The document discusses stacks and their applications. It provides 3 key points:
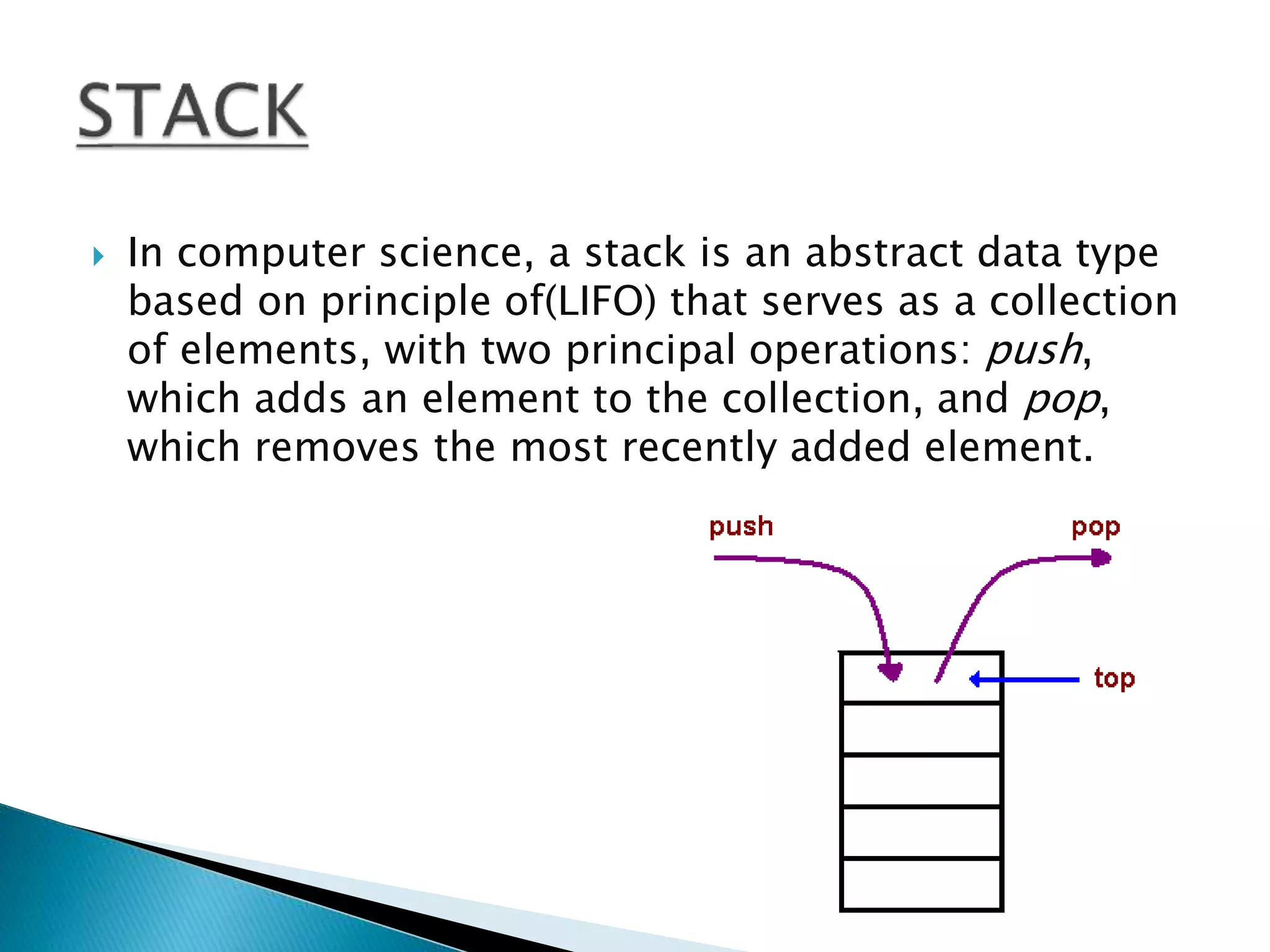
1. A stack is an abstract data type that follows LIFO (last-in, first-out) principles with push and pop operations. Functions like stack_full and stack_empty are used to implement stacks.
