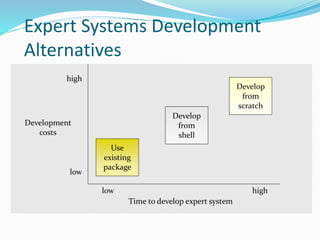
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), including its history, major branches, expert systems, and applications. It discusses how AI aims to build intelligent machines that can think and act like humans. The major branches covered are perceptive systems, robotics, expert systems, learning systems, natural language processing, and neural networks. Expert systems are described as AI programs that store knowledge and make inferences to emulate human experts. The document also outlines the typical components of an expert system, including the knowledge base, inference engine, and user interface. Common AI software mentioned includes CLIPS, Weka, and MOEA Framework.