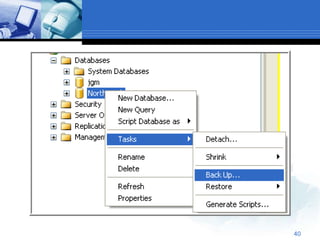
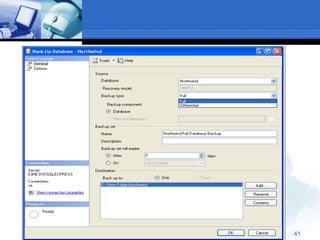
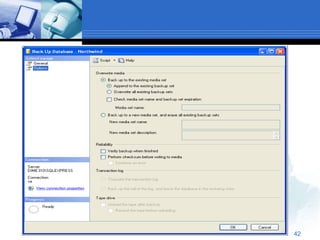
The document provides an overview of managing databases in Microsoft SQL Server 2005. It discusses topics such as creating and maintaining databases, using data definition and manipulation languages, and performing backups and restores. Specific commands for creating, altering, and dropping database objects are demonstrated. The SQL Server Management Studio tool is also demonstrated for tasks like creating new databases and tables through its graphical user interface.