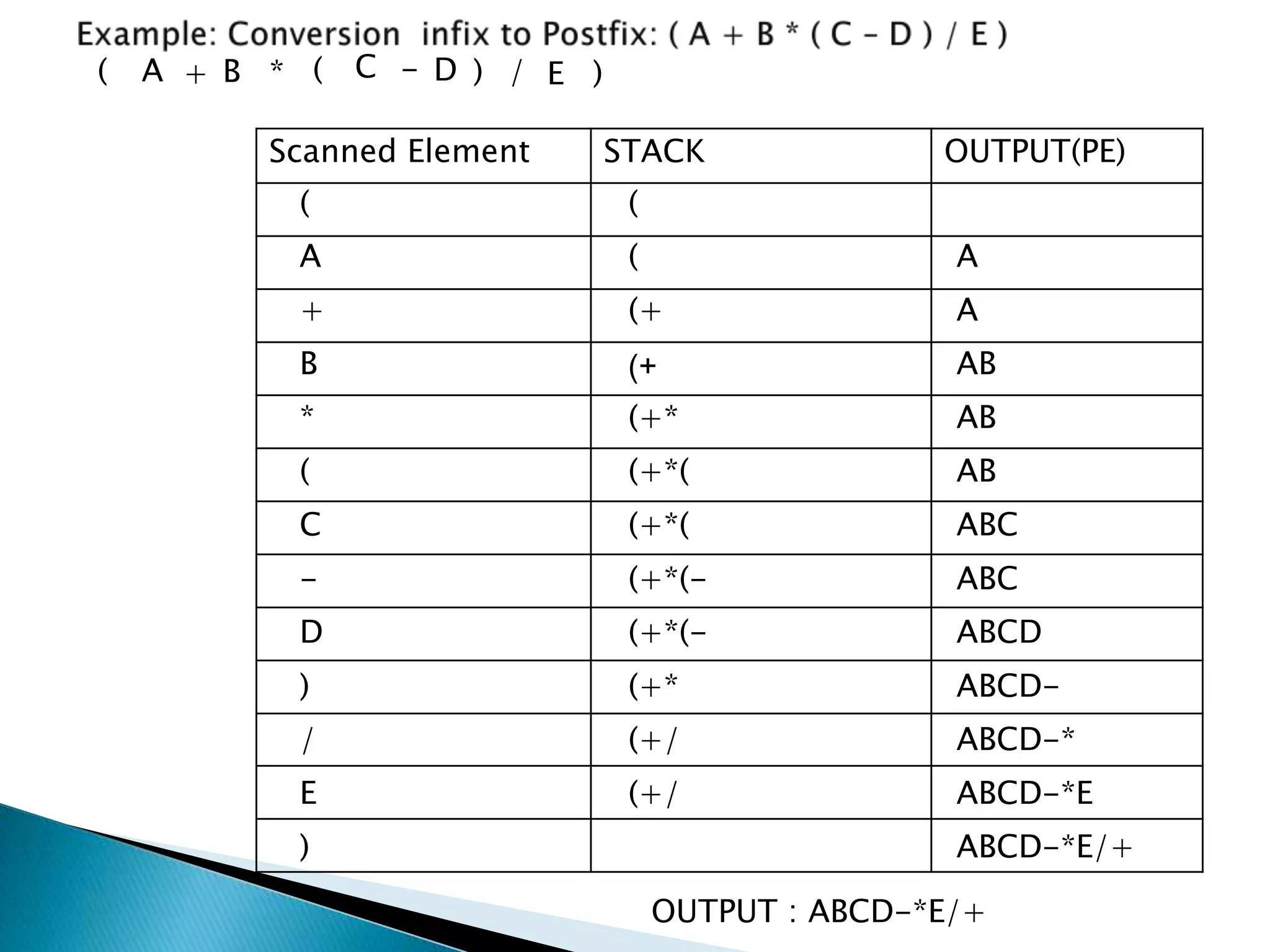
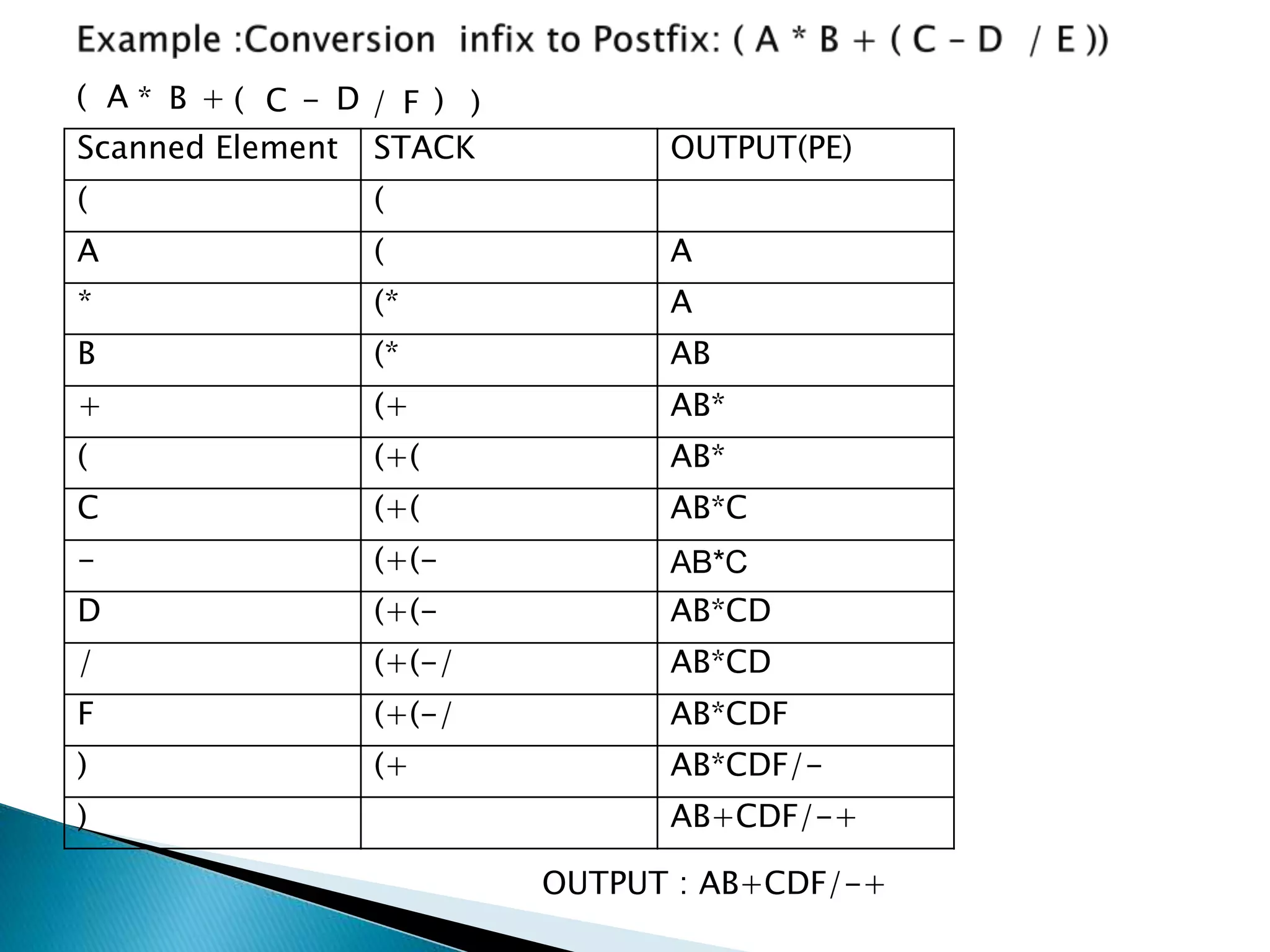
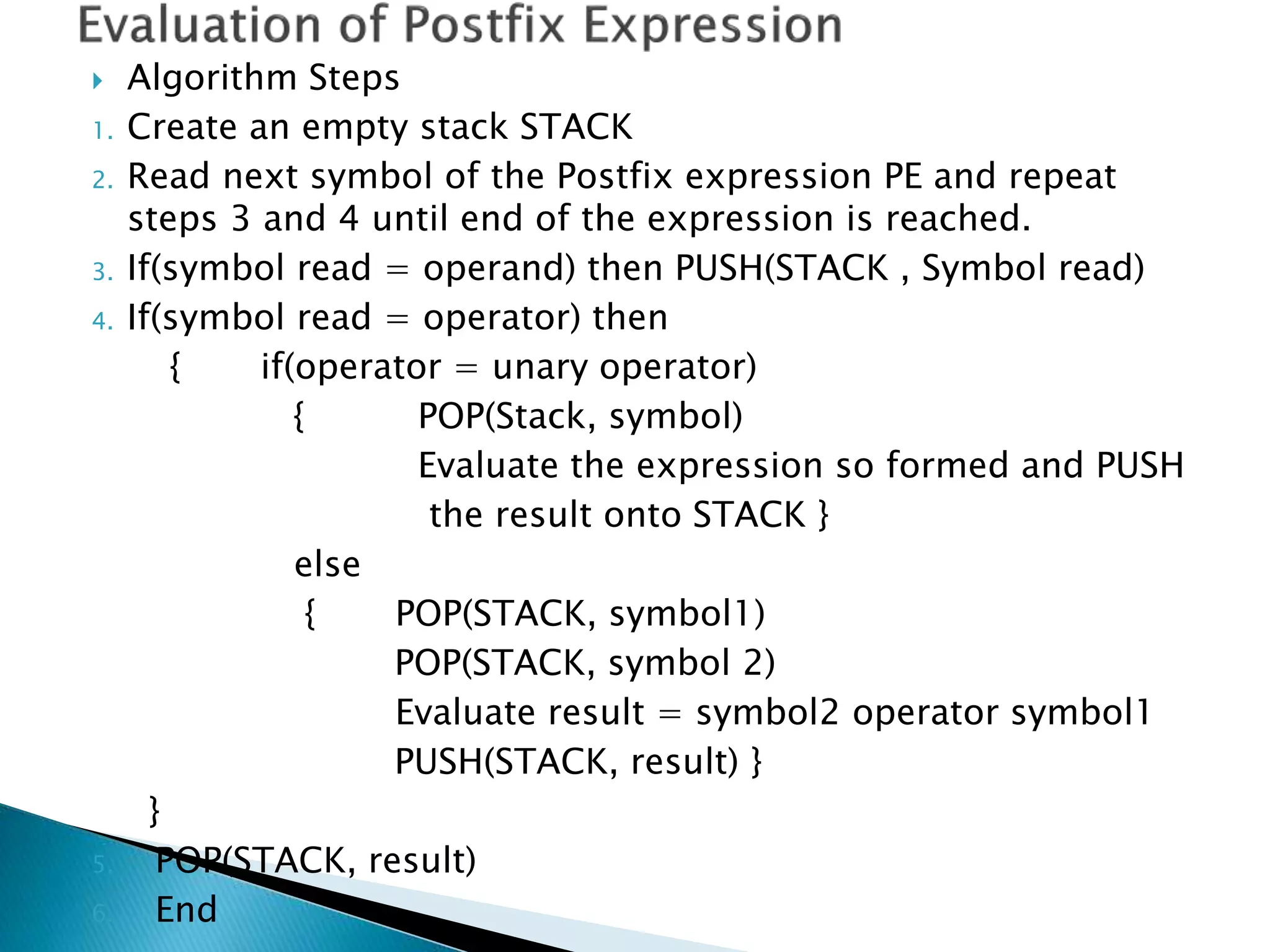
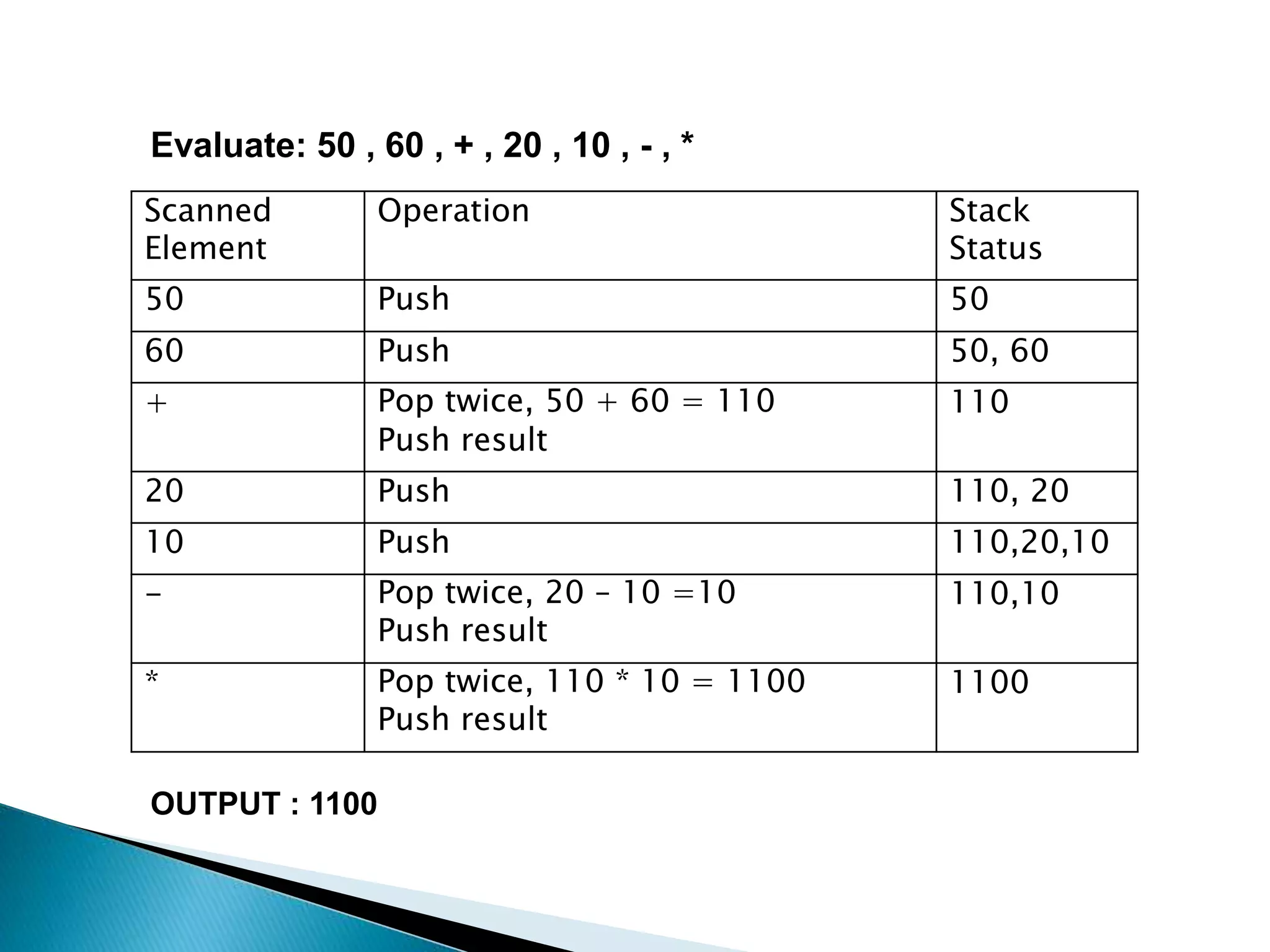
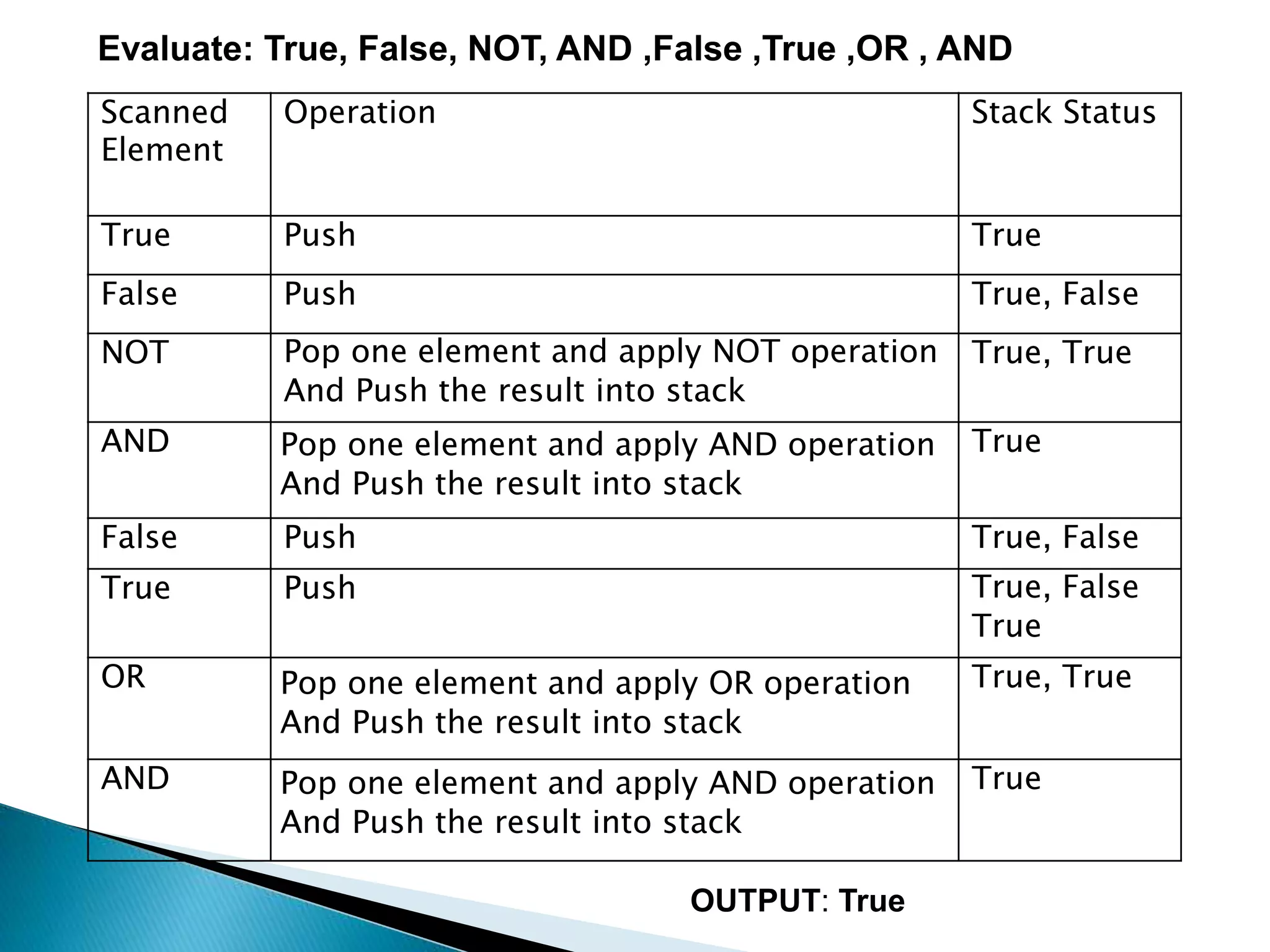
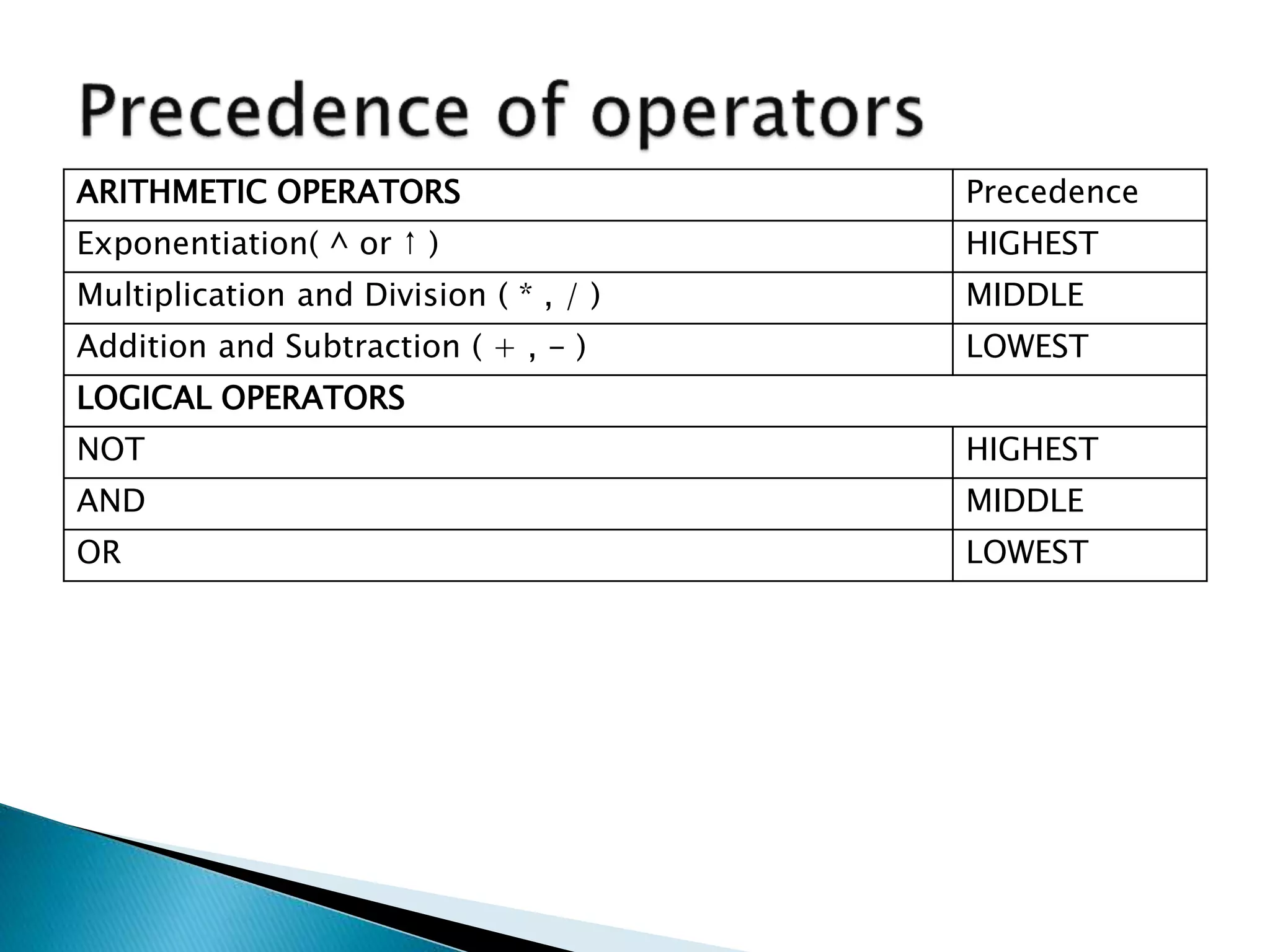
2. Stacks have applications in converting infix notation to postfix notation and evaluating postfix expressions. The algorithms pop and push operators and operands to convert between notations and perform calculations.
