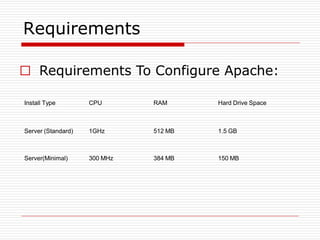
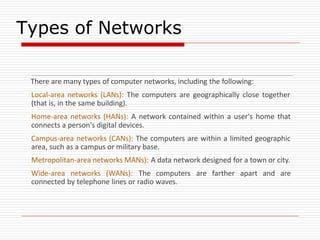
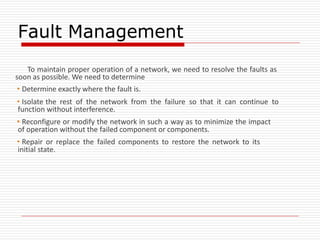
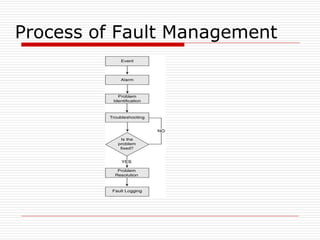
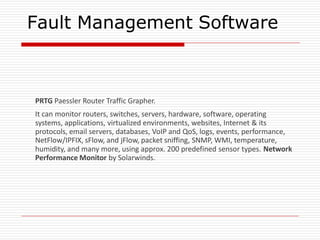
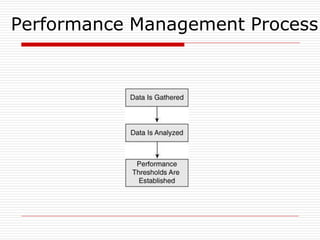
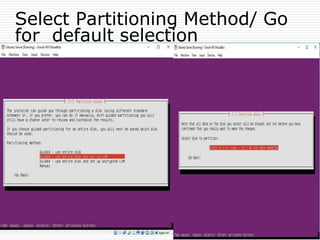
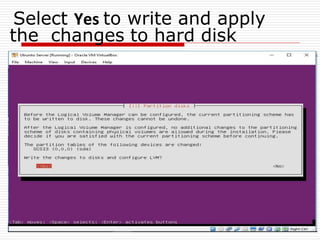
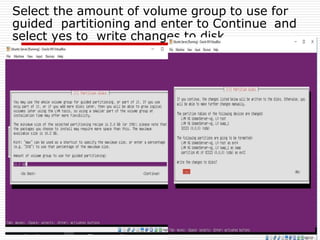
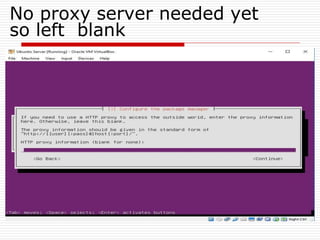
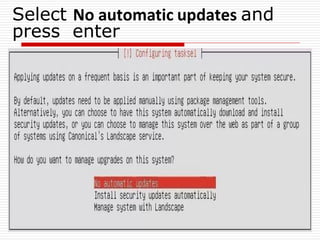
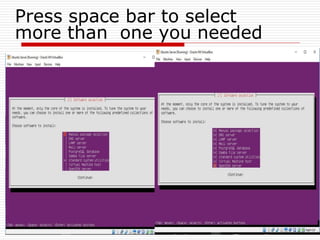
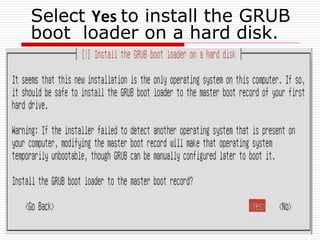
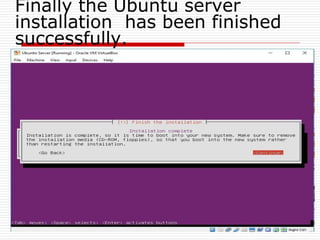
The document provides an overview of server configuration in Linux, including various network models such as client-server, peer-to-peer, and hybrid models. It discusses the types of Linux servers, notable web servers like Apache and Nginx, and essential networking protocols like TCP/IP, FTP, and DHCP. Additionally, it highlights network management processes, advantages and disadvantages of using Linux servers, and installation details for Ubuntu server.