Application development using Microsoft SQL Server 2000 discusses several key enhancements in SQL Server 2000 including application migration assistance, engine enhancements like user-defined functions and triggers, XML support, and the ability to run multiple SQL Server instances on a single machine. The document provides examples of cascading deletes and updates, scalar and table-valued user-defined functions, instead-of triggers, indexes on computed columns and views, and different options for generating XML output from SQL queries. It also lists additional resources for more information.








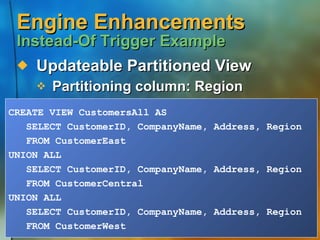

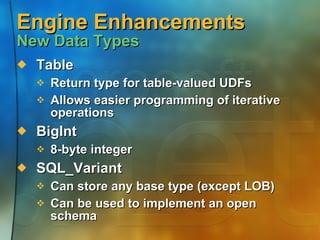

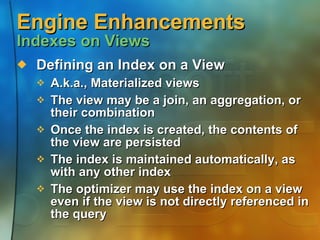

![XML Support XML Query Results SQL Language Extension SELECT… FROM… WHERE… ORDER BY… FOR XML (raw | auto [, ELEMENTS] | explicit) [, XMLData] [, BINARY base64])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/application-development-using-microsoft-sql-server-20002464/85/Application-development-using-Microsoft-SQL-Server-2000-15-320.jpg)








