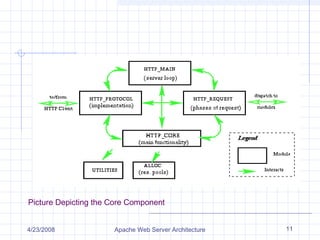
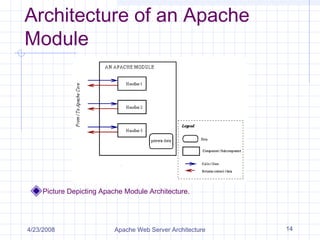
The document discusses the architecture of the Apache web server. It begins with an overview of what a web server and the Apache web server are. It then covers Apache's history and architecture in detail, including its core components, how requests are handled, modules, concurrency model using persistent processes, and configuration. The document provides an in-depth technical summary of the Apache web server architecture.