This presentation provides information about appendicitis including:
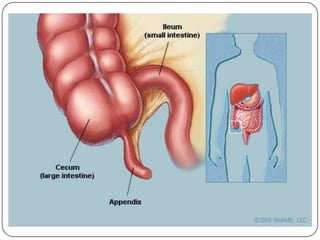
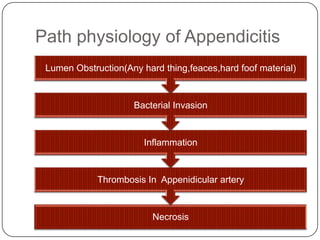
- The appendix is a small pouch connected to the cecum that has no known function. Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes inflamed and filled with pus, usually due to obstruction.
- Common symptoms include pain that starts around the navel and moves to the lower right abdomen, nausea, vomiting, fever, and inability to pass gas.
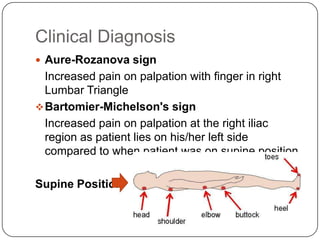
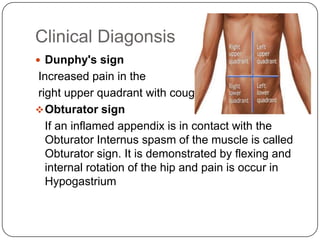
- Diagnosis involves clinical exams, blood tests, urine tests, imaging like ultrasound or CT scans.
- Treatment options include antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, and fluid replacement for mild cases or appendectomy surgery to remove the appendix for more severe cases. Surgical procedures include