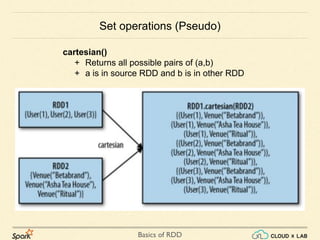
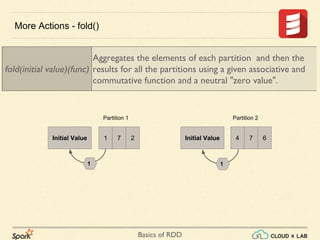
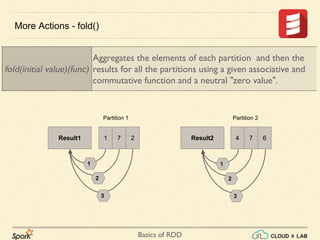
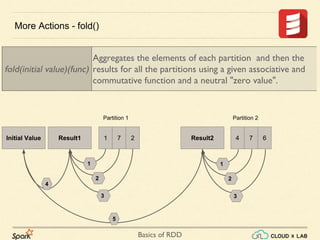
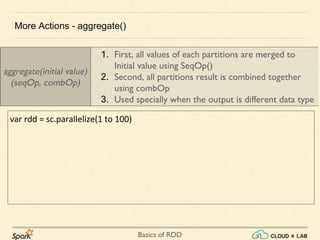
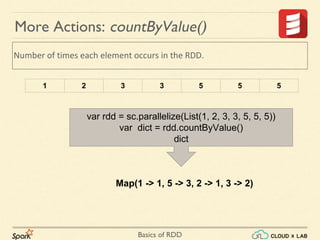
The document provides an overview of various operations and transformations associated with Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) in Apache Spark, including sampling, mapping functions, sorting, and set operations. It covers common transformations, actions like fold and aggregate, and methods to count occurrences and retrieve top elements. Additionally, it discusses differences between actions like foreach and transformations like map.

![Basics of RDD
More Transformations
sample(withReplacement, fraction, [seed])
Sample an RDD, with or without replacement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s3-180514105412/85/Apache-Spark-Basics-of-RDD-RDD-Operations-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-2-320.jpg)
![Basics of RDD
val seq = sc.parallelize(1 to 100, 5)
seq.sample(false, 0.1).collect();
[8, 19, 34, 37, 43, 51, 70, 83]
More Transformations
sample(withReplacement, fraction, [seed])
Sample an RDD, with or without replacement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s3-180514105412/85/Apache-Spark-Basics-of-RDD-RDD-Operations-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-3-320.jpg)
![Basics of RDD
More Transformations
sample(withReplacement, fraction, [seed])
Sample an RDD, with or without replacement.
val seq = sc.parallelize(1 to 100, 5)
seq.sample(false, 0.1).collect();
[8, 19, 34, 37, 43, 51, 70, 83]
seq.sample(true, 0.1).collect();
[14, 26, 40, 47, 55, 67, 69, 69]
Please note that the result will be different on every run.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s3-180514105412/85/Apache-Spark-Basics-of-RDD-RDD-Operations-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-4-320.jpg)
![Basics of RDD
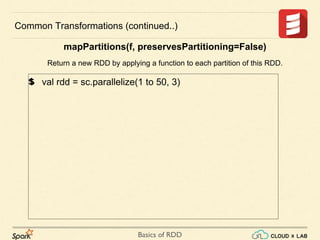
val rdd = sc.parallelize(1 to 50, 3)
def f(l:Iterator[Int]):Iterator[Int] = {
var sum = 0
while(l.hasNext){
sum = sum + l.next
}
return List(sum).iterator
}
Common Transformations (continued..)
mapPartitions(f, preservesPartitioning=False)
Return a new RDD by applying a function to each partition of this RDD.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s3-180514105412/85/Apache-Spark-Basics-of-RDD-RDD-Operations-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-7-320.jpg)
![Basics of RDD
val rdd = sc.parallelize(1 to 50, 3)
def f(l:Iterator[Int]):Iterator[Int] = {
var sum = 0
while(l.hasNext){
sum = sum + l.next
}
return List(sum).iterator
}
rdd.mapPartitions(f).collect()
Array(136, 425, 714)
17, 17, 16
Common Transformations (continued..)
mapPartitions(f, preservesPartitioning=False)
Return a new RDD by applying a function to each partition of this RDD.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s3-180514105412/85/Apache-Spark-Basics-of-RDD-RDD-Operations-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-8-320.jpg)

