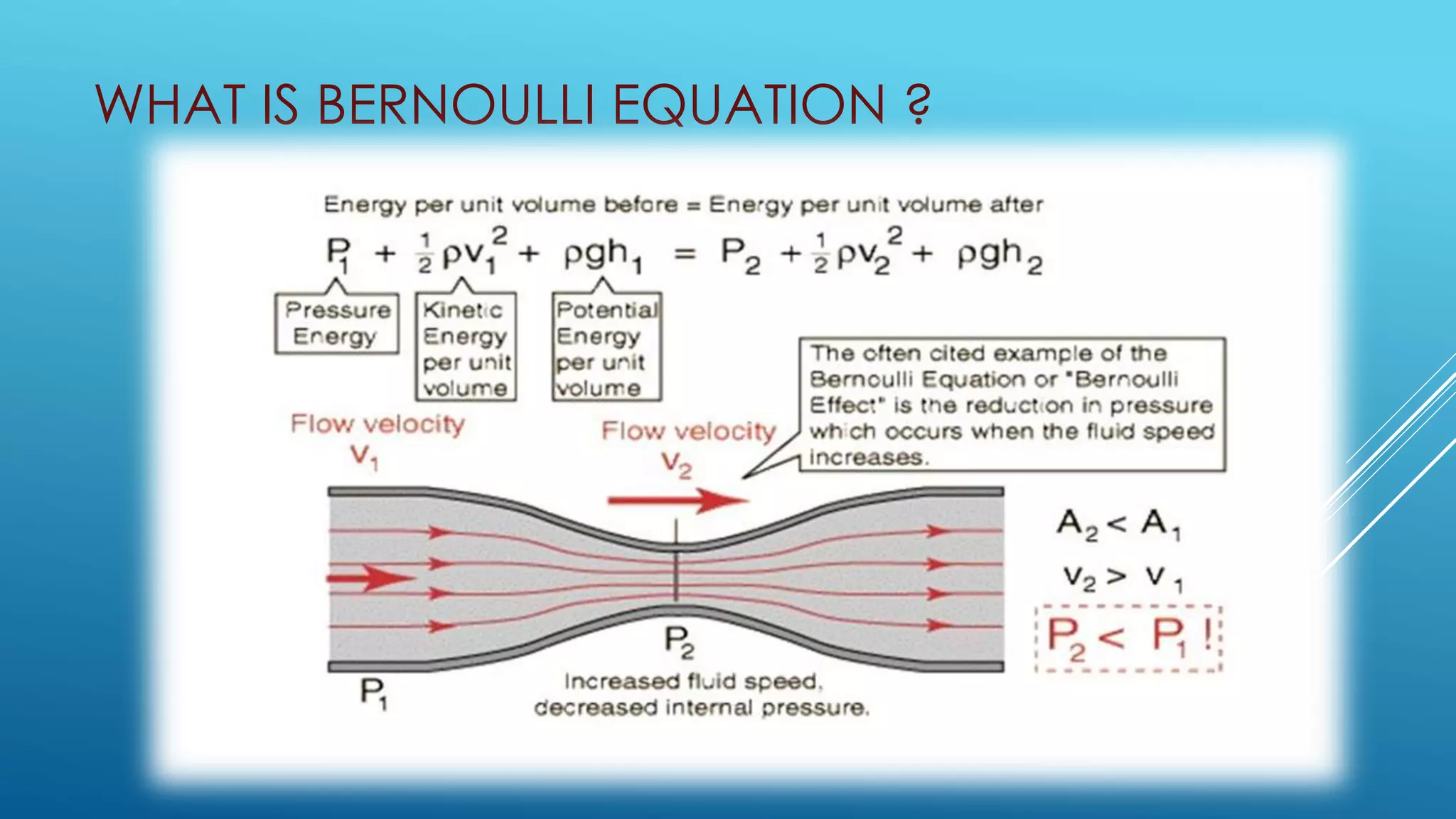
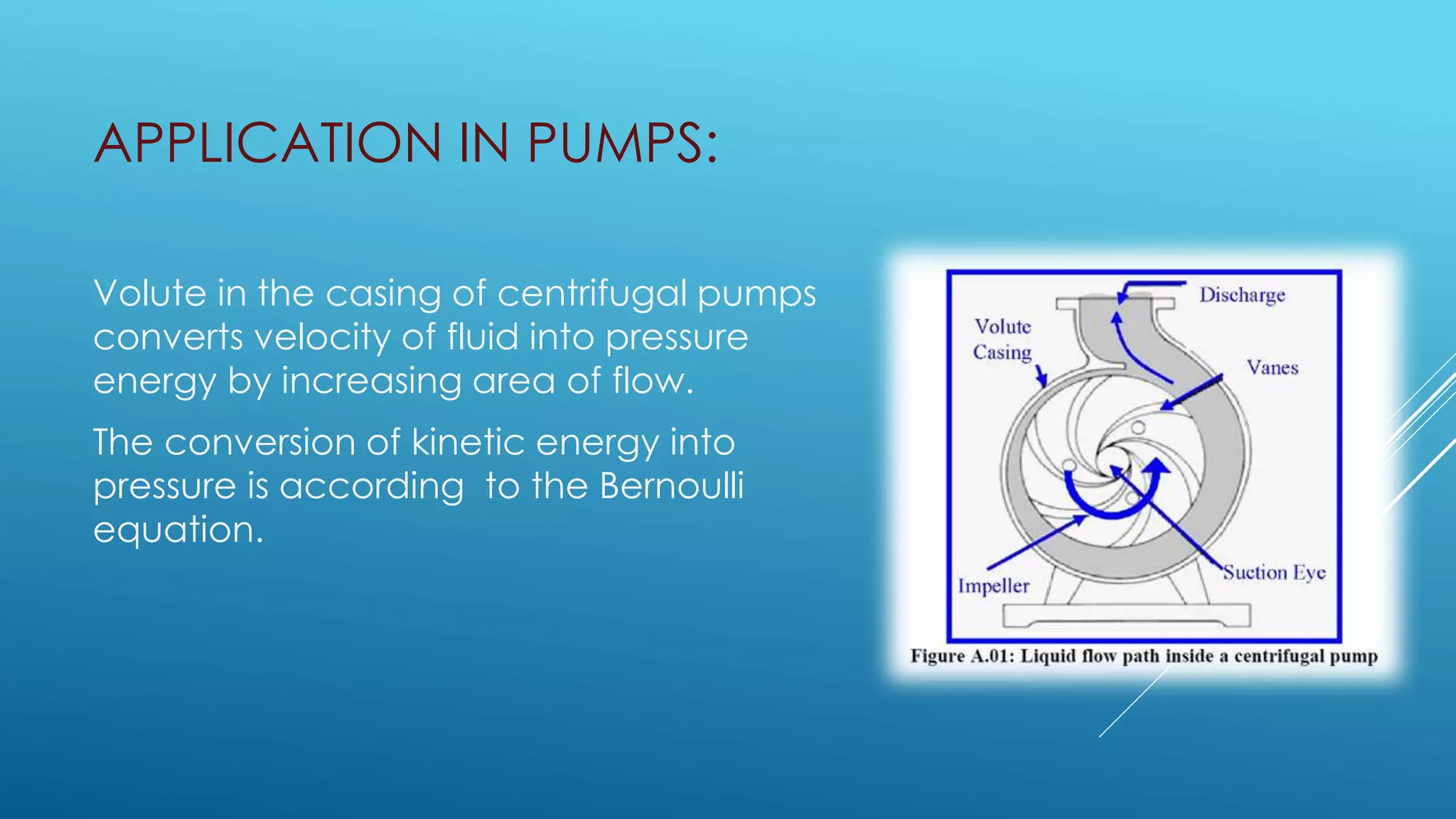
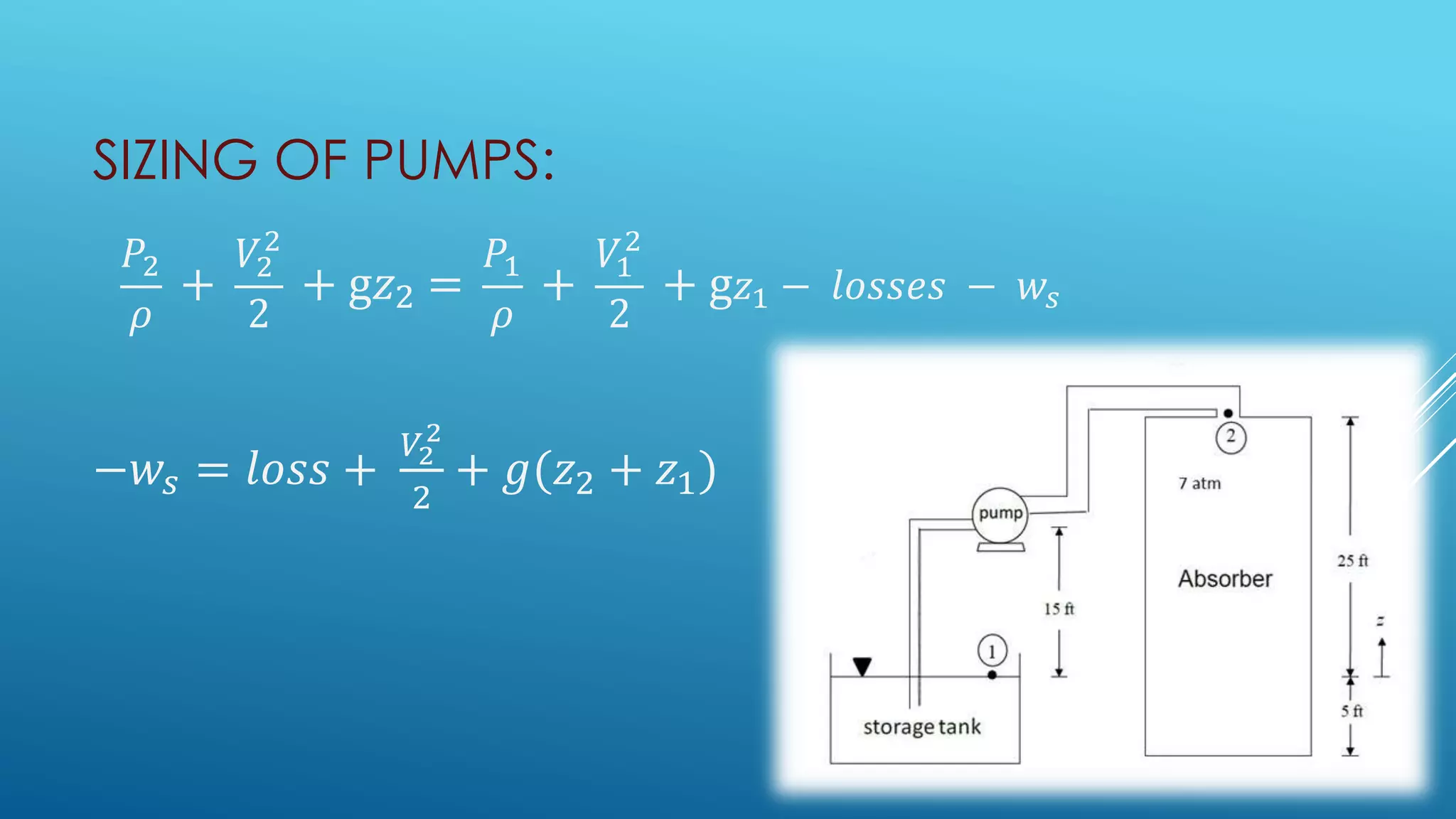
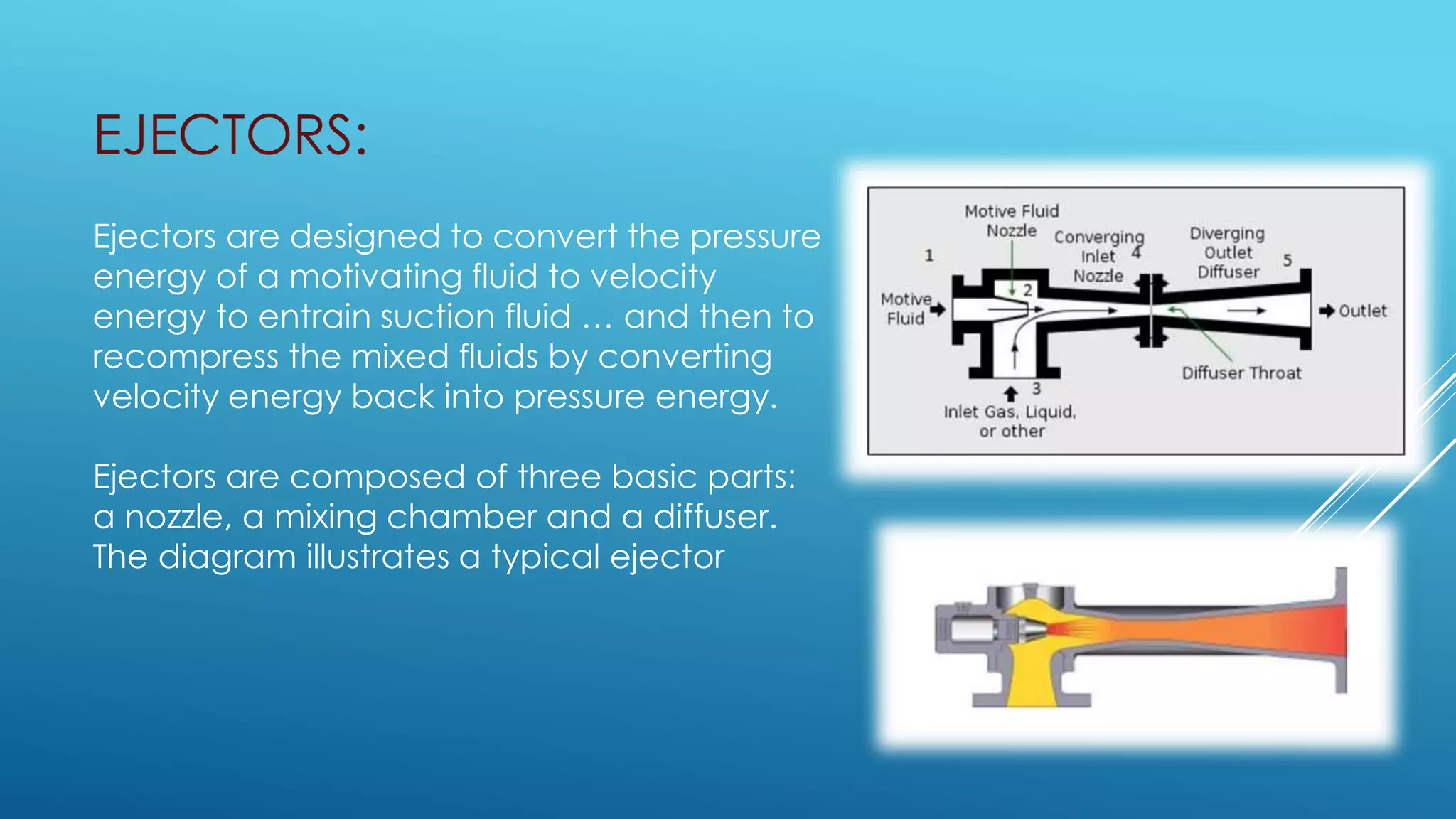
