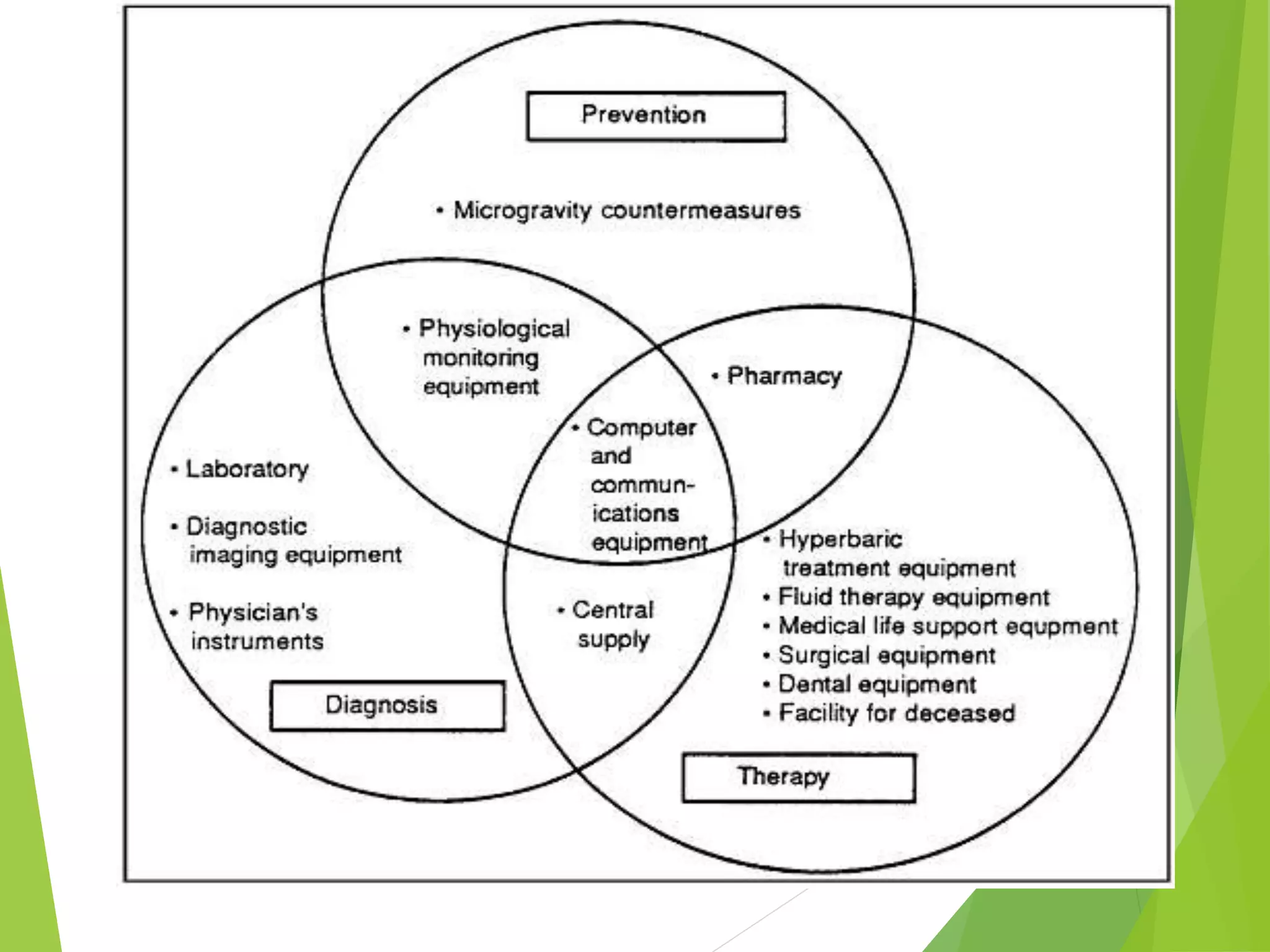
Computers are now essential tools in pharmacy. They are used for database management of drugs and patients, order entry systems, billing, purchasing, inventory control, and more. The use of computers in pharmacy started in the 1980s and provides advantages like increased accuracy, reduced time and workload, and ability to access information across boundaries. Computers are used in retail pharmacy for accounting, management, and drug information retrieval. In hospitals, computers aid in patient record maintenance, purchasing, and therapeutic drug monitoring. They are also crucial for data processing and storage in pharmaceutical analysis, drug design, publishing, education, and simulations. Pharmacy informatics and drug information services further clinical decision making. Telepharmacy allows remote delivery of pharmaceutical care while internet