This document discusses various functions in R for exporting data, including print(), cat(), paste(), paste0(), sprintf(), writeLines(), write(), write.table(), write.csv(), and sink(). It provides descriptions, syntax, examples, and help documentation for each function. The functions can be used to output data to the console, files, or save R objects. write.table() and write.csv() convert data to a data frame or matrix before writing to a text file or CSV. sink() diverts R output to a file instead of the console.



![r-squared
Slide 7
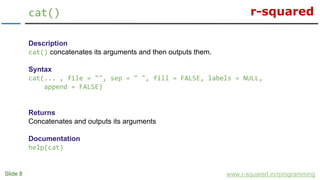
print()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> x <- 3
> print(x)
[1] 3
> x
[1] 3
> # example 2
> name <- "Jovial"
> lname <- "Mann"
> print(name, lname)
Error in print.default(name, lname) : invalid 'digits' argument
> print(c(name, lname))
[1] "Jovial" "Mann"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-7-320.jpg)
![r-squared
Slide 10
cat()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
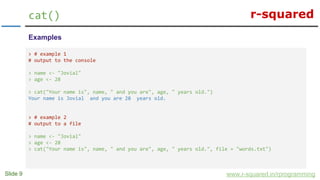
> # example 3
# difference between print and cat
> fname <- "Jovial"
> lname <- "Mann"
> print(c(fname, lname)) # throws an error
[1] "Jovial" "Mann"
> name <- c(fname, lname)
> name
[1] "Jovial" "Mann"
> name <- "Jovial Mann"
> print(name)
[1] "Jovial Mann"
> cat(fname, lname)
Jovial Mann](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-10-320.jpg)

![r-squared
Slide 12
paste()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> x <- 1:10
> paste(x)
[1] "1" "2" "3" "4" "5" "6" "7" "8" "9" "10"
> paste(x, collapse = "")
[1] "12345678910"
> # example 2
> x <- LETTERS
> x
[1] "A" "B" "C" "D" "E" "F" "G" "H" "I" "J" "K" "L" "M" "N" "O" "P" "Q" "R" "S" "T" "U" "V"
[23] "W" "X" "Y" "Z"
> paste(x)
[1] "A" "B" "C" "D" "E" "F" "G" "H" "I" "J" "K" "L" "M" "N" "O" "P" "Q" "R" "S" "T" "U" "V"
[23] "W" "X" "Y" "Z"
> paste(x, collapse = "")
[1] "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-12-320.jpg)
![r-squared
Slide 13
paste()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 3
> name <- "Jovial"
> age <- 28
> paste(name, age)
[1] "Jovial 28"
> paste(name, age, sep = ",")
[1] "Jovial,28"
> paste(name, age, sep = "")
[1] "Jovial28"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-13-320.jpg)
![r-squared
Slide 14
paste()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 4
> alpha <- LETTERS[1:4]
> numeric <- 1:4
> alpha_numeric <- paste(alpha, numeric)
> alpha_numeric
[1] "A 1" "B 2" "C 3" "D 4"
> alpha_numeric <- paste(alpha, numeric, sep = "")
> alpha_numeric
[1] "A1" "B2" "C3" "D4"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-14-320.jpg)

![r-squared
Slide 16
paste0()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> alpha <- LETTERS[1:4]
> numeric <- 1:4
> paste0(alpha, numeric)
[1] "A1" "B2" "C3" "D4"
> paste(alpha, numeric, sep = "")
[1] "A1" "B2" "C3" "D4"
> # example 2
> name <- "Jovial"
> age <- 28
> paste0(name, age)
[1] "Jovial28"
> paste(name, age, sep = "")
[1] "Jovial28"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-16-320.jpg)

![r-squared
Slide 18
sprintf()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> name <- "Jovial"
> age <- 28
> sprintf("Your name is %s and you are %d years old", name, age)
[1] "Your name is Jovial and you are 28 years old"
# %s is replaced by the value in name and %d is replaced by value in age. s indicates string
type and d indicates integer type.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-18-320.jpg)


![r-squared
Slide 21
writeLines()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> details <- "My name is Jovial."
> writeLines(details, "write.txt")
> readLines("write.txt")
[1] "My name is Jovial."
> # example 2
> details_2 <- "I am 28 years old."
> writeLines(details_2, "write.txt")
> readLines("write.txt")
[1] "I am 28 years old."
# As you might have observed, writeLines overwrites the contents of a file. To append text to
a file, we will use the write function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-21-320.jpg)

![r-squared
Slide 23
write()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> name <- "My name is Jovial."
> write(name, file = "write.txt")
> readLines("write.txt")
[1] "My name is Jovial."
> age <- "I am 28 years old."
> write(age, file = "write.txt", append = TRUE)
> readLines("write.txt")
[1] "My name is Jovial." "I am 28 years old."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-23-320.jpg)
![r-squared
Slide 24
write()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 2
> x <- 1:5
> x
[1] 1 2 3 4 5
> write(x, file = "write.txt", append = TRUE)
> readLines("write.txt")
[1] "My name is Jovial." "I am 28 years old." "1 2 3 4 5"
> write(x, file = "write.txt", append = TRUE)
> readLines("write.txt")
[1] "My name is Jovial." "I am 28 years old." "1 2 3 4 5" "1 2 3 4 5"
> write(x, file = "write.txt", append = TRUE, sep = "-")
> readLines("write.txt")
[1] "My name is Jovial." "I am 28 years old." "1 2 3 4 5" "1 2 3 4 5"
[5] "1-2-3-4-5"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-24-320.jpg)

