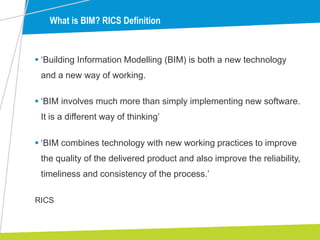
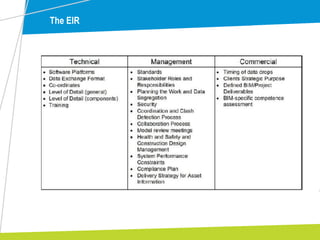
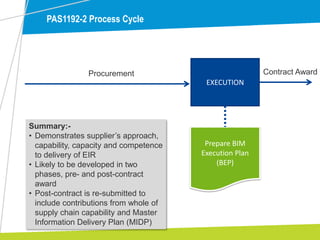
The document outlines the significance of Building Information Modelling (BIM) in construction project management, emphasizing its role in enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving collaborative practices. It highlights the UK government's mandate for BIM by 2016 and discusses various levels of BIM implementation, as well as case studies demonstrating its successful adoption. Key processes, standards, and lessons learned from practical applications are also described to guide project managers in effectively utilizing BIM.