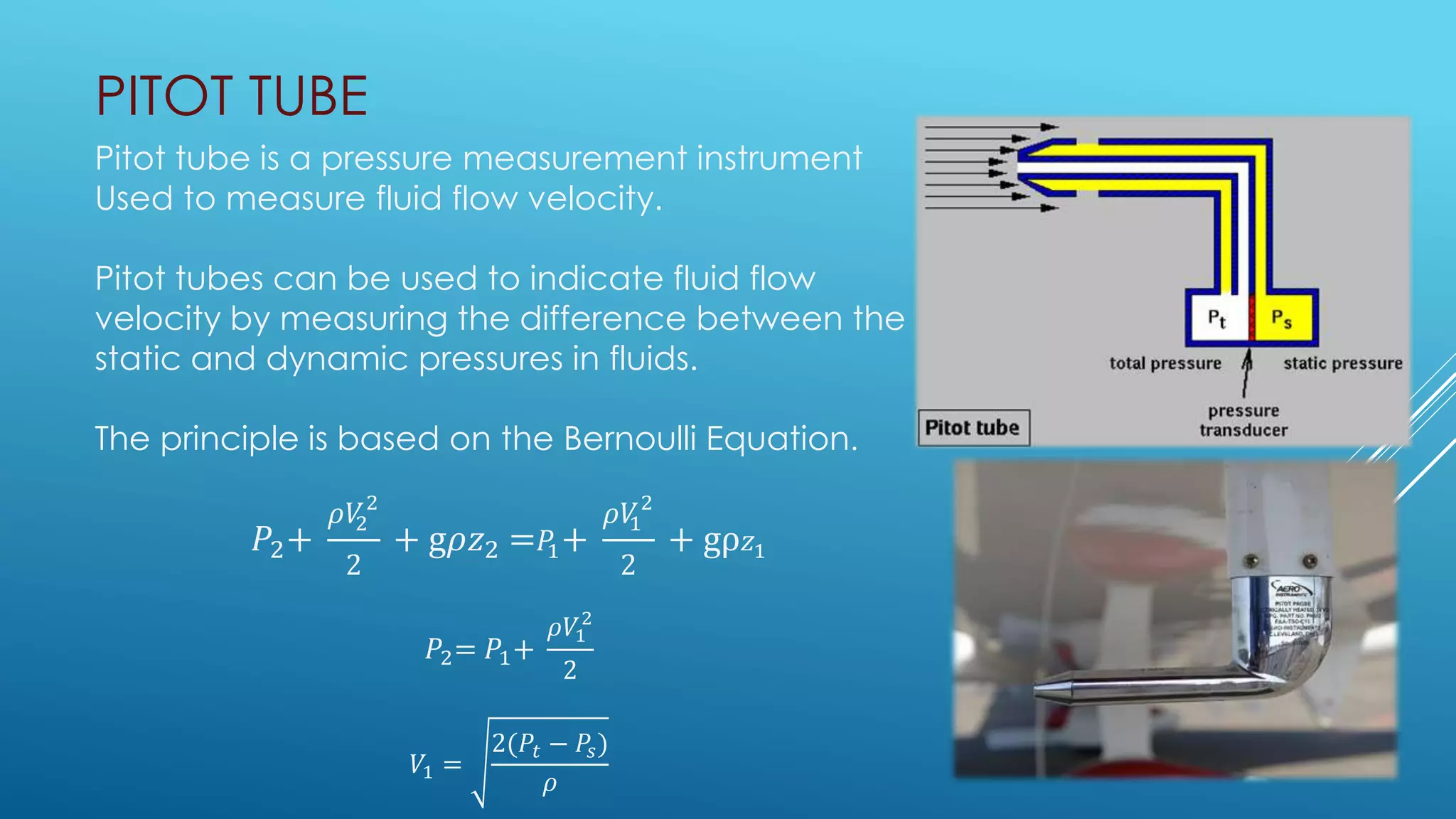
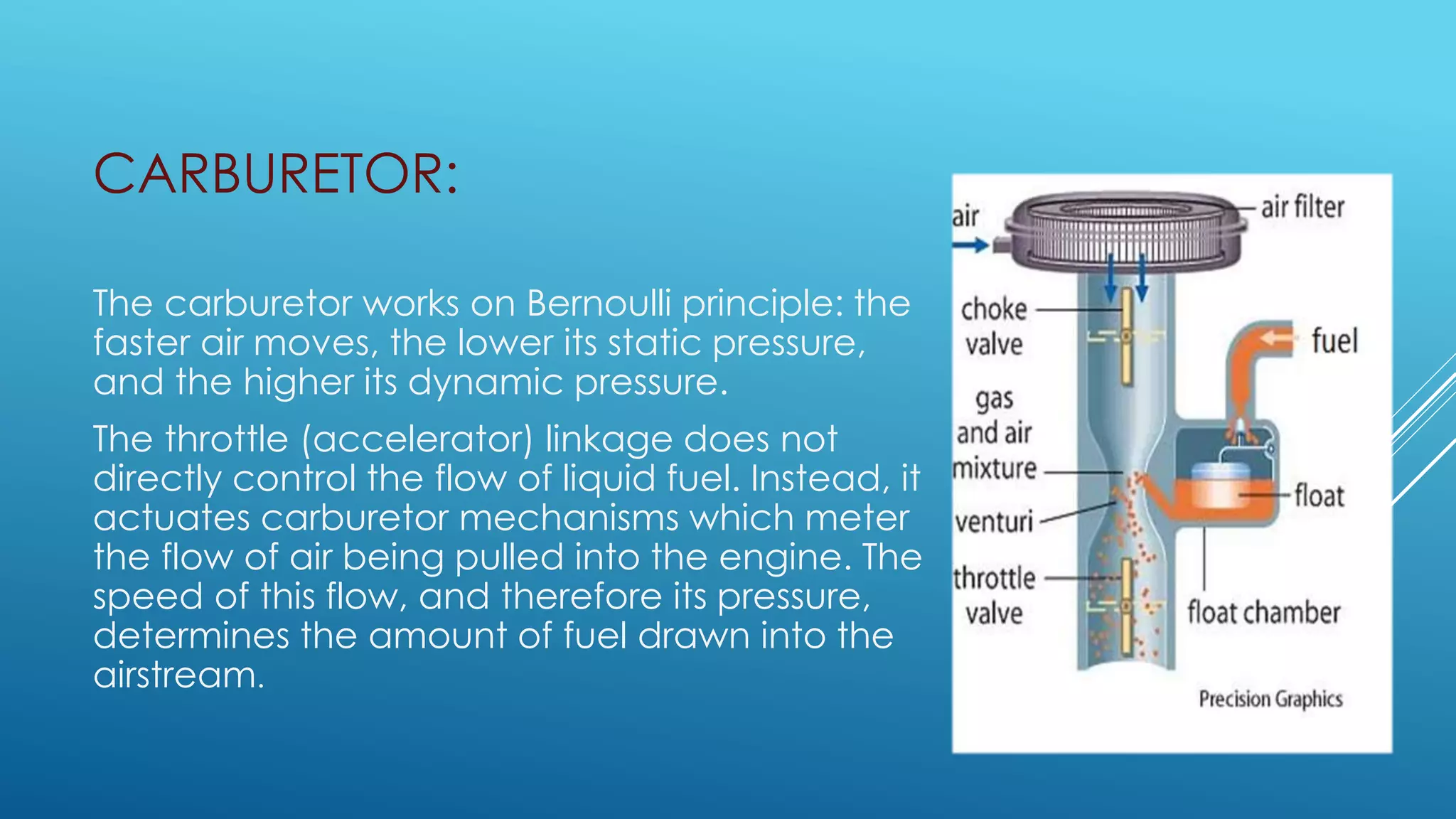
Bernoulli's equation states that the total mechanical energy of an incompressible and inviscid fluid is constant. It relates pressure, velocity, and elevation. Some key applications of Bernoulli's equation include sizing pumps, flow sensors, ejectors, carburetors, siphons, and Pitot tubes. In pumps, the volute converts kinetic energy to pressure energy. Ejectors use pressure energy to accelerate a suction fluid. A Pitot tube measures velocity from the difference in static and dynamic pressure. A carburetor meters fuel flow based on air velocity lowering static pressure. Siphons use Bernoulli's equation to move liquid over an obstruction without pumping.