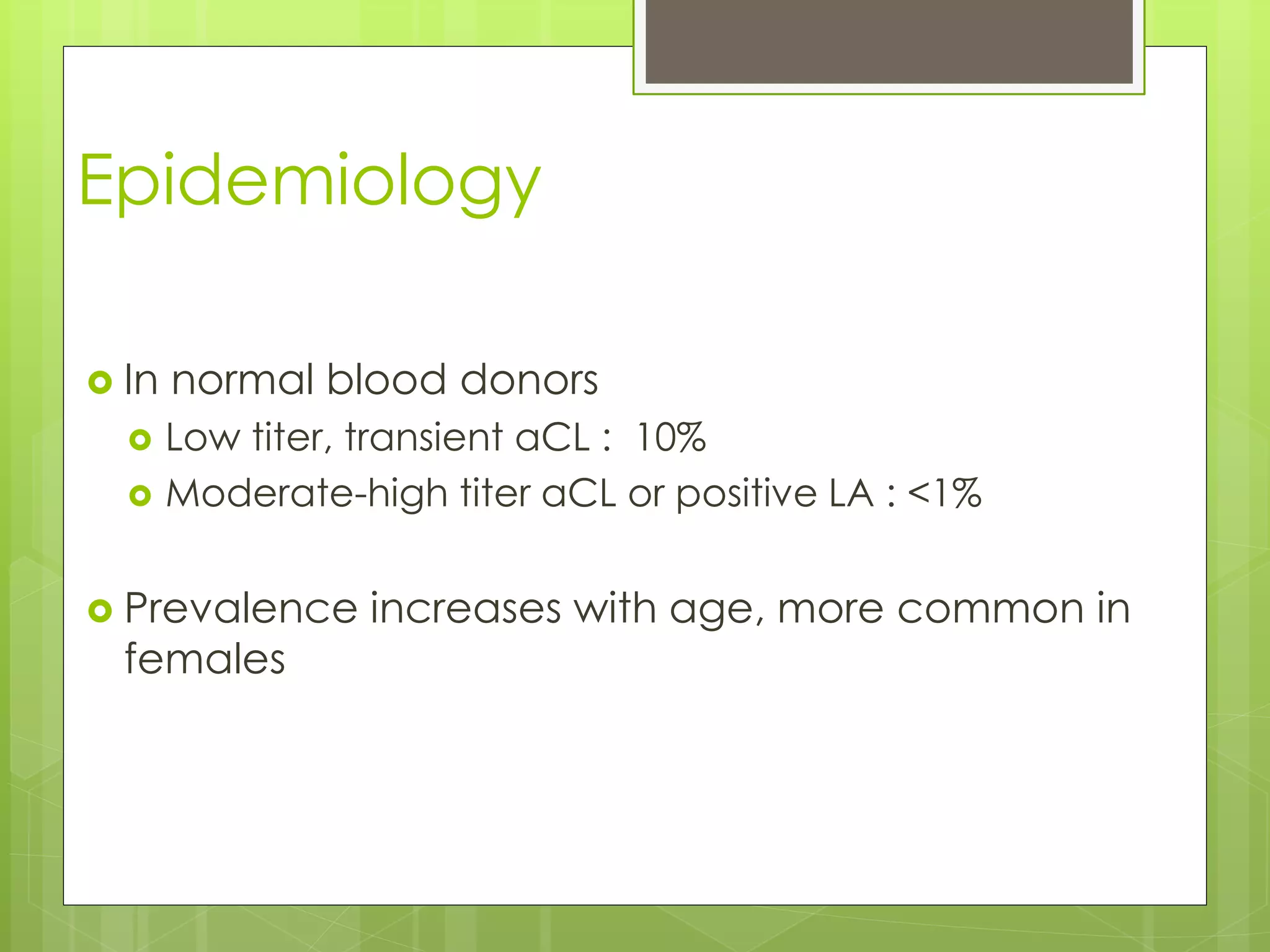
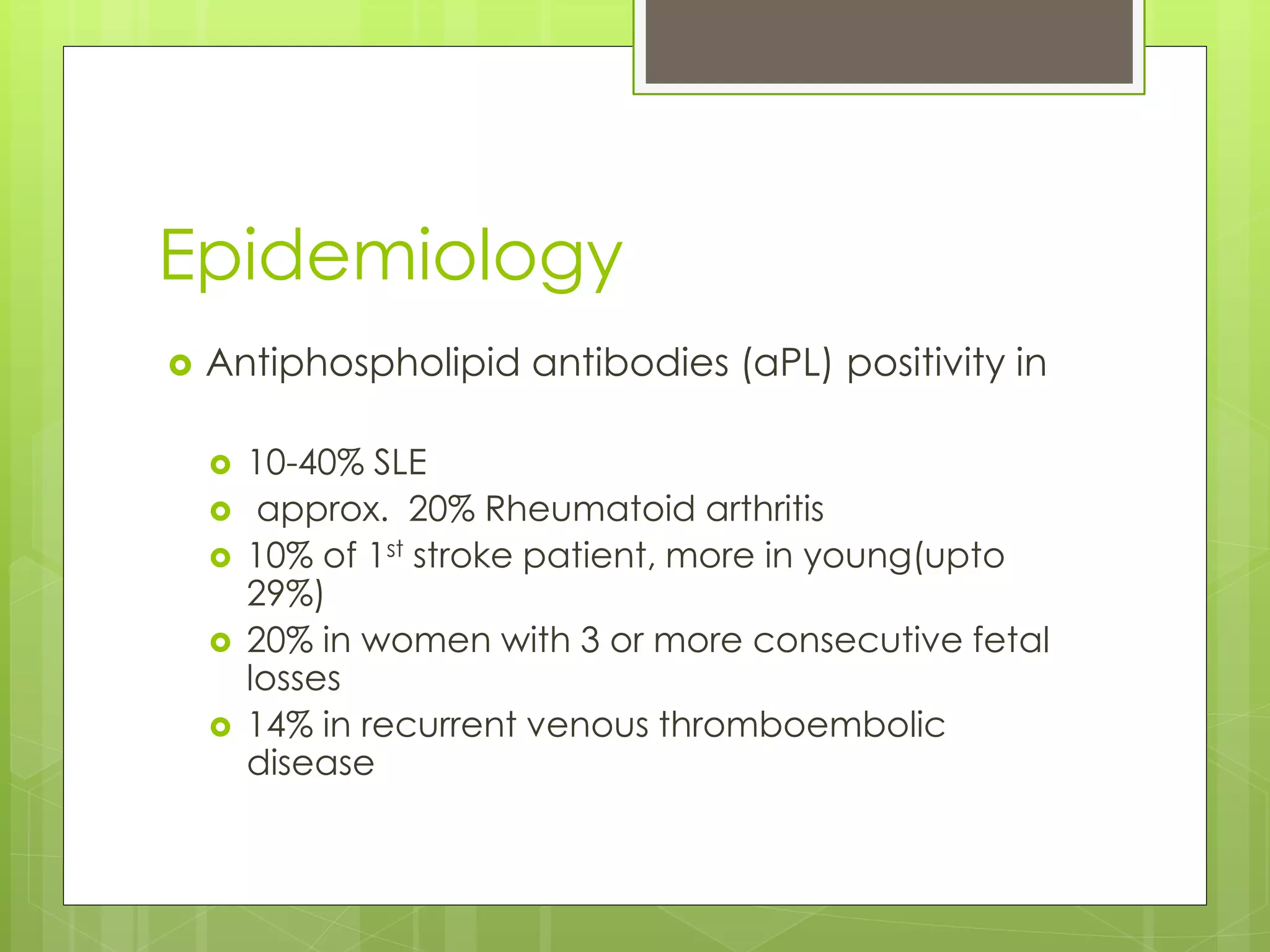
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune condition characterized by arterial or venous blood clots and/or pregnancy morbidity in the presence of antibodies that target phospholipid-binding plasma proteins. It can occur on its own (primary) or with other autoimmune diseases (secondary). APS is diagnosed based on clinical criteria of blood clots or pregnancy complications along with positive laboratory tests for antiphospholipid antibodies. Treatment involves blood thinners like warfarin to prevent clots. Prognosis can be poor as permanent organ damage or disability can occur in a third of patients within 10 years.