![r-squared
Slide 26
write.table()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> m <- matrix(1:9, nrow = 3)
> m
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 1 4 7
[2,] 2 5 8
[3,] 3 6 9
> # write to a text file
> write.table(m, file = "table.txt")
> readLines("table.txt")
[1] ""V1" "V2" "V3"" ""1" 1 4 7" ""2" 2 5 8"
[4] ""3" 3 6 9"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-26-320.jpg)
![r-squared
Slide 27
write.table()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 2
> # write to a csv file
> write.table(m, file = "table.csv")
> readLines("table.csv")
[1] ""V1" "V2" "V3"" ""1" 1 4 7" ""2" 2 5 8"
[4] ""3" 3 6 9"
> # example 3
> # append the transpose of the matrix
> write.table(t(m), file = "table.txt", append = TRUE)
> readLines("table.txt")
[1] ""V1" "V2" "V3"" ""1" 1 4 7" ""2" 2 5 8"
[4] ""3" 3 6 9" ""V1" "V2" "V3"" ""1" 1 2 3"
[7] ""2" 4 5 6" ""3" 7 8 9"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-27-320.jpg)
![r-squared
Slide 28
write.table()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
> # example 4
> # use comma as a separator
> write.table(t(m), file = "table.txt", append = TRUE, sep = ",")
> readLines("table.txt")
[1] ""V1" "V2" "V3"" ""1" 1 4 7" ""2" 2 5 8"
[4] ""3" 3 6 9" ""V1" "V2" "V3"" ""1" 1 2 3"
[7] ""2" 4 5 6" ""3" 7 8 9" ""V1","V2","V3""
[10] ""1",1,2,3" ""2",4,5,6" ""3",7,8,9"
> # example 5
> # without row and column names
> write.table(t(m), file = "table.txt", append = TRUE, row.names = FALSE,
+ col.names = FALSE)
> readLines("table.txt")
[1] ""V1" "V2" "V3"" ""1" 1 4 7" ""2" 2 5 8"
[4] ""3" 3 6 9" ""V1" "V2" "V3"" ""1" 1 2 3"
[7] ""2" 4 5 6" ""3" 7 8 9" ""V1","V2","V3""
[10] ""1",1,2,3" ""2",4,5,6" ""3",7,8,9"
[13] "1 2 3" "4 5 6" "7 8 9"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-28-320.jpg)

![r-squared
Slide 30
write.csv()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> write.csv(mtcars, "mt.csv")
> readLines("mt.csv")
[1]""","mpg","cyl","disp","hp","drat","wt","qsec","vs","am","gear","carb""
[2] ""Mazda RX4",21,6,160,110,3.9,2.62,16.46,0,1,4,4"
[3] ""Mazda RX4 Wag",21,6,160,110,3.9,2.875,17.02,0,1,4,4"
[4] ""Datsun 710",22.8,4,108,93,3.85,2.32,18.61,1,1,4,1"
> # example 2
> # without row names
> write.csv(mtcars, "mt.csv", row.names = FALSE)
> readLines("mt.csv")
[1] ""mpg","cyl","disp","hp","drat","wt","qsec","vs","am","gear","carb""
[2] "21,6,160,110,3.9,2.62,16.46,0,1,4,4"
[3] "21,6,160,110,3.9,2.875,17.02,0,1,4,4"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-30-320.jpg)

![r-squared
Slide 32
sink()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> sink(file = "write.txt", append = TRUE, type = "output")
> x <- 1:5
> x * 2
> readLines("write.txt") # nothing is printed on console
> sink() # stop diverting output to file
> readLines("write.txt")
[1] "[1] 2 4 6 8 10"
[2] "[1] "[1] 2 4 6 8 10""
[3] "[1] 2 4 6 8 10"
[4] "[1] "[1] 2 4 6 8 10" "[1] "[1] 2 4 6 8 10"""
[5] "[3] "[1] 2 4 6 8 10" "](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-32-320.jpg)
![r-squared
Slide 33
sink()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 2
> sink("example.txt") # start writing to example.txt file
> x <- sample(1:10)
> y <- sample(1:10)
> cat("===============================n")
> cat(" T-test between x and y n")
> cat("===============================n")
> t.test(x, y)
> sink() # stop writing to the file
> readLines("example.txt")
[1] " [1] 2 5 4 6 9 3 10 1 7 8"
[2] " [1] 6 10 5 1 4 2 9 7 3 8"
[3] "==============================="
[4] " T-test between x and y "
[5] "==============================="
[6] ""
[7] "tWelch Two Sample t-test"
[8] ""
[9] "data: x and y"
[10] "t = 0, df = 18, p-value = 1"
[11] "alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0"
[12] "95 percent confidence interval:"
[13] " -2.844662 2.844662"
[14] "sample estimates:"
[15] "mean of x mean of y "
[16] " 5.5 5.5 "
[17] ""](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-33-320.jpg)

![r-squared
Slide 35
dump()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> x <- sample(1:10)
> y <- sample(1:10)
> xy <- list(x = x, y = y) # create a list
> dump("xy", file = "dump.Rdmped") # write xy to dump.R file
> unlink("dump.R") # close connection to dump.R file
> rm("x", "y", "xy") # remove objects x, y and xy from the workspace
> x # x is not available in the workspace
Error: object 'x' not found
> source("dump.Rdmped") # source dump.R file
> xy
$x
[1] 6 4 9 10 2 8 5 3 7 1
$y
[1] 8 7 6 9 3 1 5 2 4 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-35-320.jpg)

![r-squared
Slide 37
save()
www.r-squared.in/rprogramming
Examples
> # example 1
> # save the following data in a R data file
> x <- 1:10
> save(x, file = "x.RData")
> # remove x from the workspace
> rm(x)
> # load x into workspace
> load("x.RData") # we will look at this function in a file
> # view the data
> x
[1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exportingdatafromr-150415112208-conversion-gate02/85/R-Programming-Export-Output-Data-In-R-37-320.jpg)