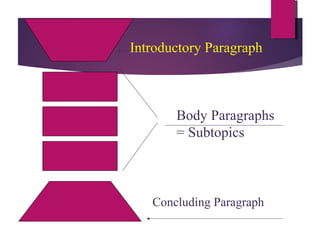
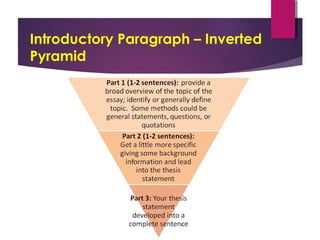
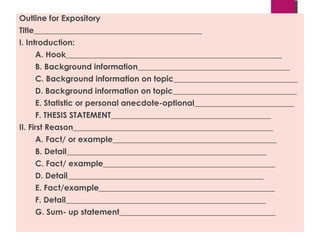
The document defines expository writing as presenting reasons, explanations, or steps in a process in an informational manner. An expository essay should follow a logical sequence with three main points and focus on logic and coherence. Expository writing does not tell a story or persuade, but rather provides facts. It can also outline steps in a process. An effective expository essay includes an introductory paragraph with a thesis, three body paragraphs each focusing on a main point and providing evidence, and a concluding paragraph that restates the main points.