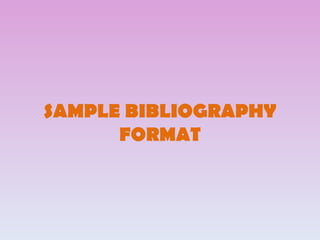
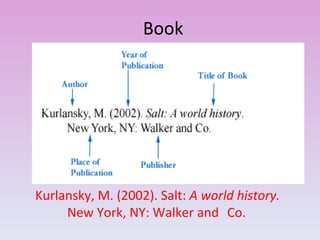
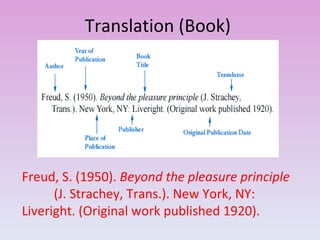
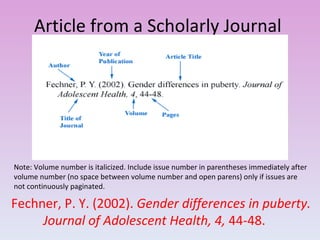
This document provides guidelines for citing sources in APA style, both in-text citations and references. It discusses citing direct quotations, paraphrased ideas, and works by multiple authors. It also covers citing electronic sources, sources without authors or page numbers, and legal materials. Specific examples are given to illustrate citation formats for different source types such as books, articles, reports, and websites.










![Additional Circumstances: Rule: Work by an association, government agency, or corporation Examples: First citation: (National Institute of Mental Health [NIMH], 1996) Later citations: (NIMH, 1996)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apacitation-101212001742-phpapp01/85/APA-In-text-Citations-12-320.jpg)