3. Examples show converting the infix expression (A * B + (C - D / E)) to postfix and evaluating the postfix expression 50, 60, +, 20, 10, -, *.

![ Functions necessary to implement a stack :
#include<iostream.h>
#define STACK_SIZE 20
int stack[STACK_SIZE]; /*space for stacking
integers*/
int top=-1; / *top_of_stack is
defined as global
variable for a global stack */
/*Function to check whether the stack is ‘full’ */
int stack_full()
{
if(top==STACK_SIZE-1)
return(1);
else
return(0);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofstack-160529042307-161107075900/75/Applicationofstack-by-Ali-F-RAshid-3-2048.jpg)
![ /* Function to check whether the stack is ‘empty’ */
int stack_empty()
{
if(top==-1)
return(1);
else
return(0);
}
/*Function to push or add an element on the stack.*/
void push(int number)
{
stack[++top]=number; /*add element on top of
stack */
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofstack-160529042307-161107075900/75/Applicationofstack-by-Ali-F-RAshid-4-2048.jpg)
![ /* Function to pop an element from the stack*/
int pop()
{
int number;
number=stack[top]; /*remove top element from
stack */
top--;
return(number);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofstack-160529042307-161107075900/75/Applicationofstack-by-Ali-F-RAshid-5-2048.jpg)




![Algorithm: Infix to Postfix conversion
1. Enclose the expression in parentheses, that is, ( ).
2. Read next symbol of expression and repeat step 3 to 6 until
STACK is empty.
3. If the symbol is operand add to Postfix Expression
4.If the symbol read is ‘(‘ then push it into STACK.
5. If symbol read = operator then
(1) Repeat while ( Precedence of TOP(STACK)
>= precedence of
operator read)
{ POP operator from STACK and add operator to PE}
(2) Push operator into STACK
6. If the symbol read is ‘)’ then
(1) Repeat while( TOP[Stack] != ‘(‘ )
{ POP operator from stack and add to PE}
(2) Remove the ‘(‘ . [ it must not be added to PE ]
7. PE is the desired equivalent Postfix Expression
8. End](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofstack-160529042307-161107075900/75/Applicationofstack-by-Ali-F-RAshid-11-2048.jpg)