![Basics of RDD
⋙ var tmp = List(('a', 1), ('b', 2), ('1', 3), ('d', 4), ('2', 5))
⋙ var rdd = sc.parallelize(tmp)
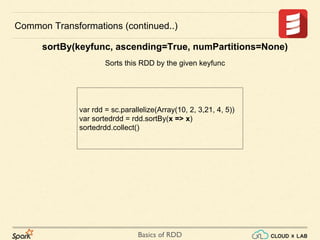
⋙ rdd.sortBy(x => x._1).collect()
[('1', 3), ('2', 5), ('a', 1), ('b', 2), ('d', 4)]
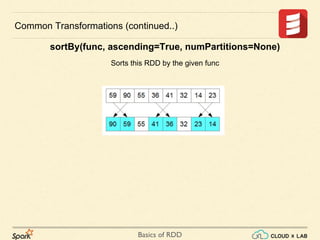
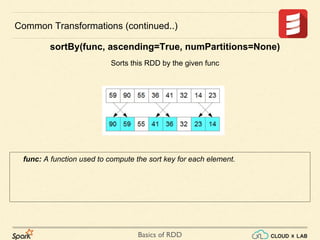
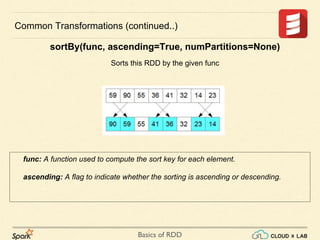
Common Transformations (continued..)
sortBy(keyfunc, ascending=True, numPartitions=None)
Sorts this RDD by the given keyfunc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s3-180514105412/85/Apache-Spark-Basics-of-RDD-RDD-Operations-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-14-320.jpg)
![Basics of RDD
⋙ var tmp = List(('a', 1), ('b', 2), ('1', 3), ('d', 4), ('2', 5))
⋙ var rdd = sc.parallelize(tmp)
⋙ rdd.sortBy(x => x._2).collect()
[('a', 1), ('b', 2), ('1', 3), ('d', 4), ('2', 5)]
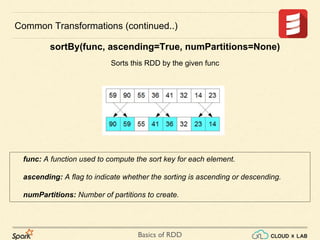
Common Transformations (continued..)
sortBy(keyfunc, ascending=True, numPartitions=None)
Sorts this RDD by the given keyfunc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s3-180514105412/85/Apache-Spark-Basics-of-RDD-RDD-Operations-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-15-320.jpg)
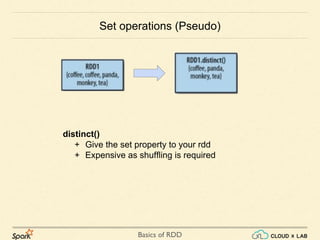
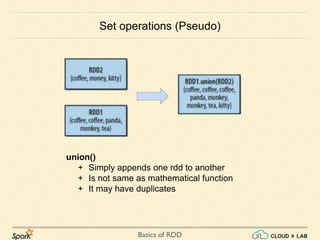
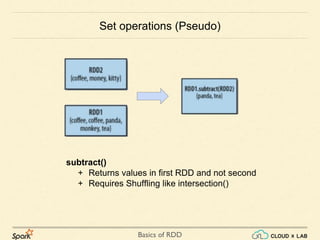
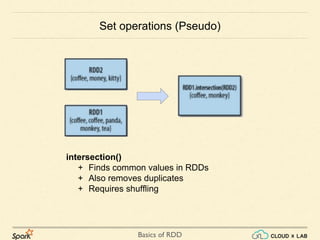











![Basics of RDD
sc.parallelize(List(10, 1, 2, 9, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)).takeOrdered(6)
var l = List((10, "SG"), (1, "AS"), (2, "AB"), (9, "AA"), (3, "SS"), (4, "RG"), (5, "AU"), (6, "DD"), (7, "ZZ"))
var r = sc.parallelize(l)
r.takeOrdered(6)(Ordering[Int].reverse.on(x => x._1))
(10,SG), (9,AA), (7,ZZ), (6,DD), (5,AU), (4,RG)
r.takeOrdered(6)(Ordering[String].reverse.on(x => x._2))
(7,ZZ), (3,SS), (10,SG), (4,RG), (6,DD), (5,AU)
r.takeOrdered(6)(Ordering[String].on(x => x._2))
(9,AA), (2,AB), (1,AS), (5,AU), (6,DD), (4,RG)
Get the N elements from an RDD ordered in ascending order or as specified by
the optional key function.
More Actions: takeOrdered()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s3-180514105412/85/Apache-Spark-Basics-of-RDD-RDD-Operations-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-43-320.jpg)



![Basics of RDD
def partitionSum(itr: Iterator[Int]) =
println("The sum of the parition is " + itr.sum.toString)
Applies a function to each partition of this RDD.
More Actions: foreachPartition(f)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s3-180514105412/85/Apache-Spark-Basics-of-RDD-RDD-Operations-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-47-320.jpg)
![Basics of RDD
Applies a function to each partition of this RDD.
More Actions: foreachPartition(f)
def partitionSum(itr: Iterator[Int]) =
println("The sum of the parition is " + itr.sum.toString)
sc.parallelize(1 to 40, 4).foreachPartition(partitionSum)
The sum of the parition is 155
The sum of the parition is 55
The sum of the parition is 355
The sum of the parition is 255](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/s3-180514105412/85/Apache-Spark-Basics-of-RDD-RDD-Operations-Big-Data-Hadoop-Spark-Tutorial-CloudxLab-48-320.jpg)
